Jump Start Solution: Generative AI Knowledge Base
This guide helps you understand and deploy theGenerative AI Knowledge Base solution. This solution demonstrates how to build an extractivequestion-answering (EQA) pipeline to produce content for an internal knowledgebase.
An EQA pipeline processes documents, extracts question-and-answer pairs from thedocuments, and provides you with structured information to fine-tune a largelanguage model (LLM). For example, you could upload a document containing manyfrequently asked questions (FAQs), tune an LLM using those FAQs, and then usethe trained model to help customer support agents find information whileresolving cases.
This document is intended for developers who have some background with LLMs. Itassumes that you're familiar with basic cloud concepts.
Note: This solution helps you explore the capabilities ofGoogle Cloud. The solution is not intended to be used as is for productionenvironments. For information about designing and setting up production-gradeenvironments in Google Cloud, seeLanding zone design in Google Cloud andGoogle Cloud setup checklist.Objectives
This solution guide helps you do the following:
- Deploy an application that extracts question-and-answer pairs from yourdocuments.
- Deploy a pipeline that triggers your application when a document is uploaded.
- Train a prompt-based AI model using the output from yourapplication.
Architecture
This solution deploys a Generative AI Knowledge Base application.The following diagram shows the architecture of theapplication infrastructure:
Request flow
The following steps detail the request processing flow of the application.The steps in the flow are numbered as shown in the preceding architecture diagram.
You start the Generative AI Knowledge Base application byuploading a document directly to a Cloud Storage bucket, eitherthrough the Google Cloud console or gcloud CLI.
When the document is uploaded, it triggers a Cloud Run function.This function runs the Extractive Question-Answering process.
The function uses Document AI OCR to extract all text fromthe document.
The function indexes the document into Vector Search. TheVector Search index provides context for the LLM to extractquestion-and-answer pairs based only on content that's extracted directlyfrom the uploaded documents.
The function uses Vertex AI to extract andgenerate questions and answers from the document.
The function stores the extracted question-and-answer pairs inFirestore.
A JSONL fine tuning dataset is generated from the Firestore database and stored in Cloud Storage.
After manually validating that you are satisfied with the dataset,you can launch a fine tuning job on Vertex AI.
When the tuning job is complete, the tuned model is deployed to an endpoint.After it's deployed to an endpoint, you can submit queries to the tuned modelin a Colab notebook, and compare it with the foundation model.
Products used
This section describes the products that the solution uses.
If you're familiar with theTerraform configuration language, you can changesome of the settings for the services.
| Component | Product description | Purpose in this solution |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Storage | An enterprise-ready service that provides low-cost, no-limit object storage for diverse data types. | Stores the PDF documents, extracted text, tuning dataset, and tuned model. |
| Eventarc | A service that manages the flow of state changes (events) between decoupled microservices, routing events to various destinations while managing delivery, security, authorization, observability, and error handling. | Watches for new documents in the Cloud Storage bucket and triggers an event in Cloud Run functions. |
| Cloud Run functions | A lightweight serverless compute service that lets you create single-purpose, standalone functions that respond to Google Cloud events without the need to manage a server or runtime environment. | Orchestrates the document processing steps. |
| Document AI | A document understanding platform that takes unstructured data from documents and transforms it into structured data. You can automate tedious tasks, improve data extraction, and gain deeper insights from data. | Extracts the text from the documents. |
| Vertex AI | A machine learning platform that lets you train, test, tune, and deploy LLMs and generative AI applications. | Generates questions and answers from the documents. |
| Vector Search | A service that lets you use the same infrastructure that provides a foundation for Google products such as Google Search, YouTube, and Play. | Lets you search embeddings to find semantically similar or related entities. |
| Firestore | A fully managed, low-latency file system for VMs and clusters that offers high availability and high throughput. | Stores the generated questions and answers. |
Cost
For an estimate of the cost of the Google Cloud resources that thegenerative ai knowledge base solution uses, see the precalculated estimate in theGoogle Cloud Pricing Calculator.
Use the estimate as a starting point to calculate the cost of your deployment.You can modify the estimate to reflect any configuration changes that you planto make for the resources that are used in the solution.
The precalculated estimate is based on assumptions for certain factors,including the following:
- The Google Cloud locations where the resources are deployed.
The amount of time that the resources are used.
The amount of data stored in Cloud Storage.
The number of times the knowledge base application is invoked.
The computing resources used for tuning the model.
Before you begin
To deploy this solution, you first need a Google Cloud project and someIAM permissions.
Create or choose a Google Cloud project
When you deploy the solution, you choose theGoogle Cloud project where the resources are deployed. You can either create a new project or use anexisting project for the deployment.
If you want to create a new project, do sobefore you begin the deployment.Using a new project can help avoid conflicts with previously provisionedresources, such as resources that are used for production workloads.
To create a project, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that you have the Project Creator IAM role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator).Learn how to grant roles. In the Google Cloud console, go to the project selector page.
ClickCreate project.
Name your project. Make a note of your generated project ID.
Edit the other fields as needed.
ClickCreate.
Get the required IAM permissions
To start the deployment process, you need the Identity and Access Management (IAM)permissions that are listed in the following table.
If you created a new project for this solution, then you have theroles/ownerbasic role in that project and have all the necessary permissions. If you don't have theroles/owner role, then ask your administrator to grant these permissions (orthe roles that include these permissions) to you.
| IAM permission required | Predefined role that includes the required permissions |
|---|---|
| Service Usage Admin ( roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin) |
| Service Account Admin ( roles/iam.serviceAccountAdmin) |
| Project IAM Admin ( roles/resourcemanager.projectIamAdmin) |
config.deployments.createconfig.deployments.list | Cloud Infrastructure Manager Admin ( roles/config.admin) |
iam.serviceAccount.actAs | Service Account User ( roles/iam.serviceAccountUser) |
About temporary service account permissions
If you start the deployment process through the console, Google creates aservice account to deploy the solution on your behalf (and to delete the deployment later if youchoose). This service account is assigned certain IAM permissionstemporarily; that is, the permissions are revoked automatically after thesolution deployment and deletion operations are completed. Google recommendsthat after you delete the deployment, you delete the service account, asdescribed later in this guide.
View the roles that are assigned to the service account
These roles are listed here in case an administrator of your Google Cloud project or organization needs this information.
roles/aiplatform.userroles/artifactregistry.adminroles/documentai.editorroles/firebase.adminroles/iam.serviceAccountUserroles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdminroles/iam.serviceAccountAdminroles/resourcemanager.projectIamAdminroles/config.agent
Deploy the solution
To help you deploy this solution with minimal effort, a Terraform configurationis provided in GitHub. The Terraform configuration defines all theGoogle Cloud resources that are required for the solution.
You can deploy the solution by using one of the following methods:
Through the console: Use this method if you wantto try the solution with the default configuration and see how it works.Cloud Build deploys all the resources that are required for thesolution. When you no longer need the deployed solution, you can delete itthrough the console. Any resources that you create afteryou deploy the solution might need to be deleted separately.
To use this deployment method, follow the instructions inDeploy through the console.
Using the Terraform CLI: Use this method if you want to customize thesolution or if you want to automate the provisioning and management of theresources by using the infrastructure as code (IaC) approach. Download theTerraform configuration from GitHub, optionally customize the code asnecessary, and then deploy the solution by using the Terraform CLI. Afteryou deploy the solution, you can continue to use Terraform to manage thesolution.
To use this deployment method, follow the instructions inDeploy using the Terraform CLI.
Deploy through the console
Complete the following steps to deploy the preconfigured solution.
Note: If you want to customize the solution or automate theprovisioning and management of the solution by using the infrastructure as code(IaC) approach, then seeDeploy using the Terraform CLI.In the Google Cloud Jump Start Solutions catalog, go to theGenerative AI Knowledge Base solution.
Review the information that's provided on the page, such as the estimatedcost of the solution and the estimated deployment time.
When you're ready to start deploying the solution, clickDeploy.
A step-by-step configuration pane is displayed.
Complete the steps in the configuration pane.
Note the name that you enter for the deployment. This name is requiredlater when you delete the deployment.
When you clickDeploy, theSolution deployments page is displayed.TheStatus field on this page showsDeploying.
Wait for the solution to be deployed.
If the deployment fails, theStatus field showsFailed. You canuse the Cloud Build log to diagnose the errors. For moreinformation, seeErrors when deploying through the console.
After the deployment is completed, theStatus field changes toDeployed.
To view the Google Cloud resources that are deployed and theirconfiguration, take an interactive tour in the console.
For next steps, seeUse the solution.
When you no longer need the solution, you can delete the deployment to avoidcontinued billing for the Google Cloud resources. For more information,seeDelete the deployment.
Deploy using the Terraform CLI
This section describes how you can customize the solution or automate theprovisioning and management of the solution by using the Terraform CLI.Solutions that you deploy by using the Terraform CLI are not displayed in theSolution deployments page in the Google Cloud console.
Note: If you want to deploy the solution with the default configuration to seehow it works, then follow the instructions inDeploy through the console.Set up the Terraform client
You can run Terraform either in Cloud Shell or on your local host. Thisguide describes how to run Terraform in Cloud Shell, which hasTerraform preinstalled and configured to authenticate with Google Cloud.
The Terraform code for this solution is available in a GitHub repository.
Clone the GitHub repository to Cloud Shell.
A prompt is displayed to confirm downloading the GitHub repository toCloud Shell.
ClickConfirm.
Cloud Shell is launched in a separate browser tab, and theTerraform code is downloaded to the
$HOME/cloudshell_opendirectory ofyour Cloud Shell environment.In Cloud Shell, check whether the current working directory is
$HOME/cloudshell_open/terraform-genai-knowledge-base/. This is thedirectory that contains the Terraform configuration files for the solution.If you need to change to that directory, run the following command:cd $HOME/cloudshell_open/terraform-genai-knowledge-base/Initialize Terraform by running the following command:
terraform initWait until you see the following message:
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
Configure the Terraform variables
The Terraform code that you downloaded includes variables that you can use tocustomize the deployment based on your requirements. For example, you canspecify the Google Cloud project and theregion where you want the solution to bedeployed.
Make sure that the current working directory is
$HOME/cloudshell_open/terraform-genai-knowledge-base/. If itisn't, go to that directory.In the same directory, create a text file named
terraform.tfvars.In the
terraform.tfvarsfile, copy the following code snippet, and setvalues for the required variables.- Follow the instructions that are provided as comments in the codesnippet.
- This code snippet includes only the variables for which youmust setvalues. The Terraform configuration includes other variables that havedefault values. To review all the variables and the default values, seethe
variables.tffile that's available in the$HOME/cloudshell_open/terraform-genai-knowledge-base/directory. - Make sure that each value that you set in the
terraform.tfvarsfilematches the variabletype as declared in thevariables.tffile. For example, if the type that'sdefined for a variable in thevariables.tffile isbool, then youmust specifytrueorfalseas the value of that variable in theterraform.tfvarsfile.
# This is an example of the terraform.tfvars file.# The values in this file must match the variable types declared in variables.tf.# The values in this file override any defaults in variables.tf.# ID of the project in which you want to deploy the solutionproject_id="PROJECT_ID"
Validate and review the Terraform configuration
Make sure that the current working directory is
$HOME/cloudshell_open/terraform-genai-knowledge-base/. If itisn't, go to that directory.Verify that the Terraform configuration has no errors:
terraform validateIf the command returns any errors, make the required corrections in theconfiguration and then run the
terraform validatecommand again. Repeatthis step until the command returns the following message:Success! The configuration is valid.Review the resources that are defined in the configuration:
terraform planIf you didn't create the
terraform.tfvarsfile asdescribed earlier, Terraform prompts you to enter values for the variablesthat don't have default values.Enter the required values.The output of the
terraform plancommand is a list of the resources thatTerraform provisions when you apply the configuration.If you want to make any changes, edit the configuration and then run the
terraform validateandterraform plancommands again.
Provision the resources
When no further changes are necessary in the Terraform configuration, deploythe resources.
Make sure that the current working directory is
$HOME/cloudshell_open/terraform-genai-knowledge-base/. If itisn't, go to that directory.Apply the Terraform configuration:
terraform applyIf you didn't create the
terraform.tfvarsfile asdescribed earlier, Terraform prompts you to enter values for the variablesthat don't have default values.Enter the required values.Terraform displays a list of the resources that will be created.
When you're prompted to perform the actions, enter
yes.Terraform displays messages showing the progress of the deployment.
If the deployment can't be completed, Terraform displays the errors thatcaused the failure. Review the error messages and update the configurationto fix the errors. Then run the
terraform applycommand again. For helpwith troubleshooting Terraform errors, seeErrors when deploying the solution using the Terraform CLI.After all the resources are created, Terraform displays the followingmessage:
Apply complete!To view the Google Cloud resources that are deployed and theirconfiguration, take an interactive tour in the console.
Next, you canuse the solution and see how it works.
When you no longer need the solution, you can delete the deployment to avoidcontinued billing for the Google Cloud resources. For more information,seeDelete the deployment.
Use the solution
Once the solution is deployed, you can upload a document to index it and askquestions about it. Additionally, a JSON lines (JSONL) tuning dataset file isgenerated, which you can use to prompt-tune an LLM.
Upload a document and query the model
Begin using this solution by uploading a document, then ask the pre-trained LLMquestions about the document.
To follow step-by-step guidance for this task directly in Google Cloud console, clickGuide me.
This task takes about 10 minutes to complete.Tune the LLM
After you upload documents for the solution, you can use Vertex AI totune an LLM with your question-and-answer pairs. Tuning the LLM is not anautomated process. Before you tune the LLM, inspect your data and make surethat it's valid and accurate. After you are satisfied with the data, you canmanually launch a tuning job and launch the LLM from the Model Registry.
The JSONL tuning file contains extracted content from your question-and-answerpairs. Each line in the file is a JSON entry withinput_text andoutput_textfields. Theinput_text field contains the content from each question, and theoutput_text contains content from each respective answer.
For example, the following JSONL file contains the question "How many peoplelive in Beijing" and the respective answer:
{"input_text": "CONTEXT: With over 21 million residents, Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city and is China's second largest city after Shanghai. QUESTION: How many people live in Beijing?,"output_text": "21 million people"}To follow step-by-step guidance for tuning your model directly in Google Cloud console, clickGuide me.
This walkthrough takes about 10 minutes to complete, but the model tuning can takean hour or more to finish processing.Delete the deployment
When you no longer need the solution, delete the deployment.When you delete the deployment, you are no longer billed for the resourcesthat you created.
Before you delete
Before you delete this solution, delete the Vector Search index deployment:
Go to theVector Search page.
Click
knowledge-base-index.UnderDeployed indexes, clickmore_vertMore.
ClickUndeploy.
You don't need to wait for the index deletion process to finish.
Delete through the console
Use this procedure if you deployed the solution throughthe console.
In the Google Cloud console, go to theSolution deployments page.
Select the project that contains the deployment that you want to delete.
Locate the deployment that you want to delete.
In the row for the deployment, clickActionsand then selectDelete.
You might need to scroll to seeActions in the row.
Enter the name of the deployment and then clickConfirm.
TheStatus field showsDeleting.
If the deletion fails, see the troubleshooting guidance inError when deleting a deployment.
When you no longer need the Google Cloud project that you used for the solution, youcan delete the project. For more information, seeOptional: Delete the project.
Delete using the Terraform CLI
Use this procedure if you deployed the solution by using the Terraform CLI.
In Cloud Shell, make sure that the current working directory is
$HOME/cloudshell_open/terraform-genai-knowledge-base/. If itisn't, go to that directory.Remove the resources that were provisioned by Terraform:
terraform destroyTerraform displays a list of the resources that will be destroyed.
When you're prompted to perform the actions, enter
yes.Terraform displays messages showing the progress. After all the resourcesare deleted, Terraform displays the following message:
Destroy complete!If the deletion fails, see the troubleshooting guidance inError when deleting a deployment.
When you no longer need the Google Cloud project that you used for the solution, youcan delete the project. For more information, seeOptional: Delete the project.
Delete the tuned model
You must manually delete the tuned model.
To delete the tuned mode, seeDelete a model from Vertex AI Model Registry.
Optional: Delete the project
If you deployed the solution in a new Google Cloud project, and if you no longerneed the project, then delete it by completing the following steps:
Caution: If you delete a project, all the resources in the project arepermanently deleted.- In the Google Cloud console, go to theManage resources page.
- In the project list, select the project that you want to delete, and then clickDelete.
- At the prompt, type the project ID, and then clickShut down.
If you decide to retain the project, then delete the service account that wascreated for this solution, as described in the next section.
Optional: Delete the service account
If you deleted the project that you used for the solution, then skip thissection.
As mentioned earlier in this guide, when you deployed the solution, a serviceaccount was created on your behalf. The service account was assigned certainIAM permissionstemporarily; that is, the permissions wererevoked automatically after the solution deployment and deletion operations werecompleted, but the service account isn't deleted. Google recommends thatyou delete this service account.
If you deployed the solution through the Google Cloud console, go to theSolution deployments page. (If you're already on that page, refresh the browser.) A process istriggered in the background to delete the service account. No further actionis necessary.
If you deployed the solution by using the Terraform CLI, complete thefollowing steps:
In the Google Cloud console, go to theService accounts page.
Select the project that you used for the solution.
Select the service account that you want to delete.
The email ID of the service account that was created for the solution isin the following format:
goog-sc-DEPLOYMENT_NAME-NNN@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.comThe email ID contains the following values:
- DEPLOYMENT_NAME: the name of the deployment.
- NNN: a random 3-digit number.
- PROJECT_ID: the ID of the project in which youdeployed the solution.
ClickDelete.
Troubleshoot errors
The actions that you can take to diagnose and resolve errors depend on thedeployment method and the complexity of the error.
Errors when deploying through the console
If the deployment fails when you use the console, do thefollowing:
Go to theSolution deployments page.
If the deployment failed, theStatus field showsFailed.
View the details of the errors that caused the failure:
In the row for the deployment, clickActions.
You might need to scroll to seeActions in the row.
SelectView Cloud Build logs.
Review the Cloud Build log and take appropriate action to resolvethe issue that caused the failure.
Errors when deploying using the Terraform CLI
If the deployment fails when you use Terraform, the output of theterraformapply command includes error messages that you can review to diagnose theproblem.
The examples in the following sections show deployment errors that you mightencounter when you use Terraform.
API not enabled error
If you create a project and then immediately attempt to deploy the solution inthe new project, the deployment might fail with an error like the following:
Error: Error creating Network: googleapi: Error 403: Compute Engine API has notbeen used in projectPROJECT_ID before or it is disabled. Enable it by visitinghttps://console.developers.google.com/apis/api/compute.googleapis.com/overview?project=PROJECT_IDthen retry. If you enabled this API recently, wait a few minutes for the actionto propagate to our systems and retry.If this error occurs, wait a few minutes and then run theterraform applycommand again.
Cannot assign requested address error
When you run theterraform apply command, acannot assign requested addresserror might occur, with a message like the following:
Error: Error creating service account: Post "https://iam.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/serviceAccounts: dial tcp [2001:db8:ffff:ffff::5f]:443: connect: cannot assign requested addressIf this error occurs, run theterraform apply command again.
Configuration error
If you modify resource arguments in yourmain.tf file using unsupported values,an error like the following occurs:
Error: Error creating Instance: googleapi: Error 400: Provided Redis version isnot supported: REDIS_5_X│ com.google.apps.framework.request.StatusException: <eye3 title='INVALID_ARGUMENT'/> generic::INVALID_ARGUMENT: Provided Redis version is not supported: REDIS_5_XDetails:│ [>│ {│ "@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.rpc.BadRequest",│ "fieldViolations": [│ {│ "description": "Invalid value: REDIS_5_X",│ "field": "instance.redis_version"│ }│ ]│ }│ ]││ with google_redis_instance.main,│ on main.tf line 96, in resource "google_redis_instance" "main":│ 96: resource "google_redis_instance" "main" {In this case, the intent was to use Redis version 5, but the value specified fortheinstance.redis_version argument (REDIS_5_X) in themain.tf file is notvalid.The correct value isREDIS_5_0, as enumerated in theMemorystore REST API documentation.
Error when deleting a deployment
In certain cases, attempts to delete a deployment might fail:
- After deploying a solution through the console, if youchange any resource that was provisioned by the solution, and if you then tryto delete the deployment, the deletion might fail. TheStatus field on theSolution deployments page showsFailed, and theCloud Build log shows the cause of the error.
- After deploying a solution by using the Terraform CLI, if you change anyresource by using a non-Terraform interface (for example,the console), and if you then try to delete the deployment,the deletion might fail. The messages in the output of the
terraform destroycommand show the cause of the error.
Review the error logs and messages, identify and delete the resources thatcaused the error, and then try deleting the deployment again.
If a console-based deployment doesn't get deleted and if you can'tdiagnose the error by using the Cloud Build log, then you can deletethe deployment by using the Terraform CLI, as described in the next section.
Delete a console-based deployment by using the Terraform CLI
This section describes how to delete a console-based deployment iferrors occur when you try to delete it through the console. Inthis approach, you download the Terraform configuration for the deployment thatyou want to delete and then use the Terraform CLI to delete the deployment.
Identify the region where the deployment's Terraform code, logs, and otherdata are stored. This region might be different from the region thatyou selected while deploying the solution.
In the Google Cloud console, go to theSolution deploymentspage.
Select the project that contains the deployment that you want to delete.
In the list of deployments, identify the row for the deployment that youwant to delete.
ClickView all rowcontent.
In theLocation column, note thesecond location, as highlightedin the following example:
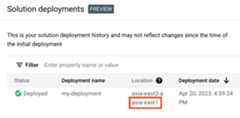
In the Google Cloud console, activate Cloud Shell.
At the bottom of the Google Cloud console, aCloud Shell session starts and displays a command-line prompt. Cloud Shell is a shell environment with the Google Cloud CLI already installed and with values already set for your current project. It can take a few seconds for the session to initialize.
Create environment variables for the project ID, region, and name ofthe deployment that you want to delete:
exportREGION="REGION"exportPROJECT_ID="PROJECT_ID"exportDEPLOYMENT_NAME="DEPLOYMENT_NAME"In these commands, replace the following:
- REGION: the location that you noted earlier inthis procedure.
- PROJECT_ID: the ID of the project where youdeployed the solution.
- DEPLOYMENT_NAME: the name of the deploymentthat you want to delete.
Get the ID of the latest revision of the deployment that you wantto delete:
exportREVISION_ID=$(curl\-H"Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)"\-H"Content-Type: application/json"\"https://config.googleapis.com/v1alpha2/projects/${PROJECT_ID}/locations/${REGION}/deployments/${DEPLOYMENT_NAME}"\|jq.latestRevision-r)echo$REVISION_IDThe output is similar to the following:
projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/REGION/deployments/DEPLOYMENT_NAME/revisions/r-0Get the Cloud Storage location of the Terraform configuration forthe deployment:
exportCONTENT_PATH=$(curl\-H"Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)"\-H"Content-Type: application/json"\"https://config.googleapis.com/v1alpha2/${REVISION_ID}"\|jq.applyResults.content-r)echo$CONTENT_PATHThe following is an example of the output of this command:
gs://PROJECT_ID-REGION-blueprint-config/DEPLOYMENT_NAME/r-0/apply_results/contentDownload the Terraform configuration from Cloud Storage toCloud Shell:
gcloud storage cp $CONTENT_PATH $HOME --recursivecd $HOME/content/Wait until the
Operation completedmessage is displayed, as shown inthe following example:Operation completed over 45 objects/268.5 KiBInitialize Terraform:
terraform initWait until you see the following message:
Terraform has been successfully initialized!Remove the deployed resources:
terraform destroyTerraform displays a list of the resources that will be destroyed.
If any warnings about undeclared variables are displayed, ignore thewarnings.
When you're prompted to perform the actions, enter
yes.Terraform displays messages showing the progress. After all theresources are deleted, Terraform displays the following message:
Destroy complete!Delete the deployment artifact:
curl-XDELETE\-H"Authorization:Bearer$(gcloudauthprint-access-token)"\-H"Content-Type:application/json"\"https://config.googleapis.com/v1alpha2/projects/${PROJECT_ID}/locations/${REGION}/deployments/${DEPLOYMENT_NAME}?force=true&delete_policy=abandon"Wait a few seconds and then verify that the deployment artifact wasdeleted:
curl-H"Authorization:Bearer$(gcloudauthprint-access-token)"\-H"Content-Type:application/json"\"https://config.googleapis.com/v1alpha2/projects/${PROJECT_ID}/locations/${REGION}/deployments/${DEPLOYMENT_NAME}"\|jq.error.messageIf the output shows
null, wait a few seconds and then run the commandagain.After the deployment artifact is deleted, a message as shown in thefollowing example is displayed:
Resource 'projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/REGION/deployments/DEPLOYMENT_NAME' was not found
Submit feedback
Jump Start Solutions are for informational purposes only and are not officiallysupported products. Google may change or remove solutions without notice.
To troubleshoot errors, review the Cloud Build logs and the Terraformoutput.
To submit feedback, do the following:
- For documentation, in-console tutorials, or the solution, usetheSend Feedback button on the page.
- For unmodified Terraform code, create issues in theGitHub repository.GitHub issues are reviewed on a best-effort basis and are not intended forgeneral usage questions.
- For issues with the products that are used in the solution, contactCloud Customer Care.
What's next
- Learn more aboutGenerative AI on Vertex AI.
- For an overview of architectural principles and recommendations that are specific to AIand ML workloads in Google Cloud, see theAI and ML perspectivein the Well-Architected Framework.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2024-03-01 UTC.
