DOI:10.1145/3373017.3373028 - Corpus ID: 211040895
A Short Survey of Pre-trained Language Models for Conversational AI-A New Age in NLP
@article{Zaib2020ASS, title={A Short Survey of Pre-trained Language Models for Conversational AI-A New Age in NLP}, author={Munazza Zaib and Quan Z. Sheng and W. Zhang}, journal={Proceedings of the Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference}, year={2020}, url={https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:211040895}}- Munazza ZaibQuan Z. ShengW. Zhang
- Published inAustralasian Computer Science…29 January 2020
- Computer Science, Linguistics
This paper intends to establish whether these pre-trained models can overcome the challenges pertinent to dialogue systems, and how their architecture could be exploited in order to overcome these challenges.
78 Citations
Topics
Dialogue System (opens in a new tab)Natural Language Processing (opens in a new tab)ImageNet (opens in a new tab)Architecture (opens in a new tab)Agent-Based Computing (opens in a new tab)Conversational Agents (opens in a new tab)Long-term Dependencies (opens in a new tab)Syntax (opens in a new tab)
78 Citations
Advances in Multi-turn Dialogue Comprehension: A Survey
- Zhuosheng ZhangHai Zhao
- 2021
Computer Science, Linguistics
The characteristics and challenges of dialogue comprehension in contrast to plain-text reading comprehension are summarized and categorize dialogue-related pre-training techniques which are employed to enhance PrLMs in dialogue scenarios.
technical review on knowledge intensive NLP for pre-trained language development
- Snehal AwachatShwetal RaipureKavita B. Kalambe
- 2022
Computer Science, Linguistics
The present progress of pre-trained language model-based knowledge-enhanced models (PLMKEs) is described by deconstructing their three key elements: information sources, knowledge-intensive NLP tasks, and knowledge fusion methods.
Conversational question answering: a survey
- Munazza ZaibWei Emma ZhangQuan Z. ShengA. MahmoodYang Zhang
- 2022
Computer Science
There has been a trend shift from single-turn to multi-turn QA which empowers the field of Conversational AI from different perspectives, and this survey is intended to provide an epitome for the research community with the hope of laying a strong foundation for theField of CQA.
Fusing Sentence Embeddings Into LSTM-based Autoregressive Language Models
- Vilém ZouharMarius MosbachD. Klakow
- 2022
Computer Science
An LSTM-based autoregressive language model which uses prefix embeddings via fusion (e.g. concatenation) to obtain a richer context representation for language modelling to find that fusion helps reliably in lowering the perplexity.
Towards a Universal NLG for Dialogue Systems and Simulators with Future Bridging
- Philipp EnnenYen-Ting LinDa-shan Shiu
- 2021
Computer Science
A prototype FBNLG is evaluated to show that future bridging can be a viable approach to a universal few-shot NLG for task-oriented and chit-chat dialogues.
Keeping the Questions Conversational: Using Structured Representations to Resolve Dependency in Conversational Question Answering
- Munazza ZaibQuan Z. ShengW. ZhangA. Mahmood
- 2023
Computer Science, Linguistics
A novel framework, CONVSR (CONVQA using Structured Representations) is proposed for capturing and generating intermediate representations as conversational cues to enhance the capability of the QA model to better interpret the incomplete questions.
Towards End-to-End Open Conversational Machine Reading
- Sizhe ZhouSiru OuyangA. Institute
- 2023
Computer Science
This work model OR-CMR as a unified text- to-text task in a fully end-to-end style and shows the effectiveness of the proposed end-To-end framework on both sub-tasks by a large margin, achieving new state-of-the-art results.
Pretrained Language Models for Text Generation: A Survey
- Junyi LiTianyi TangWayne Xin ZhaoJi-rong Wen
- 2021
Computer Science, Linguistics
This paper presents an overview of the major advances achieved in the topic of pretrained language models for text generation, and discusses how to adapt existing PLMs to model different input data and satisfy special properties in the generated text.
Pre-Trained Language Models for Text Generation: A Survey
- Junyi LiTianyi TangWayne Xin ZhaoJ. NieJi-rong Wen
- 2024
Computer Science, Linguistics
A survey on the utilization of PLMs in text generation to help researchers interested in text generation problems to learn the core concepts, the main techniques and the latest developments in this area based on PLMs.
Effective Sequence-to-Sequence Dialogue State Tracking
- Jeffrey ZhaoMahdis MahdiehYe ZhangYuan CaoYonghui Wu
- 2021
Computer Science, Linguistics
It is demonstrated that the choice of pre-training objective makes a significant difference to the state tracking quality and it is found that masked span prediction is more effective than auto-regressive language modeling for dialogue state tracking.
...
20 References
Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners
- Alec RadfordJeff WuR. ChildD. LuanDario AmodeiI. Sutskever
- 2019
Computer Science, Linguistics
It is demonstrated that language models begin to learn these tasks without any explicit supervision when trained on a new dataset of millions of webpages called WebText, suggesting a promising path towards building language processing systems which learn to perform tasks from their naturally occurring demonstrations.
Hello, It’s GPT-2 - How Can I Help You? Towards the Use of Pretrained Language Models for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
- Paweł BudzianowskiIvan Vulic
- 2019
Computer Science, Linguistics
This paper proposes a task-oriented dialogue model that operates solely on text input: it effectively bypasses explicit policy and language generation modules and holds promise to mitigate the data scarcity problem, and to support the construction of more engaging and more eloquent task- oriented conversational agents.
Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training
- Alec RadfordKarthik Narasimhan
- 2018
Computer Science, Linguistics
The general task-agnostic model outperforms discriminatively trained models that use architectures specifically crafted for each task, improving upon the state of the art in 9 out of the 12 tasks studied.
Deep Contextualized Word Representations
- Matthew E. PetersMark NeumannLuke Zettlemoyer
- 2018
Computer Science, Linguistics
A new type of deep contextualized word representation is introduced that models both complex characteristics of word use and how these uses vary across linguistic contexts, allowing downstream models to mix different types of semi-supervision signals.
QuAC: Question Answering in Context
- Eunsol ChoiHe HeLuke Zettlemoyer
- 2018
Computer Science
QuAC introduces challenges not found in existing machine comprehension datasets: its questions are often more open-ended, unanswerable, or only meaningful within the dialog context, as it shows in a detailed qualitative evaluation.
MultiWOZ - A Large-Scale Multi-Domain Wizard-of-Oz Dataset for Task-Oriented Dialogue Modelling
- Paweł BudzianowskiTsung-Hsien WenMilica Gasic
- 2018
Computer Science, Linguistics
The Multi-Domain Wizard-of-Oz dataset (MultiWOZ), a fully-labeled collection of human-human written conversations spanning over multiple domains and topics is introduced, at a size of 10k dialogues, at least one order of magnitude larger than all previous annotated task-oriented corpora.
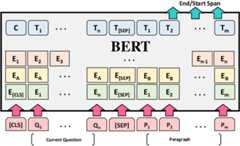
BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding
- Jacob DevlinMing-Wei ChangKenton LeeKristina Toutanova
- 2019
Computer Science
A new language representation model, BERT, designed to pre-train deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text by jointly conditioning on both left and right context in all layers, which can be fine-tuned with just one additional output layer to create state-of-the-art models for a wide range of tasks.
CoQA: A Conversational Question Answering Challenge
- Siva ReddyDanqi ChenChristopher D. Manning
- 2019
Computer Science, Linguistics
CoQA is introduced, a novel dataset for building Conversational Question Answering systems and it is shown that conversational questions have challenging phenomena not present in existing reading comprehension datasets (e.g., coreference and pragmatic reasoning).
Semantics-aware BERT for Language Understanding
- Zhuosheng ZhangYuwei WuXiang Zhou
- 2020
Computer Science, Linguistics
This work proposes to incorporate explicit contextual semantics from pre-trained semantic role labeling, and introduces an improved language representation model, Semantics-aware BERT (SemBERT), which is capable of explicitly absorbing contextual semantics over a BERT backbone.
A Simple but Effective Method to Incorporate Multi-turn Context with BERT for Conversational Machine Comprehension
- Yasuhito OhsugiItsumi SaitoKyosuke NishidaHisako AsanoJunji Tomita
- 2019
Computer Science
Proceedings of the First Workshop on NLP for…
A simple but effective method with BERT for CMC that uses BERT to encode a paragraph independently conditioned with each question and each answer in a multi-turn context and finds that the gold answer history contributed to the model performance most on both datasets.
Related Papers
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers