DOI:10.1145/356678.356680 - Corpus ID: 207736773
Fault Tolerant Operating Systems
@article{Denning1976FaultTO, title={Fault Tolerant Operating Systems}, author={Peter J. Denning}, journal={ACM Comput. Surv.}, year={1976}, volume={8}, pages={359-389}, url={https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:207736773}}- P. Denning
- Published inCSUR1 December 1976
- Computer Science
- ACM Comput. Surv.
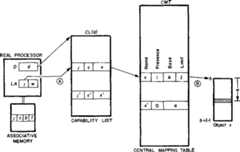
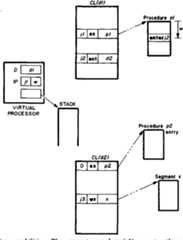
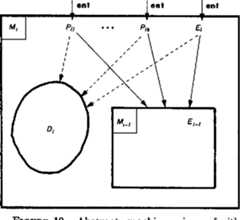
This paper develops four related architectural principles which can guide the construction of error-tolerant operating systems and implements of these principles are given for process management, interrupts and traps, store access through capabilities, protected procedure entry, and tagged architecture.
217 Citations
217 Citations
Design and principles of a fault tolerant system
This paper will discuss the determination of a global system architecture by a top-down approach and the principles of protection by capability and management of synchronization and object sharing between processes, by generalized monitors and path expression in this hierarchized system.
An approach to a fault-tolerant system architecture
The principles of domains and the architecture of a capability machine are discussed and management of scheduling and object sharing between processes, by monitors is detailed.
Data Security: The 1100/90 as a Closed, Fault-Tolerant Environment
- Stephen J. Rawlins
- 1985
Computer Science
Prax. Inf.verarb. Kommun.
Distributed system fault tolerance using message logging and checkpointing
- David B. JohnsonW. Zwaenepoel
- 1990
Computer Science, Engineering
A new optimistic message logging system is presented that guarantees to find the maximum possible recoverable system state, which is not ensured by previous optimistic methods.
Building a Reliable Operating System
- Francis M. David
- 2008
Computer Science, Engineering
CuriOS is presented, an operating system that incorporates several new error management techniques that significantly improve reliability and achieves inter-client isolation by curtailing error propagation within services.
The introduction of fault-tolerance in a hierarchical operating system
- M.D. SoneruW. Huen
- 1984
Computer Science
Fehlertolerierende Rechensysteme
A general method for introducing fault-tolerance in a hierarchical operating system is presented here, such that known techniques for fault-Tolerant operations can be represented as particular cases.
Design and implementation of a resource-secure system
- Matthieu LemerreV. DavidG. Vidal-Naquet
- 2009
Computer Science
It is proved that building resource-secure systems is pos-sible by describing the design and implementation of the prototype, Anaxagoros, and proposing several novel ways to solve synchronization problems.
Building a Self-Healing Operating System
- Francis M. DavidR. Campbell
- 2007
Computer Science
F Fault injection experiments show that these techniques can be used to continue running user applications after transparently recovering the operating system in a large percentage of cases and individual process recovery can be attempted as a last resort.
Building a Self-Healing Operating System
- Francis M. DavidRoy H. Campbell
- 2007
Computer Science
F Fault injection experiments show that these techniques can be used to continue running user applications after transparently recovering the operating system in a large percentage of cases and individual process recovery can be attempted as a last resort.
Resourceful systems for fault tolerance, reliability, and safety
- Russ Abbott
- 1990
Computer Science, Engineering
CSUR
The current state of the art of system reliability, safety, and fault tolerance is reviewed, and an approach to designing resourceful systems based upon a functionally rich architecture and an explicit goal orientation is developed.
...
55 References
Dynamic protection structures
- B. Lampson
- 1969
Computer Science
AFIPS '69 (Fall)
This paper deals with one aspect of the subject, which might be called the meta-theory of protection systems: how can the information which specifies protection and authorizes access, itself be protected and manipulated.
Formal requirements for virtualizable third generation architectures
- G. PopekR. Goldberg
- 1973
Computer Science
The hardware architectural requirements for virtual machine systems are discussed and a fairly specific definition of a virtual machine is presented which includes the aspects of efficiency, isolation, and identical behavior.
System structure for software fault tolerance
- B. Randell
- 1975
Computer Science, Engineering
The aim is to facilitate the provision of dependable error detection and recovery facilities which can cope with errors caused by residual design inadequacies, particularly in the system software, rather than merely the occasional malfunctioning of hardware components.
A hardware architecture for implementing protection rings
- M. D. SchroederJ. Saltzer
- 1972
Computer Science
CACM
Hardware processor mechanisms for implementing concentric rings of protection that allow cross-ring calls and subsequent returns to occur without trapping to the supervisor are described.
Operating systems principles
- S. KurzbanT. S. HeinesAnthony P. Sayers
- 1975
Computer Science
This chapter discusses the development of the Operating System Kernel: Implementing Processes and Threads and the Protection and Security Interface, which describes the interaction between Processes and Threads and the Kernel.
Dynamic verification of operating system decisions
- R. S. Fabry
- 1973
Computer Science
CACM
The dynamic verification of operating system decisions is used on the PRIME system to ensure that one user's information cannot become available to another user gratuitously even in the presence of a single hardware or software fault.
HYDRA
- W. WulfE. CohenF. Pollack
- 1974
Computer Science
This paper describes the design philosophy of HYDRA—the kernel of an operating system for C.mmp, the Carnegie-Mellon Multi-Mini-Processor, through the introduction of a generalized notion of “resource,” both physical and virtual, called an “object.”
A verifiable protection system
The design and implementation of the UCLA Virtual Machine System, a multiuser operating system base that has been developed to provide ultra high reliability protection and security, are reported on.
Protection in the Hydra Operating System
- E. CohenD. Jefferson
- 1975
Computer Science, Engineering
This paper describes the capability based protection mechanisms provided by the Hydra Operating System Kernel. These mechanisms support the construction of user-defined protected subsystems,…
A Computer Architecture for Level Structured Systems
- A. BernsteinP. Siegel
- 1975
Computer Science
The purpose of this paper is to point out where the hardware support is needed and to suggest one way of implementing these features, as well as providing some simple mechanisms in the hardware to support the level structure.
...
Related Papers
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers