DOI:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.01577.x - Corpus ID: 196448
Refining the Oort and Galactic constants
@article{Olling1998RefiningTO, title={Refining the Oort and Galactic constants}, author={Rob P. Olling and Michael R. Merrifield}, journal={Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society}, year={1998}, volume={297}, pages={943-952}, url={https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:196448}}- R. OllingM. Merrifield
- Published3 February 1998
- Physics
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
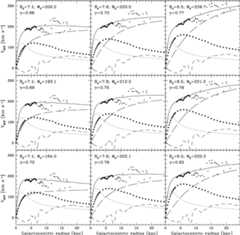
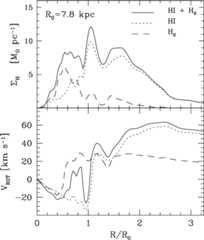
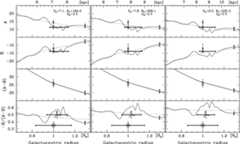
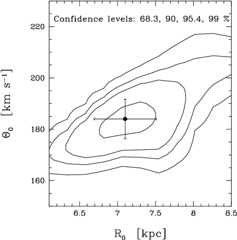
The local stellar kinematics of the Milky Way offer a useful tool for studying the rotation curve of the Galaxy. These kinematics — usually parametrized by the Oort constants AB— depend on the local gradient of the rotation curve as well as its absolute value (Θ0), and the Sun's distance to the Galactic Centre (R0). The density of interstellar gas in the Milky Way is shown to vary non-monotonically with radius, and so contributes significantly to the local gradient of the rotation curve. We…
114 Citations
114 Citations
ROTATION CURVE OF THE MILKY WAY OUT TO ∼200 kpc
- P. BhattacharjeeSoumini ChaudhuryS. Kundu
- 2014
Physics
The rotation curve (RC) of our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is constructed starting from its very inner regions (few hundred parsecs) out to a large galactocentric distance of ∼200 kpc using kinematical…
The galactic constants and rotation curve from molecular-gas observations
- V. Avedisova
- 2005
Physics
We obtained the photometric distances and radial velocities for the molecular gas for 270 star-forming regions and estimated the distance to the Galactic center from ten tangent points to be R0 =…
Kinematics and stellar content of the Milky Way populations toward the North Galactic Pole
Aims. The formation and evolution of galaxies is one of the forefront problems of Astrophysics. Detailed studies of our own Galaxy are the first step to understand these complex processes. In this…
Milky Way Mass Models and MOND
- S. McGaugh
- 2008
Physics
Using the Tuorla-Heidelberg model for the mass distribution of the Milky Way, I determine the rotation curve predicted by MOND (modified Newtonian dynamics). The result is in good agreement with the…
ON THE SHOULDERS OF GIANTS: PROPERTIES OF THE STELLAR HALO AND THE MILKY WAY MASS DISTRIBUTION
Halo stars orbit within the potential of the Milky Way, and hence their kinematics can be used to understand the underlying mass distribution. However, the inferred mass distribution depends…
The Oort Constants Measured from Proper Motions
The Oort constants describe the local spatial variations of the stellar streaming field. The classic way for their determination employs their effect on stellar proper motions. We discuss various…
Inversion of stellar statistics equation for the Galactic bulge
A method based on Lucy (1974) iterative algorithm is developed to invert the equation of stellar statistics for the Galactic bulge and is then applied to the K-band star counts from the Two-Micron…
Star-forming complexes and the spiral structure of our Galaxy
- D. Russeil
- 2003
Physics
We have carried out a multiwavelength study of the plane of our Galaxy in order to establish a star-forming-complex catalogue which is as complete as possible. Features observed include H, H109, CO,…
Luminous and dark matter in the Milky Way
- R. OllingM. Merrifield
- 2001
Physics
Axisymmetric models of the Milky Way exhibit strong interrelations between the Galactic constants [the Sun's distance to the Galactic Centre (R0), and the local rotation speed (θ0)], the local…
DETERMINATION OF THE GALACTIC ROTATION USING OPEN STAR CLUSTERS
- P. Majewski
- 2005
Physics
The dark matter distribution of the Milky Way remains among the major unsolved problems about our home galaxy. The masses of other spiral galaxies can be determined from their rotation curves through…
...
6 References
Galactic and Extragalactic Radio Astronomy
- S. KulkarniC. Heiles
- 1988
Physics
An ulrasonic liquid level measurement device is used to measure the depth of a flowing liquid in a channel using an ultrasonic transducer that is positioned out of contact with the liquid and above…
UNSOLVED PROBLEMS OF THE MILKY WAY
- K. KuijkenM. BalcellsM. Weinberg
- 1996
Agricultural and Food Sciences, Environmental Science
Related Papers
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers