Real-Time Depth of Anaesthesia Assessment Based on Hybrid Statistical Features of EEG
- PMID:36015860
- PMCID: PMC9414837
- DOI: 10.3390/s22166099
Real-Time Depth of Anaesthesia Assessment Based on Hybrid Statistical Features of EEG
Abstract
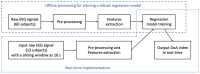
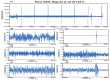
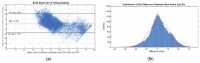
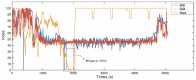
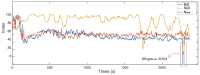
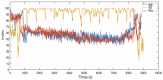
This paper proposed a new depth of anaesthesia (DoA) index for the real-time assessment of DoA using electroencephalography (EEG). In the proposed new DoA index, a wavelet transform threshold was applied to denoise raw EEG signals, and five features were extracted to construct classification models. Then, the Gaussian process regression model was employed for real-time assessment of anaesthesia states. The proposed real-time DoA index was implemented using a sliding window technique and validated using clinical EEG data recorded with the most popular commercial DoA product Bispectral Index monitor (BIS). The results are evaluated using the correlation coefficients and Bland-Altman methods. The outcomes show that the highest and the average correlation coefficients are 0.840 and 0.814, respectively, in the testing dataset. Meanwhile, the scatter plot of Bland-Altman shows that the agreement between BIS and the proposed index is 94.91%. In contrast, the proposed index is free from the electromyography (EMG) effect and surpasses the BIS performance when the signal quality indicator (SQI) is lower than 15, as the proposed index can display high correlation and reliable assessment results compared with clinic observations.
Keywords: EEG; depth of anaesthesia; machine learning; real-time.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
- Consciousness and depth of anesthesia assessment based on Bayesian analysis of EEG signals.Nguyen-Ky T, Wen PP, Li Y.Nguyen-Ky T, et al.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2013 Jun;60(6):1488-98. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2236649. Epub 2013 Jan 9.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2013.PMID:23314762
- Measuring the hypnotic depth of anaesthesia based on the EEG signal using combined wavelet transform, eigenvector and normalisation techniques.Nguyen-Ky T, Wen P, Li Y, Malan M.Nguyen-Ky T, et al.Comput Biol Med. 2012 Jun;42(6):680-91. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 May 9.Comput Biol Med. 2012.PMID:22575174
- Developing a robust model to predict depth of anesthesia from single channel EEG signal.Alsafy I, Diykh M.Alsafy I, et al.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2022 Sep;45(3):793-808. doi: 10.1007/s13246-022-01145-z. Epub 2022 Jul 5.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2022.PMID:35790625Free PMC article.
- Harnessing machine learning for EEG signal analysis: Innovations in depth of anaesthesia assessment.Schmierer T, Li T, Li Y.Schmierer T, et al.Artif Intell Med. 2024 May;151:102869. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2024.102869. Epub 2024 Apr 4.Artif Intell Med. 2024.PMID:38593683Review.
- Depth of anaesthesia monitors and the latest algorithms.Li TN, Li Y.Li TN, et al.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014 Jun;7(6):429-37. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60070-5.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014.PMID:25066390Review.
Cited by
- Accurate depth of anesthesia monitoring based on EEG signal complexity and frequency features.Li T, Huang Y, Wen P, Li Y.Li T, et al.Brain Inform. 2024 Nov 21;11(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40708-024-00241-y.Brain Inform. 2024.PMID:39570515Free PMC article.
References
- Bard J.W. The BIS monitor: A review and technology assessment. AANA J. 2001;69:477–483. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Related information
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
