Automatic Recognition of Human Interaction via Hybrid Descriptors and Maximum Entropy Markov Model Using Depth Sensors
- PMID:33286588
- PMCID: PMC7517385
- DOI: 10.3390/e22080817
Automatic Recognition of Human Interaction via Hybrid Descriptors and Maximum Entropy Markov Model Using Depth Sensors
Abstract
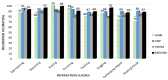
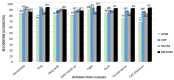
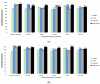
Automatic identification of human interaction is a challenging task especially in dynamic environments with cluttered backgrounds from video sequences. Advancements in computer vision sensor technologies provide powerful effects in human interaction recognition (HIR) during routine daily life. In this paper, we propose a novel features extraction method which incorporates robust entropy optimization and an efficient Maximum Entropy Markov Model (MEMM) for HIR via multiple vision sensors. The main objectives of proposed methodology are: (1) to propose a hybrid of four novel features-i.e., spatio-temporal features, energy-based features, shape based angular and geometric features-and a motion-orthogonal histogram of oriented gradient (MO-HOG); (2) to encode hybrid feature descriptors using a codebook, a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) and fisher encoding; (3) to optimize the encoded feature using a cross entropy optimization function; (4) to apply a MEMM classification algorithm to examine empirical expectations and highest entropy, which measure pattern variances to achieve outperformed HIR accuracy results. Our system is tested over three well-known datasets: SBU Kinect interaction; UoL 3D social activity; UT-interaction datasets. Through wide experimentations, the proposed features extraction algorithm, along with cross entropy optimization, has achieved the average accuracy rate of 91.25% with SBU, 90.4% with UoL and 87.4% with UT-Interaction datasets. The proposed HIR system will be applicable to a wide variety of man-machine interfaces, such as public-place surveillance, future medical applications, virtual reality, fitness exercises and 3D interactive gaming.
Keywords: Gaussian mixture model; cross entropy; depth sensors; maximum entropy Markov model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



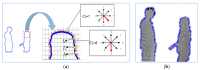
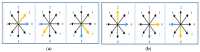




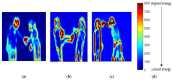
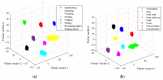





Similar articles
- Wearable Inertial Sensors for Daily Activity Analysis Based on Adam Optimization and the Maximum Entropy Markov Model.Tahir SBUD, Jalal A, Kim K.Tahir SBUD, et al.Entropy (Basel). 2020 May 20;22(5):579. doi: 10.3390/e22050579.Entropy (Basel). 2020.PMID:33286351Free PMC article.
- An Online Continuous Human Action Recognition Algorithm Based on the Kinect Sensor.Zhu G, Zhang L, Shen P, Song J.Zhu G, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Jan 28;16(2):161. doi: 10.3390/s16020161.Sensors (Basel). 2016.PMID:26828497Free PMC article.
- A Novel Maximum Entropy Markov Model for Human Facial Expression Recognition.Siddiqi MH, Alam MG, Hong CS, Khan AM, Choo H.Siddiqi MH, et al.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 16;11(9):e0162702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162702. eCollection 2016.PLoS One. 2016.PMID:27635654Free PMC article.
- Engineering Aspects of Olfaction.Persaud KC.Persaud KC.In: Persaud KC, Marco S, Gutiérrez-Gálvez A, editors. Neuromorphic Olfaction. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2013. Chapter 1.In: Persaud KC, Marco S, Gutiérrez-Gálvez A, editors. Neuromorphic Olfaction. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2013. Chapter 1.PMID:26042329Free Books & Documents.Review.
- The Synthetic Moth: A Neuromorphic Approach toward Artificial Olfaction in Robots.Vouloutsi V, Lopez-Serrano LL, Mathews Z, Escuredo Chimeno A, Ziyatdinov A, Perera i Lluna A, Bermúdez i Badia S, Verschure PFMJ.Vouloutsi V, et al.In: Persaud KC, Marco S, Gutiérrez-Gálvez A, editors. Neuromorphic Olfaction. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2013. Chapter 4.In: Persaud KC, Marco S, Gutiérrez-Gálvez A, editors. Neuromorphic Olfaction. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2013. Chapter 4.PMID:26042327Free Books & Documents.Review.
Cited by
- Multi-Person Tracking and Crowd Behavior Detection via Particles Gradient Motion Descriptor and Improved Entropy Classifier.Abdullah F, Ghadi YY, Gochoo M, Jalal A, Kim K.Abdullah F, et al.Entropy (Basel). 2021 May 18;23(5):628. doi: 10.3390/e23050628.Entropy (Basel). 2021.PMID:34069994Free PMC article.
- Syntactic model-based human body 3D reconstruction and event classification via association based features mining and deep learning.Ghadi Y, Akhter I, Alarfaj M, Jalal A, Kim K.Ghadi Y, et al.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021 Nov 19;7:e764. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.764. eCollection 2021.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021.PMID:34901426Free PMC article.
- TCN-attention-HAR: human activity recognition based on attention mechanism time convolutional network.Wei X, Wang Z.Wei X, et al.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 28;14(1):7414. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57912-3.Sci Rep. 2024.PMID:38548859Free PMC article.
- A robust multimodal detection system: physical exercise monitoring in long-term care environments.Al Mudawi N, Batool M, Alazeb A, Alqahtani Y, Almujally NA, Algarni A, Jalal A, Liu H.Al Mudawi N, et al.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 8;12:1398291. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1398291. eCollection 2024.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024.PMID:39175622Free PMC article.
- Smart Home Automation-Based Hand Gesture Recognition Using Feature Fusion and Recurrent Neural Network.Alabdullah BI, Ansar H, Mudawi NA, Alazeb A, Alshahrani A, Alotaibi SS, Jalal A.Alabdullah BI, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;23(17):7523. doi: 10.3390/s23177523.Sensors (Basel). 2023.PMID:37687978Free PMC article.
References
- Li J., Tian L., Wang H., An Y., Wang K., Yu L. Segmentation and Recognition of Basic and Transitional Activities for Continuous Physical Human Activity. IEEE Access. 2019;7:42565–42576. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905575. - DOI
- Ajmal M., Ahmad F., Naseer M., Jamjoom M. Recognizing Human Activities from Video Using Weakly Supervised Contextual Features. IEEE Access. 2019;7:98420–98435. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2929262. - DOI
- Susan S., Agrawal P., Mittal M., Bansal S. New shape descriptor in the context of edge continuity. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2019;4:101–109. doi: 10.1049/trit.2019.0002. - DOI
- Shokri M., Tavakoli K. A review on the artificial neural network approach to analysis and prediction of seismic damage in infrastructure. Int. J. Hydromechatron. 2019;4:178–196. doi: 10.1504/IJHM.2019.104386. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
