Dynamics Analysis of a Nonlinear Stochastic SEIR Epidemic System with Varying Population Size
- PMID:33265467
- PMCID: PMC7512895
- DOI: 10.3390/e20050376
Dynamics Analysis of a Nonlinear Stochastic SEIR Epidemic System with Varying Population Size
Abstract
This paper considers a stochastic susceptible exposed infectious recovered (SEIR) epidemic model with varying population size and vaccination. We aim to study the global dynamics of the reduced nonlinear stochastic proportional differential system. We first investigate the existence and uniqueness of global positive solution of the stochastic system. Then the sufficient conditions for the extinction and permanence in mean of the infectious disease are obtained. Furthermore, we prove that the solution of the stochastic system has a unique ergodic stationary distribution under appropriate conditions. Finally, the discussion and numerical simulation are given to demonstrate the obtained results.
Keywords: Stochastic SEIR model; permanence in mean; stationary distribution; vaccination; varying population size.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
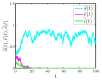
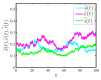
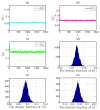
Similar articles
- Stationary distribution and probability density for a stochastic SEIR-type model of coronavirus (COVID-19) with asymptomatic carriers.Liu Q, Jiang D.Liu Q, et al.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2023 Apr;169:113256. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113256. Epub 2023 Feb 15.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2023.PMID:36820073Free PMC article.
- Deterministic and stochastic dynamics of a modified Leslie-Gower prey-predator system with simplified Holling-type Ⅳ scheme.Li L, Zhao W.Li L, et al.Math Biosci Eng. 2021 Mar 24;18(3):2813-2831. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021143.Math Biosci Eng. 2021.PMID:33892573
- Analysis and Numerical Simulations of a Stochastic SEIQR Epidemic System with Quarantine-Adjusted Incidence and Imperfect Vaccination.Li F, Meng X, Wang X.Li F, et al.Comput Math Methods Med. 2018 Feb 20;2018:7873902. doi: 10.1155/2018/7873902. eCollection 2018.Comput Math Methods Med. 2018.PMID:29675054Free PMC article.
- Threshold Dynamics in Stochastic SIRS Epidemic Models with Nonlinear Incidence and Vaccination.Wang L, Teng Z, Tang T, Li Z.Wang L, et al.Comput Math Methods Med. 2017;2017:7294761. doi: 10.1155/2017/7294761. Epub 2017 Jan 16.Comput Math Methods Med. 2017.PMID:28194223Free PMC article.
- Robust permanence and impermanence for stochastic replicator dynamics.Benaïm M, Hofbauer J, Sandholm WH.Benaïm M, et al.J Biol Dyn. 2008 Apr;2(2):180-95. doi: 10.1080/17513750801915269.J Biol Dyn. 2008.PMID:22880700Review.
Cited by
- Forecasting the final disease size: comparing calibrations of Bertalanffy-Pütter models.Brunner N, Kühleitner M.Brunner N, et al.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Dec 28;149:e6. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820003039.Epidemiol Infect. 2020.PMID:33357248Free PMC article.
- Dynamics Analysis of a Wireless Rechargeable Sensor Network for Virus Mutation Spreading.Liu G, Peng Z, Liang Z, Li J, Cheng L.Liu G, et al.Entropy (Basel). 2021 May 6;23(5):572. doi: 10.3390/e23050572.Entropy (Basel). 2021.PMID:34066582Free PMC article.
- The stochastic -SEIHRD model: Adding randomness to the COVID-19 spread.Leitao Á, Vázquez C.Leitao Á, et al.Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2022 Dec;115:106731. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2022.106731. Epub 2022 Jul 23.Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2022.PMID:35910551Free PMC article.
- The Peculiar Emergence of Mpox (Monkeypox): Directions for the Search for the Natural Reservoir and Vaccination Strategies.Breban R.Breban R.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Oct 4;12(10):1142. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12101142.Vaccines (Basel). 2024.PMID:39460309Free PMC article.
- Modeling the dynamics of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) via stochastic epidemic model.Khan T, Zaman G, El-Khatib Y.Khan T, et al.Results Phys. 2021 May;24:104004. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104004. Epub 2021 Mar 27.Results Phys. 2021.PMID:33816091Free PMC article.
References
- Kermack W.O., McKendrick A.G. Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics-I. Bull. Math. Biol. 1991;53:33–55. - PubMed
- Cai Y., Kang Y., Banerjee M., Wang W. A stochastic SIRS epidemic model with infectious force under intervention strategies. J. Differ. Equat. 2015;259:7463–7502. doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2015.08.024. - DOI
- Zhang T., Meng X., Zhang T. Global analysis for a delayed SIV model with direct and environmental transmissions. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2016;6:479–491.
- Zhou L., Fan M. Dynamics of an SIR epidemic model with limited medical resources revisited. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2012;13:312–324. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2011.07.036. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
