Vision-Based Pose Estimation for Robot-Mediated Hand Telerehabilitation
- PMID:26861333
- PMCID: PMC4801584
- DOI: 10.3390/s16020208
Vision-Based Pose Estimation for Robot-Mediated Hand Telerehabilitation
Abstract
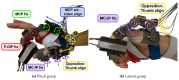
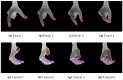
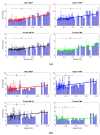
Vision-based Pose Estimation (VPE) represents a non-invasive solution to allow a smooth and natural interaction between a human user and a robotic system, without requiring complex calibration procedures. Moreover, VPE interfaces are gaining momentum as they are highly intuitive, such that they can be used from untrained personnel (e.g., a generic caregiver) even in delicate tasks as rehabilitation exercises. In this paper, we present a novel master-slave setup for hand telerehabilitation with an intuitive and simple interface for remote control of a wearable hand exoskeleton, named HX. While performing rehabilitative exercises, the master unit evaluates the 3D position of a human operator's hand joints in real-time using only a RGB-D camera, and commands remotely the slave exoskeleton. Within the slave unit, the exoskeleton replicates hand movements and an external grip sensor records interaction forces, that are fed back to the operator-therapist, allowing a direct real-time assessment of the rehabilitative task. Experimental data collected with an operator and six volunteers are provided to show the feasibility of the proposed system and its performances. The results demonstrate that, leveraging on our system, the operator was able to directly control volunteers' hands movements.
Keywords: hand exoskeleton; hand telerehabilitation; motion tracking; upper limb rehabilitation.
Figures





Similar articles
- The "Beam-Me-In Strategy" - remote haptic therapist-patient interaction with two exoskeletons for stroke therapy.Baur K, Rohrbach N, Hermsdörfer J, Riener R, Klamroth-Marganska V.Baur K, et al.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2019 Jul 12;16(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12984-019-0547-3.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2019.PMID:31296226Free PMC article.
- A Wearable IMU System for Flexible Teleoperation of a Collaborative Industrial Robot.Škulj G, Vrabič R, Podržaj P.Škulj G, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;21(17):5871. doi: 10.3390/s21175871.Sensors (Basel). 2021.PMID:34502761Free PMC article.
- A Survey on Hand Pose Estimation with Wearable Sensors and Computer-Vision-Based Methods.Chen W, Yu C, Tu C, Lyu Z, Tang J, Ou S, Fu Y, Xue Z.Chen W, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Feb 16;20(4):1074. doi: 10.3390/s20041074.Sensors (Basel). 2020.PMID:32079124Free PMC article.Review.
- Joint amplitude MEMS based measurement platform for low cost and high accessibility telerehabilitation: Elbow case study.Callejas-Cuervo M, Gutierrez RM, Hernandez AI.Callejas-Cuervo M, et al.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2017 Jul;21(3):574-581. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2016.08.016. Epub 2016 Sep 9.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2017.PMID:28750967
- Journey from human hands to robot hands: biological inspiration of anthropomorphic robotic manipulators.Han MS, Harnett CK.Han MS, et al.Bioinspir Biomim. 2024 Feb 19;19(2). doi: 10.1088/1748-3190/ad262c.Bioinspir Biomim. 2024.PMID:38316033Review.
Cited by
- Design and Construction of a Bilateral Haptic System for the Remote Assessment of the Stiffness and Range of Motion of the Hand.Oscari F, Oboe R, Daud Albasini OA, Masiero S, Rosati G.Oscari F, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Oct 1;16(10):1633. doi: 10.3390/s16101633.Sensors (Basel). 2016.PMID:27706085Free PMC article.
- A Review of Hand Function Rehabilitation Systems Based on Hand Motion Recognition Devices and Artificial Intelligence.Gu Y, Xu Y, Shen Y, Huang H, Liu T, Jin L, Ren H, Wang J.Gu Y, et al.Brain Sci. 2022 Aug 15;12(8):1079. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12081079.Brain Sci. 2022.PMID:36009142Free PMC article.Review.
- Disturbance-Estimated Adaptive Backstepping Sliding Mode Control of a Pneumatic Muscles-Driven Ankle Rehabilitation Robot.Ai Q, Zhu C, Zuo J, Meng W, Liu Q, Xie SQ, Yang M.Ai Q, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Dec 28;18(1):66. doi: 10.3390/s18010066.Sensors (Basel). 2017.PMID:29283406Free PMC article.
- Patient-Therapist Cooperative Hand Telerehabilitation through a Novel Framework Involving the Virtual Glove System.Placidi G, Di Matteo A, Lozzi D, Polsinelli M, Theodoridou E.Placidi G, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 25;23(7):3463. doi: 10.3390/s23073463.Sensors (Basel). 2023.PMID:37050523Free PMC article.
- Are We Ready to Build a System for Assisting Blind People in Tactile Exploration of Bas-Reliefs?Buonamici F, Carfagni M, Furferi R, Governi L, Volpe Y.Buonamici F, et al.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Aug 24;16(9):1361. doi: 10.3390/s16091361.Sensors (Basel). 2016.PMID:27563906Free PMC article.
References
- Dobkin B. The economic impact of stroke. Neurology. 1995;45:S6–S9. - PubMed
- Fox S. EVAL-revolutionizing hand exams. Adv. Occup. Ther. 1991;7:1–7.
- Giansanti D., Morelli S., Maccioni G., Macellari V. Validation of a tele-home-care for hand-telerehabilitation. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2007;2007:3830–3832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
