Hippocampal replay captures the unique topological structure of a novel environment
- PMID:24806672
- PMCID: PMC4012305
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3414-13.2014
Hippocampal replay captures the unique topological structure of a novel environment
Abstract
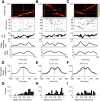
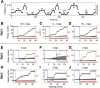
Hippocampal place-cell replay has been proposed as a fundamental mechanism of learning and memory, which might support navigational learning and planning. An important hypothesis of relevance to these proposed functions is that the information encoded in replay should reflect the topological structure of experienced environments; that is, which places in the environment are connected with which others. Here we report several attributes of replay observed in rats exploring a novel forked environment that support the hypothesis. First, we observed that overlapping replays depicting divergent trajectories through the fork recruited the same population of cells with the same firing rates to represent the common portion of the trajectories. Second, replay tended to be directional and to flip the represented direction at the fork. Third, replay-associated sharp-wave-ripple events in the local field potential exhibited substructure that mapped onto the maze topology. Thus, the spatial complexity of our recording environment was accurately captured by replay: the underlying neuronal activities reflected the bifurcating shape, and both directionality and associated ripple structure reflected the segmentation of the maze. Finally, we observed that replays occurred rapidly after small numbers of experiences. Our results suggest that hippocampal replay captures learned information about environmental topology to support a role in navigation.
Figures
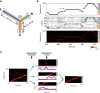
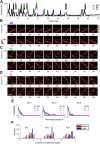

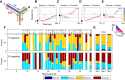
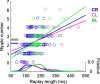
Comment in
- Hippocampal neurons: simulating the spatial structure of a complex maze.Jeffery K, Casali G.Jeffery K, et al.Curr Biol. 2014 Jul 21;24(14):R643-R645. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.001.Curr Biol. 2014.PMID:25050959
Similar articles
- Hippocampal replay is not a simple function of experience.Gupta AS, van der Meer MA, Touretzky DS, Redish AD.Gupta AS, et al.Neuron. 2010 Mar 11;65(5):695-705. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.01.034.Neuron. 2010.PMID:20223204Free PMC article.
- Enhanced Reactivation of Remapping Place Cells during Aversive Learning.Ormond J, Serka SA, Johansen JP.Ormond J, et al.J Neurosci. 2023 Mar 22;43(12):2153-2167. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1450-22.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 3.J Neurosci. 2023.PMID:36596695Free PMC article.
- Prioritized experience replays on a hippocampal predictive map for learning.Igata H, Ikegaya Y, Sasaki T.Igata H, et al.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 5;118(1):e2011266118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2011266118. Epub 2020 Dec 18.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021.PMID:33443144Free PMC article.
- Reactivation, replay, and preplay: how it might all fit together.Buhry L, Azizi AH, Cheng S.Buhry L, et al.Neural Plast. 2011;2011:203462. doi: 10.1155/2011/203462. Epub 2011 Sep 13.Neural Plast. 2011.PMID:21918724Free PMC article.Review.
- Parallel processing across neural systems: implications for a multiple memory system hypothesis.Mizumori SJ, Yeshenko O, Gill KM, Davis DM.Mizumori SJ, et al.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2004 Nov;82(3):278-98. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2004.07.007.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2004.PMID:15464410Review.
Cited by
- Uncovering representations of sleep-associated hippocampal ensemble spike activity.Chen Z, Grosmark AD, Penagos H, Wilson MA.Chen Z, et al.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 30;6:32193. doi: 10.1038/srep32193.Sci Rep. 2016.PMID:27573200Free PMC article.
- From Topological Analyses to Functional Modeling: The Case of Hippocampus.Dabaghian Y.Dabaghian Y.Front Comput Neurosci. 2021 Jan 11;14:593166. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2020.593166. eCollection 2020.Front Comput Neurosci. 2021.PMID:33505262Free PMC article.
- Robust spatial memory maps encoded by networks with transient connections.Babichev A, Morozov D, Dabaghian Y.Babichev A, et al.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Sep 18;14(9):e1006433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006433. eCollection 2018 Sep.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018.PMID:30226836Free PMC article.
- Mesoscopic description of hippocampal replay and metastability in spiking neural networks with short-term plasticity.Pietras B, Schmutz V, Schwalger T.Pietras B, et al.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Dec 22;18(12):e1010809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010809. eCollection 2022 Dec.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022.PMID:36548392Free PMC article.
- Multiple-Timescale Representations of Space: Linking Memory to Navigation.Tang W, Jadhav SP.Tang W, et al.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2022 Jul 8;45:1-21. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-111020-084824. Epub 2021 Dec 22.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2022.PMID:34936810Free PMC article.Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources