🎓Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
Source Code on GitHub
This tutorial is accompanied by a working code exampleon GitHub.YouTube Video
1. What we’ll build
We are building a simpleUser Management Application which has below CRUD Rest APIs.1. Creating Spring Boot Project
Use the following details while creating the Spring Boot project:
- Generate: Maven Project
- Java Version: 17 (Default)
- Spring Boot:3.0.4
- Group: com.companyname
- Artifact: springbootcrudrest
- Name: springbootcrudrest
- Description: Rest API for a Simple User Management Application
- Package Name : com.companyname.springbootcrudrest
- Packaging: jar (This is the default value)
- Dependencies: Web, JPA, MySQL, DevTools
3. Maven Dependencies - pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.companyname</groupId><artifactId>springbootcrudrest</artifactId><version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version><packaging>jar</packaging><name>springbootcrudrest</name><description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>3.0.4</version><relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --></parent><properties><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding><project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding><java.version>17</java.version></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId></plugin></plugins></build></project>Spring Boot Maven plugin
The Spring Boot Maven plugin provides many convenient features:- It collects all the jars on the classpath and builds a single, runnable "über-jar", which makes it more convenient to execute and transport your service.
- It searches for the public static void main() method to flag as a runnable class.
- It provides a built-in dependency resolver that sets the version number to match Spring Boot dependencies. You can override any version you wish, but it will default to Boot’s chosen set of versions.
spring-boot-starter-parent
All Spring Boot projects typically use spring-boot-starter-parent as the parent in pom.xml.<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>3.0.4</version> </parent>
- Configuration - Java Version and Other Properties
- Dependency Management - Version of dependencies
- Default Plugin Configuration
spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
We added thespring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency. This pulls all the spring-data-jpa dependencies and adds Hibernate libraries because most applications use Hibernate as a JPA implementation.3. Configuring MySQL Database
Since we’re using MySQL as our database, we need to configure the database URL, username, and password so that Spring can establish a connection with the database on startup.spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/users_database?useSSL=falsespring.datasource.username = rootspring.datasource.password = root## Hibernate Properties# The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen databasespring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update)spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
You don’t need to create any tables. The tables will automatically be created by hibernate from the User entity that we will define in the next step. This is made possible by the propertyspring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update.
4. Create a JPA Entity - User
- id - primary key
- firstName - user's first name
- lastName - user last name
- emailId - user email ID
- createdAt - user object created date
- createdBy - use an object created by
- updatedAt - user object updated by
- updatedby - user object updated by
packagecom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.model;importjava.util.Date;importjakarta.persistence.*;importorg.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedBy;importorg.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;importorg.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedBy;importorg.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedDate;importorg.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;@Entity@Table(name="users")@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)publicclassUser {privatelong id;privateString firstName;privateString lastName;privateString emailId;privateDate createdAt;privateString createdBy;privateDate updatedAt;privateString updatedby;@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)publiclonggetId() {return id; }publicvoidsetId(longid) {this.id= id; }@Column(name="first_name",nullable=false)publicStringgetFirstName() {return firstName; }publicvoidsetFirstName(StringfirstName) {this.firstName= firstName; }@Column(name="last_name",nullable=false)publicStringgetLastName() {return lastName; }publicvoidsetLastName(StringlastName) {this.lastName= lastName; }@Column(name="email_address",nullable=false)publicStringgetEmailId() {return emailId; }publicvoidsetEmailId(StringemailId) {this.emailId= emailId; }@Column(name="created_at",nullable=false)@CreatedDatepublicDategetCreatedAt() {return createdAt; }publicvoidsetCreatedAt(DatecreatedAt) {this.createdAt= createdAt; }@Column(name="created_by",nullable=false)@CreatedBypublicStringgetCreatedBy() {return createdBy; }publicvoidsetCreatedBy(StringcreatedBy) {this.createdBy= createdBy; }@Column(name="updated_at",nullable=false)@LastModifiedDatepublicDategetUpdatedAt() {return updatedAt; }publicvoidsetUpdatedAt(DateupdatedAt) {this.updatedAt= updatedAt; }@Column(name="updated_by",nullable=false)@LastModifiedBypublicStringgetUpdatedby() {return updatedby; }publicvoidsetUpdatedby(Stringupdatedby) {this.updatedby= updatedby; }}
All your domain models must be annotated with@Entity annotation. It is used to mark the class as a persistent Java class.
@Table annotation is used to provide the details of the table that this entity will be mapped to.
@Id annotation is used to define the primary key.
@GeneratedValue annotation is used to define the primary key generation strategy. In the above case, we have declared the primary key to be an Auto Increment field.
@Column annotation is used to define the properties of the column that will be mapped to the annotated field. You can define several properties like name, length, nullable, updateable etc.
How to enable JPA Auditing
Let's understand important JPA Auditing annotations:- @CreatedDate - Declares a field as the one representing the date the entity containing the field was created.
- @LastModifiedDate - Declares a field as the one representing the date the entity containing the field was recently modified.
- @CreatedBy- Declares a field as the one representing the principal that created the entity containing the field.
- @LastModifiedBy - Declares a field as the one representing the principal that recently modified the entity containing the field.
1. Add Spring Data JPA’s AuditingEntityListener to the domain model. We have already done this in ourUser model with the annotation@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class).
@Entity@Table(name="users")@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)publicclassUser {// rest of the code here}
OpenSpringBootCrudRestApplication.java and add a@EnableJpaAuditing annotation.
importorg.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;importorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;importorg.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaAuditing;@SpringBootApplication@EnableJpaAuditingpublicclassSpringBootCrudRestApplication {publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCrudRestApplication.class, args); }}
5. Create Spring Data JPA Repository - UserRepository
importorg.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;importcom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.model.User;publicinterfaceUserRepositoryextendsJpaRepository<User,Long>{}
List<T> findAll();List<T> findAll(Sort sort);List<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids);<S extendsT>List<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities);void flush();<S extendsT>S saveAndFlush(S entity);void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities);void deleteAllInBatch();T getOne(ID id);@Override<S extendsT>List<S> findAll(Example<S> example);<S extendsT>List<S> findAll(Example<S> example,Sort sort);
6. Exception(Error) Handling for RESTful Services
ResourceNotFoundException
packagecom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.exception;importorg.springframework.http.HttpStatus;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;@ResponseStatus(value=HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)publicclassResourceNotFoundExceptionextendsException{privatestaticfinallong serialVersionUID=1L;publicResourceNotFoundException(Stringmessage){super(message); }}
ErrorDetails
Let's createErrorDetails that we will use to customize the error response structure:packagecom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.exception;importjava.util.Date;publicclassErrorDetails {privateDate timestamp;privateString message;privateString details;publicErrorDetails(Datetimestamp,Stringmessage,Stringdetails) {super();this.timestamp= timestamp;this.message= message;this.details= details; }publicDategetTimestamp() {return timestamp; }publicStringgetMessage() {return message; }publicStringgetDetails() {return details; }}
GlobalExceptionHandler
To use ErrorDetails to return the error response, let’s create aGlobalExceptionHandler class annotated with@ControllerAdvice annotation. This class handles exception-specific and global exceptions in a single place.packagecom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.exception;importjava.util.Date;importorg.springframework.http.HttpStatus;importorg.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;importorg.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;@ControllerAdvicepublicclassGlobalExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)publicResponseEntity<?>resourceNotFoundException(ResourceNotFoundExceptionex,WebRequestrequest) {ErrorDetails errorDetails=newErrorDetails(newDate(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));returnnewResponseEntity<>(errorDetails,HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); }@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)publicResponseEntity<?>globleExcpetionHandler(Exceptionex,WebRequestrequest) {ErrorDetails errorDetails=newErrorDetails(newDate(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));returnnewResponseEntity<>(errorDetails,HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); }}
7. Creating UserController(Contains REST APIs)
Now, it's time to create CRUD Rest APIs for theUser model.packagecom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.controller;importjava.util.Date;importjava.util.HashMap;importjava.util.List;importjava.util.Map;importjakarta.validation.Valid;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;importorg.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;importcom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;importcom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.model.User;importcom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.repository.UserRepository;@RestController@RequestMapping("/api/v1")publicclassUserController {@AutowiredprivateUserRepository userRepository;@GetMapping("/users")publicList<User>getAllUsers() {return userRepository.findAll(); }@GetMapping("/users/{id}")publicResponseEntity<User>getUserById(@PathVariable(value="id")LonguserId)throwsResourceNotFoundException {User user= userRepository.findById(userId) .orElseThrow(()->newResourceNotFoundException("User not found on ::"+ userId));returnResponseEntity.ok().body(user); }@PostMapping("/users")publicUsercreateUser(@Valid@RequestBodyUseruser) {return userRepository.save(user); }@PutMapping("/users/{id}")publicResponseEntity<User>updateUser(@PathVariable(value="id")LonguserId,@Valid@RequestBodyUseruserDetails)throwsResourceNotFoundException {User user= userRepository.findById(userId) .orElseThrow(()->newResourceNotFoundException("User not found on ::"+ userId)); user.setEmailId(userDetails.getEmailId()); user.setLastName(userDetails.getLastName()); user.setFirstName(userDetails.getFirstName()); user.setUpdatedAt(newDate());finalUser updatedUser= userRepository.save(user);returnResponseEntity.ok(updatedUser); }@DeleteMapping("/user/{id}")publicMap<String,Boolean>deleteUser(@PathVariable(value="id")LonguserId)throwsException {User user= userRepository.findById(userId) .orElseThrow(()->newResourceNotFoundException("User not found on ::"+ userId)); userRepository.delete(user);Map<String,Boolean> response=newHashMap<>(); response.put("deleted",Boolean.TRUE);return response; }}
@RestController - annotation is a combination of Spring’s @Controller and @ResponseBody annotations.
@PostMapping - annotation is a short form of @RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.POST). This annotation is used to map incoming HTTP POST requests to a specific method handler.
@PutMapping - annotation is a short form of @RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.PUT).This annotation is used to map incoming HTTP PUT requests to a specific method handler.
@DeleteMapping - annotation is a short form of @RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.DELETE). This annotation is used to map incoming HTTP DELETE requests to a specific method handler.
@PathVariable - annotation is used to bind a path variable with a method parameter.
8. Running the Application
We have successfully developed all the CRUD Rest APIs for theUser model. now it's time to deploy our application in a servlet container(embedded tomcat). Two ways we can start the standalone Spring boot application.$ mvn spring-boot:run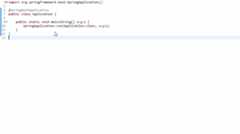
9. Unit Testing REST APIs
Let's write JUnit test cases for all Rest APIs of theUser entity.packagecom.companyname.projectname.springbootcrudrest;import staticorg.junit.Assert.assertEquals;import staticorg.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;importorg.junit.Test;importorg.junit.runner.RunWith;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;importorg.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;importorg.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;importorg.springframework.boot.web.server.LocalServerPort;importorg.springframework.http.HttpEntity;importorg.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;importorg.springframework.http.HttpMethod;importorg.springframework.http.HttpStatus;importorg.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;importorg.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;importorg.springframework.web.client.HttpClientErrorException;importcom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.SpringBootCrudRestApplication;importcom.companyname.springbootcrudrest.model.User;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest(classes=SpringBootCrudRestApplication.class,webEnvironment=SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)publicclassSpringBootCrudRestApplicationTests {@AutowiredprivateTestRestTemplate restTemplate;@LocalServerPortprivateint port;privateStringgetRootUrl() {return"http://localhost:"+ port; }@TestpublicvoidcontextLoads() { }@TestpublicvoidtestGetAllUsers() {HttpHeaders headers=newHttpHeaders();HttpEntity<String> entity=newHttpEntity<String>(null, headers);ResponseEntity<String> response= restTemplate.exchange(getRootUrl()+"/users",HttpMethod.GET, entity,String.class); assertNotNull(response.getBody()); }@TestpublicvoidtestGetUserById() {User user= restTemplate.getForObject(getRootUrl()+"/users/1",User.class);System.out.println(user.getFirstName()); assertNotNull(user); }@TestpublicvoidtestCreateUser() {User user=newUser(); user.setEmailId("admin@gmail.com"); user.setFirstName("admin"); user.setLastName("admin"); user.setCreatedBy("admin"); user.setUpdatedby("admin");ResponseEntity<User> postResponse= restTemplate.postForEntity(getRootUrl()+"/users", user,User.class); assertNotNull(postResponse); assertNotNull(postResponse.getBody()); }@TestpublicvoidtestUpdatePost() {int id=1;User user= restTemplate.getForObject(getRootUrl()+"/users/"+ id,User.class); user.setFirstName("admin1"); user.setLastName("admin2"); restTemplate.put(getRootUrl()+"/users/"+ id, user);User updatedUser= restTemplate.getForObject(getRootUrl()+"/users/"+ id,User.class); assertNotNull(updatedUser); }@TestpublicvoidtestDeletePost() {int id=2;User user= restTemplate.getForObject(getRootUrl()+"/users/"+ id,User.class); assertNotNull(user); restTemplate.delete(getRootUrl()+"/users/"+ id);try { user= restTemplate.getForObject(getRootUrl()+"/users/"+ id,User.class); }catch (finalHttpClientErrorException e) { assertEquals(e.getStatusCode(),HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); } }}
Output
From the above Spring Boot application development let's list out the advantages of using Spring boot.
- Simpler dependency management
- Default auto-configuration
- Embedded web server
- Application metrics and health checks
- Advanced externalized configuration
10. Test Using Postman Client
1. Create User REST API
{"firstName":"Ramesh","lastName":"fadatare","emailId":"ramesh@gmail.com","createdBy":"Ramesh","updatedby":"Ramesh"}2. Get User by ID REST API
RequestURL: http://localhost:8080/api/v1/users/2
3. Get all users REST API
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/v1/users
4. Update User REST API
{"firstName":"Ram","lastName":"Jadhav","emailId":"ramesh123@gmail.com","createdBy":"Ramesh","updatedby":"Ramesh"}



![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)












![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](/image.pl?url=https%3a%2f%2fimg-c.udemycdn.com%2fcourse%2f750x422%2f5338984_4d3a_5.jpg&f=jpg&w=240)











I ran this project in IntelliJ and it is giving me following error:
ReplyDeleteError:(16, 43) java: diamond operator is not supported in -source 1.5
(use -source 7 or higher to enable diamond operator)
How do I change this?
Thank you very much.
You should change jdk 1.5 to 1.8. Google it how to configure jdk 1.8 in intellij.
ReplyDeletehere table will be auto created or not?
ReplyDeleteYes, tables will be automatically created as you can see the ddl-auto configuration in application.properties file.
ReplyDeletei dont know ,why table is not creating for me
Deleteyes.. table will be auto created but not database. you need to create a database first.
DeleteI am new with Springboot. I don't even quite get why we use localhost:8080 when using postman to crud our records instead of localhost:3306? I was thinking because we are connecting those records to mysql database and our records should be visible in mysql database, but I couldn't see the update through dbeaver? Thank you.
ReplyDeleteGreat tutorial, but I have this error while I run the test, like this:
ReplyDeleteava.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to load ApplicationContext
at org.springframework.test.context.cache.DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate.loadContext(DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate.java:132)
at org.springframework.test.context.support.DefaultTestContext.getApplicationContext(DefaultTestContext.java:123)
at org.springframework.test.context.support.DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.injectDependencies(DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.java:118)
at org.springframework.test.context.support.DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.prepareTestInstance(DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.java:83)
at org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.SpringBootDependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.prepareTestInstance(SpringBootDependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.java:43)
at org.springframework.test.context.TestContextManager.prepareTestInstance(TestContextManager.java:244)
at org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension.postProcessTestInstance(SpringExtension.java:98)
at org.junit.jupiter.engine.descriptor.ClassBasedTestDescriptor.lambda$invokeTestInstancePostProcessors$5(ClassBasedTestDescriptor.java:341)
at org.junit.jupiter.engine.descriptor.ClassBasedTestDescriptor.executeAndMaskThrowable(ClassBasedTestDescriptor.java:346)
at org.junit.jupiter.engine.descriptor.ClassBasedTestDescriptor.lambda$invokeTestInstancePostProcessors$6(ClassBasedTestDescriptor.java:341)
at java.base/java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$3$1.accept(ReferencePipeline.java:195)
at java.base/java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$2$1.accept(ReferencePipeline.java:177)
at java.base/java.util.ArrayList$ArrayListSpliterator.forEachRemaining(ArrayList.java:1624)
at java.base/java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.copyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:484)
at java.base/java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.wrapAndCopyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:474)
at java.base/java.util.stream.StreamSpliterators$WrappingSpliterator.forEachRemaining(StreamSpliterators.java:312)
at java.base/java.util.stream.Streams$ConcatSpliterator.forEachRemaining(Streams.java:735)
at java.base/java.util.stream.Streams$ConcatSpliterator.forEachRemaining(Streams.java:734)
I tried to put this on build tag:
src/test/resources
...
Is there any solution for that scenery? Thanks in advance!
I ran the application but while doing the post, it shows 404. plz helpme out
Delete{
"timestamp": "2020-10-27T15:17:43.739+00:00",
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"message": "",
"path": "/api/v1/users"
}
I rearranged the main class, i moved it to the top of the package and now it works...
Delete