- java.lang.Object
- rx.Observable<T>
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the items emitted by the Observable
- Direct Known Subclasses:
- ConnectableObservable,GroupedObservable,Subject
public classObservable<T>extends java.lang.ObjectThe Observable class that implements the Reactive Pattern.This class provides methods for subscribing to the Observable as well as delegate methods to the various Observers.
The documentation for this class makes use of marble diagrams. The following legend explains these diagrams:

For more information see theReactiveX documentation.
Nested Class Summary
Nested Classes Modifier and Type Class and Description static interfaceObservable.OnSubscribe<T>Invoked when Observable.subscribe is called.static interfaceObservable.Operator<R,T>Operator function for lifting into an Observable.static interfaceObservable.Transformer<T,R>Function that receives the current Observable and should return another Observable, possibly with given element type, in exchange that will be subscribed to by the downstream operators and subscribers.
Constructor Summary
Constructors Modifier Constructor and Description protectedObservable(Observable.OnSubscribe<T> f)Creates an Observable with a Function to execute when it is subscribed to.
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Deprecated Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description Observable<java.lang.Boolean>all(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean that indicates whether all of the items emitted by the source Observable satisfy a condition.static <T> Observable<T>amb(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)Mirrors the one Observable in an Iterable of several Observables that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2)Given two Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3)Given three Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4)Given four Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5)Given five Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6)Given six Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7)Given seven Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8)Given eight Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.static <T> Observable<T>amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8,Observable<? extends T> o9)Given nine Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.Observable<T>ambWith(Observable<? extendsT> t1)Mirrors the Observable (current or provided) that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.Observable<T>asObservable()Portrays a object of an Observable subclass as a simple Observable object.<TClosing> Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> bufferClosingSelector)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(int count)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(int count, int skip)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.<TOpening,TClosing>
Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(Observable<? extends TOpening> bufferOpenings,Func1<? super TOpening,? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> bufferClosingSelector)Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable.<B> Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(Observable<B> boundary)Returns an Observable that emits non-overlapping buffered items from the source Observable each time the specified boundary Observable emits an item.<B> Observable<java.util.List<T>>buffer(Observable<B> boundary, int initialCapacity)Returns an Observable that emits non-overlapping buffered items from the source Observable each time the specified boundary Observable emits an item.Observable<T>cache()Returns an Observable that subscribes to this Observable lazily, caches all of its events and replays them, in the same order as received, to all the downstream subscribers.Observable<T>cache(int initialCapacity)Deprecated.UsecacheWithInitialCapacity(int)instead.Observable<T>cacheWithInitialCapacity(int initialCapacity)Returns an Observable that subscribes to this Observable lazily, caches all of its events and replays them, in the same order as received, to all the downstream subscribers.<R> Observable<R>cast(java.lang.Class<R> klass)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable, converted to the specified type.<R> Observable<R>collect(Func0<R> stateFactory,Action2<R,? superT> collector)Collects items emitted by the source Observable into a single mutable data structure and returns an Observable that emits this structure.static <T,R> Observable<R>combineLatest(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources,FuncN<? extends R> combineFunction)Combines a collection of source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T,R> Observable<R>combineLatest(java.util.List<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources,FuncN<? extends R> combineFunction)Combines a list of source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,R> Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Func2<? super T1,? super T2,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines two source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from either of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,T3,R>
Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Func3<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines three source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,R>
Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Func4<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines four source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,R>
Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Func5<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines five source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,R>
Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Func6<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines six source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,R>
Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Func7<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines seven source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,R>
Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Func8<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines eight source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,T9,R>
Observable<R>combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Observable<? extends T9> o9,Func9<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? super T9,? extends R> combineFunction)Combines nine source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.static <T,R> Observable<R>combineLatestDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources,FuncN<? extends R> combineFunction)Combines a collection of source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function and delays any error from the sources until all source Observables terminate.<R> Observable<R>compose(Observable.Transformer<? superT,? extends R> transformer)Transform an Observable by applying a particular Transformer function to it.static <T> Observable<T>concat(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences)Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> observables)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by each of the Observables emitted by the source Observable, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by two Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by three Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by four Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by five Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by six Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by seven Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by eight Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by nine Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)Concatenates the Iterable sequence of Observables into a single sequence by subscribing to each Observable, one after the other, one at a time and delays any errors till the all inner Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)Concatenates the Observable sequence of Observables into a single sequence by subscribing to each inner Observable, one after the other, one at a time and delays any errors till the all inner and the outer Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by two Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by three Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by four Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by five Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by six Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by seven Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by eight Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by nine Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)Concatenates a sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources, int capacityHint)Concatenates a sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)Concatenates an Observable sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources, int capacityHint)Concatenates an Observable sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2)Concatenates two source Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3)Concatenates three sources eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4)Concatenates four sources eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5)Concatenates five sources eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6)Concatenates six sources eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7)Concatenates seven sources eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8)Concatenates eight sources eagerly into a single stream of values.static <T> Observable<T>concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8,Observable<? extends T> o9)Concatenates nine sources eagerly into a single stream of values.<R> Observable<R>concatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)Returns a new Observable that emits items resulting from applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then emitting the items that result from concatenating those resulting Observables.<R> Observable<R>concatMapDelayError(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)Maps each of the items into an Observable, subscribes to them one after the other, one at a time and emits their values in order while delaying any error from either this or any of the inner Observables till all of them terminate.<R> Observable<R>concatMapEager(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> mapper)Maps a sequence of values into Observables and concatenates these Observables eagerly into a single Observable.<R> Observable<R>concatMapEager(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> mapper, int capacityHint)Maps a sequence of values into Observables and concatenates these Observables eagerly into a single Observable.<R> Observable<R>concatMapEager(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> mapper, int capacityHint, int maxConcurrent)Maps a sequence of values into Observables and concatenates these Observables eagerly into a single Observable.<R> Observable<R>concatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends R>> collectionSelector)Returns an Observable that concatenate each item emitted by the source Observable with the values in an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector.Observable<T>concatWith(Observable<? extendsT> t1)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted from the current Observable, then the next, one after the other, without interleaving them.Observable<java.lang.Boolean>contains(java.lang.Object element)Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean that indicates whether the source Observable emitted a specified item.Observable<java.lang.Integer>count()Returns an Observable that emits the count of the total number of items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<java.lang.Long>countLong()Returns an Observable that counts the total number of items emitted by the source Observable and emits this count as a 64-bit Long.static <T> Observable<T>create(Action1<Emitter<T>> emitter,Emitter.BackpressureMode backpressure)Provides an API (via a cold Observable) that bridges the reactive world with the callback-style, generally non-backpressured world.static <S,T> Observable<T>create(AsyncOnSubscribe<S,T> asyncOnSubscribe)Returns an Observable that respects the back-pressure semantics.static <T> Observable<T>create(Observable.OnSubscribe<T> f)Deprecated.1.2.7 - inherently unsafe, use the other create() methods for basic cases or seeunsafeCreate(OnSubscribe)for advanced cases (such as custom operators)static <S,T> Observable<T>create(SyncOnSubscribe<S,T> syncOnSubscribe)Returns an Observable that respects the back-pressure semantics.<U> Observable<T>debounce(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<U>> debounceSelector)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by another item within a computed debounce duration.Observable<T>debounce(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by newer items before a timeout value expires.Observable<T>debounce(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by newer items before a timeout value expires on a specified Scheduler.Observable<T>defaultIfEmpty(T defaultValue)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or a specified default item if the source Observable is empty.static <T> Observable<T>defer(Func0<Observable<T>> observableFactory)Returns an Observable that calls an Observable factory to create an Observable for each new Observer that subscribes.<U,V> Observable<T>delay(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> subscriptionDelay,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> itemDelay)Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to and emissions from the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.<U> Observable<T>delay(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<U>> itemDelay)Returns an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.Observable<T>delay(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay.Observable<T>delay(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay.<U> Observable<T>delaySubscription(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> subscriptionDelay)Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.Observable<T>delaySubscription(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable by a given amount of time.Observable<T>delaySubscription(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable by a given amount of time, both waiting and subscribing on a given Scheduler.<U> Observable<T>delaySubscription(Observable<U> other)Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to this Observable until the other Observable emits an element or completes normally.<T2> Observable<T2>dematerialize()Returns an Observable that reverses the effect ofmaterializeby transforming theNotificationobjects emitted by the source Observable into the items or notifications they represent.Observable<T>distinct()Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct.<U> Observable<T>distinct(Func1<? superT,? extends U> keySelector)Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.Observable<T>distinctUntilChanged()Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors.<U> Observable<T>distinctUntilChanged(Func1<? superT,? extends U> keySelector)Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors, according to a key selector function.Observable<T>distinctUntilChanged(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Boolean> comparator)Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors when compared with each other via the provided comparator function.Observable<T>doAfterTerminate(Action0 action)Observable<T>doOnCompleted(Action0 onCompleted)Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action when it callsonCompleted.Observable<T>doOnEach(Action1<Notification<? superT>> onNotification)Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action for each item and terminal event it emits.Observable<T>doOnEach(Observer<? superT> observer)Modifies the source Observable so that it notifies an Observer for each item and terminal event it emits.Observable<T>doOnError(Action1<? super java.lang.Throwable> onError)Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action if it callsonError.Observable<T>doOnNext(Action1<? superT> onNext)Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action when it callsonNext.Observable<T>doOnRequest(Action1<? super java.lang.Long> onRequest)Modifies the sourceObservableso that it invokes the given action when it receives a request for more items.Observable<T>doOnSubscribe(Action0 subscribe)Modifies the sourceObservableso that it invokes the given action when it is subscribed from its subscribers.Observable<T>doOnTerminate(Action0 onTerminate)Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action when it callsonCompletedoronError.Observable<T>doOnUnsubscribe(Action0 unsubscribe)Calls the unsubscribeAction0if the downstream unsubscribes the sequence.Observable<T>elementAt(int index)Returns an Observable that emits the single item at a specified index in a sequence of emissions from a source Observable.Observable<T>elementAtOrDefault(int index,T defaultValue)Returns an Observable that emits the item found at a specified index in a sequence of emissions from a source Observable, or a default item if that index is out of range.static <T> Observable<T>empty()Returns an Observable that emits no items to theObserverand immediately invokes itsonCompletedmethod.static <T> Observable<T>error(java.lang.Throwable exception)Observable<java.lang.Boolean>exists(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emitstrueif any item emitted by the source Observable satisfies a specified condition, otherwisefalse.Observable<T>filter(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Filters items emitted by an Observable by only emitting those that satisfy a specified predicate.Observable<T>finallyDo(Action0 action)Deprecated.usedoAfterTerminate(Action0)instead.Observable<T>first()Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or notifies of anNoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.Observable<T>first(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition, or notifies of anNoSuchElementExceptionif no such items are emitted.Observable<T>firstOrDefault(T defaultValue)Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable completes without emitting anything.Observable<T>firstOrDefault(T defaultValue,Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition, or a default item if the source Observable emits no such items.<R> Observable<R>flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger.<R> Observable<R>flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onNext,Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onError,Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onCompleted)Returns an Observable that applies a function to each item emitted or notification raised by the source Observable and then flattens the Observables returned from these functions and emits the resulting items.<R> Observable<R>flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onNext,Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onError,Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onCompleted, int maxConcurrent)Returns an Observable that applies a function to each item emitted or notification raised by the source Observable and then flattens the Observables returned from these functions and emits the resulting items, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.<R> Observable<R>flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func, int maxConcurrent)Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.<U,R> Observable<R>flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified function to the pair of values emitted by the source Observable and a specified collection Observable.<U,R> Observable<R>flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector, int maxConcurrent)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified function to the pair of values emitted by the source Observable and a specified collection Observable, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.Observable<T>flatMapCompletable(Func1<? superT,? extendsCompletable> mapper)Maps all upstream values to Completables and runs them together until the upstream and all inner Completables complete normally.Observable<T>flatMapCompletable(Func1<? superT,? extendsCompletable> mapper, boolean delayErrors)Maps all upstream values to Completables and runs them together, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Completables terminate.Observable<T>flatMapCompletable(Func1<? superT,? extendsCompletable> mapper, boolean delayErrors, int maxConcurrency)Maps upstream values to Completables and runs up to the given number of them together at a time, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Completables terminate.<R> Observable<R>flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends R>> collectionSelector)Returns an Observable that merges each item emitted by the source Observable with the values in an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector.<R> Observable<R>flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends R>> collectionSelector, int maxConcurrent)Returns an Observable that merges each item emitted by the source Observable with the values in an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.<U,R> Observable<R>flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector)Returns an Observable that emits the results of applying a function to the pair of values from the source Observable and an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector.<U,R> Observable<R>flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector, int maxConcurrent)Returns an Observable that emits the results of applying a function to the pair of values from the source Observable and an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.<R> Observable<R>flatMapSingle(Func1<? superT,? extendsSingle<? extends R>> mapper)Maps all upstream values to Singles and runs them together until the upstream and all inner Singles complete normally.<R> Observable<R>flatMapSingle(Func1<? superT,? extendsSingle<? extends R>> mapper, boolean delayErrors)Maps all upstream values to Singles and runs them together, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Singles terminate.<R> Observable<R>flatMapSingle(Func1<? superT,? extendsSingle<? extends R>> mapper, boolean delayErrors, int maxConcurrency)Maps upstream values to Singles and runs up to the given number of them together at a time, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Singles terminate.voidforEach(Action1<? superT> onNext)Subscribes to theObservableand receives notifications for each element.voidforEach(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError)Subscribes to theObservableand receives notifications for each element and error events.voidforEach(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError,Action0 onComplete)Subscribes to theObservableand receives notifications for each element and the terminal events.static <T> Observable<T>from(java.util.concurrent.Future<? extends T> future)Converts aFutureinto an Observable.static <T> Observable<T>from(java.util.concurrent.Future<? extends T> future, long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Converts aFutureinto an Observable, with a timeout on the Future.static <T> Observable<T>from(java.util.concurrent.Future<? extends T> future,Scheduler scheduler)Converts aFuture, operating on a specifiedScheduler, into an Observable.static <T> Observable<T>from(java.lang.Iterable<? extends T> iterable)Converts anIterablesequence into an Observable that emits the items in the sequence.static <T> Observable<T>from(T[] array)Converts an Array into an Observable that emits the items in the Array.static <T> Observable<T>fromCallable(java.util.concurrent.Callable<? extends T> func)Returns an Observable that, when an observer subscribes to it, invokes a function you specify and then emits the value returned from that function.<K> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,T>>groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector)Groups the items emitted by anObservableaccording to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items asGroupedObservables.<K,R> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,R>>groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends R> elementSelector)Groups the items emitted by anObservableaccording to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items asGroupedObservables.<K,R> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,R>>groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends R> elementSelector,Func1<Action1<K>,java.util.Map<K,java.lang.Object>> evictingMapFactory)Deprecated.since 1.3.7, usegroupBy(Func1, Func1, int, boolean, Func1)instead which uses much less memory. Please take note of the usage difference involving the evicting action which now expects the value from the map instead of the key.<K,R> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,R>>groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends R> elementSelector, int bufferSize, boolean delayError,Func1<Action1<java.lang.Object>,java.util.Map<K,java.lang.Object>> evictingMapFactory)Groups the items emitted by anObservableaccording to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items asGroupedObservables.<T2,D1,D2,R>
Observable<R>groupJoin(Observable<T2> right,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<D1>> leftDuration,Func1<? super T2,? extendsObservable<D2>> rightDuration,Func2<? superT,? superObservable<T2>,? extends R> resultSelector)Returns an Observable that correlates two Observables when they overlap in time and groups the results.Observable<T>ignoreElements()Ignores all items emitted by the source Observable and only callsonCompletedoronError.staticObservable<java.lang.Long>interval(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits a0Lafter theinitialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter.staticObservable<java.lang.Long>interval(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits a0Lafter theinitialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter, on a specifiedScheduler.staticObservable<java.lang.Long>interval(long interval, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits a sequential number every specified interval of time.staticObservable<java.lang.Long>interval(long interval, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits a sequential number every specified interval of time, on a specified Scheduler.Observable<java.lang.Boolean>isEmpty()Returns an Observable that emitstrueif the source Observable is empty, otherwisefalse.<TRight,TLeftDuration,TRightDuration,R>
Observable<R>join(Observable<TRight> right,Func1<T,Observable<TLeftDuration>> leftDurationSelector,Func1<TRight,Observable<TRightDuration>> rightDurationSelector,Func2<T,TRight,R> resultSelector)Correlates the items emitted by two Observables based on overlapping durations.static <T> Observable<T>just(T value)Returns an Observable that emits a single item and then completes.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2)Converts two items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3)Converts three items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4)Converts four items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5)Converts five items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6)Converts six items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7)Converts seven items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7, T t8)Converts eight items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7, T t8, T t9)Converts nine items into an Observable that emits those items.static <T> Observable<T>just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7, T t8, T t9, T t10)Converts ten items into an Observable that emits those items.Observable<T>last()Returns an Observable that emits the last item emitted by the source Observable or notifies observers of aNoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.Observable<T>last(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a given condition, or notifies of aNoSuchElementExceptionif no such items are emitted.Observable<T>lastOrDefault(T defaultValue)Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable completes without emitting any items.Observable<T>lastOrDefault(T defaultValue,Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition, or a default item if no such item is emitted by the source Observable.<R> Observable<R>lift(Observable.Operator<? extends R,? superT> operator)This method requires advanced knowledge about building operators; please consider other standard composition methods first; Lifts a function to the current Observable and returns a new Observable that when subscribed to will pass the values of the current Observable through the Operator function.Observable<T>limit(int count)Returns an Observable that emits only the firstcountitems emitted by the source Observable.<R> Observable<R>map(Func1<? superT,? extends R> func)Returns an Observable that applies a specified function to each item emitted by the source Observable and emits the results of these function applications.Observable<Notification<T>>materialize()Returns an Observable that represents all of the emissionsand notifications from the source Observable into emissions marked with their original types withinNotificationobjects.static <T> Observable<T>merge(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences)Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences, int maxConcurrent)Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source)Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into a single Observable that emits the items emitted by those Observables, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source, int maxConcurrent)Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into a single Observable that emits the items emitted by those Observables, without any transformation, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T>[] sequences)Flattens an Array of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T>[] sequences, int maxConcurrent)Flattens an Array of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)Flattens two Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)Flattens three Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)Flattens four Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)Flattens five Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)Flattens six Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)Flattens seven Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)Flattens eight Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)Flattens nine Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences)Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from each of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences, int maxConcurrent)Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from each of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source)Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source, int maxConcurrent)Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)Flattens two Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from each of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)Flattens three Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)Flattens four Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)Flattens five Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)Flattens six Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)Flattens seven Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)Flattens eight Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.static <T> Observable<T>mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)Flattens nine Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.Observable<T>mergeWith(Observable<? extendsT> t1)Flattens this and another Observable into a single Observable, without any transformation.Observable<Observable<T>>nest()Converts the sourceObservable<T>into anObservable<Observable<T>>that emits the source Observable as its single emission.static <T> Observable<T>never()Returns an Observable that never sends any items or notifications to anObserver.Observable<T>observeOn(Scheduler scheduler)Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer ofRxRingBuffer.SIZEslots.Observable<T>observeOn(Scheduler scheduler, boolean delayError)Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer and optionally delays onError notifications.Observable<T>observeOn(Scheduler scheduler, boolean delayError, int bufferSize)Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer of configurable size and optionally delays onError notifications.Observable<T>observeOn(Scheduler scheduler, int bufferSize)Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer of configurable size.<R> Observable<R>ofType(java.lang.Class<R> klass)Filters the items emitted by an Observable, only emitting those of the specified type.Observable<T>onBackpressureBuffer()Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer these items indefinitely until they can be emitted.Observable<T>onBackpressureBuffer(long capacity)Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer up to a given amount of items until they can be emitted.Observable<T>onBackpressureBuffer(long capacity,Action0 onOverflow)Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer up to a given amount of items until they can be emitted.Observable<T>onBackpressureBuffer(long capacity,Action0 onOverflow,BackpressureOverflow.Strategy overflowStrategy)Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer up to a given amount of items until they can be emitted.Observable<T>onBackpressureDrop()Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to discard, rather than emit, those items that its observer is not prepared to observe.Observable<T>onBackpressureDrop(Action1<? superT> onDrop)Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to discard, rather than emit, those items that its observer is not prepared to observe.Observable<T>onBackpressureLatest()Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to hold onto the latest value and emit that on request.Observable<T>onErrorResumeNext(Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsObservable<? extendsT>> resumeFunction)Instructs an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters an error.Observable<T>onErrorResumeNext(Observable<? extendsT> resumeSequence)Instructs an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters an error.Observable<T>onErrorReturn(Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsT> resumeFunction)Instructs an Observable to emit an item (returned by a specified function) rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters an error.Observable<T>onExceptionResumeNext(Observable<? extendsT> resumeSequence)Instructs an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters anException.Observable<T>onTerminateDetach()Nulls out references to the upstream producer and downstream Subscriber if the sequence is terminated or downstream unsubscribes.ConnectableObservable<T>publish()Returns aConnectableObservable, which is a variety of Observable that waits until itsconnectmethod is called before it begins emitting items to thoseObservers that have subscribed to it.<R> Observable<R>publish(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector)Returns an Observable that emits the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the underlying sequence.staticObservable<java.lang.Integer>range(int start, int count)Returns an Observable that emits a sequence of Integers within a specified range.staticObservable<java.lang.Integer>range(int start, int count,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits a sequence of Integers within a specified range, on a specified Scheduler.Observable<T>rebatchRequests(int n)Requestsninitially from the upstream and then 75% ofnsubsequently after 75% ofnvalues have been emitted to the downstream.Observable<T>reduce(Func2<T,T,T> accumulator)Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, and emits the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.<R> Observable<R>reduce(R initialValue,Func2<R,? superT,R> accumulator)Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable and a specified seed value, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.Observable<T>repeat()Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable indefinitely.Observable<T>repeat(long count)Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at mostcounttimes.Observable<T>repeat(long count,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at mostcounttimes, on a particular Scheduler.Observable<T>repeat(Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable indefinitely, on a particular Scheduler.Observable<T>repeatWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Void>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler)Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source Observable with the exception of anonCompleted.Observable<T>repeatWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Void>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source Observable with the exception of anonCompleted.ConnectableObservable<T>replay()Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the underlying Observable that will replay all of its items and notifications to any futureObserver.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on the items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replayingbufferSizenotifications.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying no more thanbufferSizeitems that were emitted within a specified time window.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying no more thanbufferSizeitems that were emitted within a specified time window.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying a maximum ofbufferSizeitems.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying all items that were emitted within a specified time window.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying all items that were emitted within a specified time window.<R> Observable<R>replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable.ConnectableObservable<T>replay(int bufferSize)Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable that replays at mostbufferSizeitems emitted by that Observable.ConnectableObservable<T>replay(int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems that were emitted during a specified time window.ConnectableObservable<T>replay(int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and that replays a maximum ofbufferSizeitems that are emitted within a specified time window.ConnectableObservable<T>replay(int bufferSize,Scheduler scheduler)Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems emitted by that Observable.ConnectableObservable<T>replay(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays all items emitted by that Observable within a specified time window.ConnectableObservable<T>replay(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays all items emitted by that Observable within a specified time window.ConnectableObservable<T>replay(Scheduler scheduler)Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable that will replay all of its items and notifications to any futureObserveron the givenScheduler.Observable<T>retry()Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, resubscribing to it if it callsonError(infinite retry count).Observable<T>retry(Func2<java.lang.Integer,java.lang.Throwable,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, resubscribing to it if it callsonErrorand the predicate returns true for that specific exception and retry count.Observable<T>retry(long count)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, resubscribing to it if it callsonErrorup to a specified number of retries.Observable<T>retryWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Throwable>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler)Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source observable with the exception of anonError.Observable<T>retryWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Throwable>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source observable with the exception of anonError.Observable<T>sample(long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits the most recently emitted item (if any) emitted by the source Observable within periodic time intervals.Observable<T>sample(long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits the most recently emitted item (if any) emitted by the source Observable within periodic time intervals, where the intervals are defined on a particular Scheduler.<U> Observable<T>sample(Observable<U> sampler)Returns an Observable that, when the specifiedsamplerObservable emits an item or completes, emits the most recently emitted item (if any) emitted by the source Observable since the previous emission from thesamplerObservable.Observable<T>scan(Func2<T,T,T> accumulator)Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.<R> Observable<R>scan(R initialValue,Func2<R,? superT,R> accumulator)Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable and a seed value, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.static <T> Observable<java.lang.Boolean>sequenceEqual(Observable<? extends T> first,Observable<? extends T> second)Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean value that indicates whether two Observable sequences are the same by comparing the items emitted by each Observable pairwise.static <T> Observable<java.lang.Boolean>sequenceEqual(Observable<? extends T> first,Observable<? extends T> second,Func2<? super T,? super T,java.lang.Boolean> equality)Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean value that indicates whether two Observable sequences are the same by comparing the items emitted by each Observable pairwise based on the results of a specified equality function.Observable<T>serialize()Forces an Observable's emissions and notifications to be serialized and for it to obeythe Observable contract in other ways.Observable<T>share()Returns a newObservablethat multicasts (shares) the originalObservable.Observable<T>single()Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable, if that Observable emits only a single item.Observable<T>single(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable that matches a specified predicate, if that Observable emits one such item.Observable<T>singleOrDefault(T defaultValue)Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable, if that Observable emits only a single item, or a default item if the source Observable emits no items.Observable<T>singleOrDefault(T defaultValue,Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable that matches a predicate, if that Observable emits only one such item, or a default item if the source Observable emits no such items.Observable<T>skip(int count)Returns an Observable that skips the firstcountitems emitted by the source Observable and emits the remainder.Observable<T>skip(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that skips values emitted by the source Observable before a specified time window elapses.Observable<T>skip(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that skips values emitted by the source Observable before a specified time window on a specifiedSchedulerelapses.Observable<T>skipLast(int count)Returns an Observable that drops a specified number of items from the end of the sequence emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>skipLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that drops items emitted by the source Observable during a specified time window before the source completes.Observable<T>skipLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that drops items emitted by the source Observable during a specified time window (defined on a specified scheduler) before the source completes.<U> Observable<T>skipUntil(Observable<U> other)Returns an Observable that skips items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.Observable<T>skipWhile(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that skips all items emitted by the source Observable as long as a specified condition holds true, but emits all further source items as soon as the condition becomes false.Observable<T>sorted()Returns an Observable that emits the events emitted by source Observable, in a sorted order.Observable<T>sorted(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Integer> sortFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the events emitted by source Observable, in a sorted order based on a specified comparison function.Observable<T>startWith(java.lang.Iterable<T> values)Returns an Observable that emits the items in a specifiedIterablebefore it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(Observable<T> values)Returns an Observable that emits the items in a specifiedObservablebefore it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1)Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6,T t7)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6,T t7,T t8)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6,T t7,T t8,T t9)Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.Subscriptionsubscribe()Subscribes to an Observable and ignoresonNextandonCompletedemissions.Subscriptionsubscribe(Action1<? superT> onNext)Subscribes to an Observable and provides a callback to handle the items it emits.Subscriptionsubscribe(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError)Subscribes to an Observable and provides callbacks to handle the items it emits and any error notification it issues.Subscriptionsubscribe(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError,Action0 onCompleted)Subscribes to an Observable and provides callbacks to handle the items it emits and any error or completion notification it issues.Subscriptionsubscribe(Observer<? superT> observer)Subscribes to an Observable and provides an Observer that implements functions to handle the items the Observable emits and any error or completion notification it issues.Subscriptionsubscribe(Subscriber<? superT> subscriber)Subscribes to an Observable and provides a Subscriber that implements functions to handle the items the Observable emits and any error or completion notification it issues.Observable<T>subscribeOn(Scheduler scheduler)Asynchronously subscribes Observers to this Observable on the specifiedScheduler.Observable<T>subscribeOn(Scheduler scheduler, boolean requestOn)Observable<T>switchIfEmpty(Observable<? extendsT> alternate)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or the items of an alternate Observable if the source Observable is empty.<R> Observable<R>switchMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)Returns a new Observable by applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable that returns an Observable, and then emitting the items emitted by the most recently emitted of these Observables.<R> Observable<R>switchMapDelayError(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)Returns a new Observable by applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable that returns an Observable, and then emitting the items emitted by the most recently emitted of these Observables and delays any error until all Observables terminate.static <T> Observable<T>switchOnNext(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequenceOfSequences)Converts an Observable that emits Observables into an Observable that emits the items emitted by the most recently emitted of those Observables.static <T> Observable<T>switchOnNextDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequenceOfSequences)Converts an Observable that emits Observables into an Observable that emits the items emitted by the most recently emitted of those Observables and delays any exception until all Observables terminate.Observable<T>take(int count)Returns an Observable that emits only the firstcountitems emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>take(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits those items emitted by source Observable before a specified time runs out.Observable<T>take(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits those items emitted by source Observable before a specified time (on a specified Scheduler) runs out.Observable<T>takeFirst(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition.Observable<T>takeLast(int count)Returns an Observable that emits at most the lastcountitems emitted by the source Observable.Observable<T>takeLast(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits at most a specified number of items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed.Observable<T>takeLast(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits at most a specified number of items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed, where the timing information is provided by a given Scheduler.Observable<T>takeLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed.Observable<T>takeLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed, where the timing information is provided by a specified Scheduler.Observable<java.util.List<T>>takeLastBuffer(int count)Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing at most the lastcountelements emitted by the source Observable.Observable<java.util.List<T>>takeLastBuffer(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing at mostcountitems from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time before the source Observable completed.Observable<java.util.List<T>>takeLastBuffer(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing at mostcountitems from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time (on a specified Scheduler) before the source Observable completed.Observable<java.util.List<T>>takeLastBuffer(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing those items from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time before the source Observable completed.Observable<java.util.List<T>>takeLastBuffer(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing those items from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time before the source Observable completed, where the timing information is provided by the given Scheduler.Observable<T>takeUntil(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> stopPredicate)Returns an Observable that emits items emitted by the source Observable, checks the specified predicate for each item, and then completes when the condition is satisfied.<E> Observable<T>takeUntil(Observable<? extends E> other)Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.Observable<T>takeWhile(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)Returns an Observable that emits items emitted by the source Observable so long as each item satisfied a specified condition, and then completes as soon as this condition is not satisfied.AssertableSubscriber<T>test()Creates a AssertableSubscriber that requestsLong.MAX_VALUEand subscribes it to this Observable.AssertableSubscriber<T>test(long initialRequestAmount)Creates an AssertableSubscriber with the initial request amount and subscribes it to this Observable.Observable<T>throttleFirst(long windowDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits only the first item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration.Observable<T>throttleFirst(long skipDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits only the first item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration, where the windows are managed by a specified Scheduler.Observable<T>throttleLast(long intervalDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration.Observable<T>throttleLast(long intervalDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration, where the duration is governed by a specified Scheduler.Observable<T>throttleWithTimeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that only emits those items emitted by the source Observable that are not followed by another emitted item within a specified time window.Observable<T>throttleWithTimeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that only emits those items emitted by the source Observable that are not followed by another emitted item within a specified time window, where the time window is governed by a specified Scheduler.Observable<TimeInterval<T>>timeInterval()Returns an Observable that emits records of the time interval between consecutive items emitted by the source Observable.Observable<TimeInterval<T>>timeInterval(Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits records of the time interval between consecutive items emitted by the source Observable, where this interval is computed on a specified Scheduler.<U,V> Observable<T>timeout(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> firstTimeoutSelector,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but notifies observers of aTimeoutExceptionif either the first item emitted by the source Observable or any subsequent item doesn't arrive within time windows defined by other Observables.<U,V> Observable<T>timeout(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> firstTimeoutSelector,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector,Observable<? extendsT> other)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but switches to a fallback Observable if either the first item emitted by the source Observable or any subsequent item doesn't arrive within time windows defined by other Observables.<V> Observable<T>timeout(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but notifies observers of aTimeoutExceptionif an item emitted by the source Observable doesn't arrive within a window of time after the emission of the previous item, where that period of time is measured by an Observable that is a function of the previous item.<V> Observable<T>timeout(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector,Observable<? extendsT> other)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but that switches to a fallback Observable if an item emitted by the source Observable doesn't arrive within a window of time after the emission of the previous item, where that period of time is measured by an Observable that is a function of the previous item.Observable<T>timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item.Observable<T>timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit,Observable<? extendsT> other)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item.Observable<T>timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit,Observable<? extendsT> other,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item using a specified Scheduler.Observable<T>timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item, where this policy is governed on a specified Scheduler.staticObservable<java.lang.Long>timer(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Deprecated.useinterval(long, long, TimeUnit)insteadstaticObservable<java.lang.Long>timer(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Deprecated.useinterval(long, long, TimeUnit, Scheduler)insteadstaticObservable<java.lang.Long>timer(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits0Lafter a specified delay, and then completes.staticObservable<java.lang.Long>timer(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits0Lafter a specified delay, on a specified Scheduler, and then completes.Observable<Timestamped<T>>timestamp()Returns an Observable that emits each item emitted by the source Observable, wrapped in aTimestampedobject.Observable<Timestamped<T>>timestamp(Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits each item emitted by the source Observable, wrapped in aTimestampedobject whose timestamps are provided by a specified Scheduler.<R> Rto(Func1<? superObservable<T>,R> converter)Calls the specified converter function during assembly time and returns its resulting value.BlockingObservable<T>toBlocking()Converts an Observable into aBlockingObservable(an Observable with blocking operators).CompletabletoCompletable()Returns a Completable that discards all onNext emissions (similar toignoreAllElements()) and calls onCompleted when this source observable calls onCompleted.Observable<java.util.List<T>>toList()Returns an Observable that emits a single item, a list composed of all the items emitted by the source Observable.<K> Observable<java.util.Map<K,T>>toMap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector)Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap containing all items emitted by the source Observable, mapped by the keys returned by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.<K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,V>>toMap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector)Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap containing values corresponding to items emitted by the source Observable, mapped by the keys returned by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.<K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,V>>toMap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector,Func0<? extends java.util.Map<K,V>> mapFactory)Returns an Observable that emits a single Map, returned by a specifiedmapFactoryfunction, that contains keys and values extracted from the items emitted by the source Observable.<K> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<T>>>toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector)Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap that contains an ArrayList of items emitted by the source Observable keyed by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.<K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>>toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector)Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap that contains an ArrayList of values extracted by a specifiedvalueSelectorfunction from items emitted by the source Observable, keyed by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.<K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>>toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector,Func0<? extends java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>> mapFactory)Returns an Observable that emits a single Map, returned by a specifiedmapFactoryfunction, that contains an ArrayList of values, extracted by a specifiedvalueSelectorfunction from items emitted by the source Observable and keyed by thekeySelectorfunction.<K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>>toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector,Func0<? extends java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>> mapFactory,Func1<? super K,? extends java.util.Collection<V>> collectionFactory)Returns an Observable that emits a single Map, returned by a specifiedmapFactoryfunction, that contains a custom collection of values, extracted by a specifiedvalueSelectorfunction from items emitted by the source Observable, and keyed by thekeySelectorfunction.Single<T>toSingle()Returns a Single that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable, if that Observable emits only a single item.Observable<java.util.List<T>>toSortedList()Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order.Observable<java.util.List<T>>toSortedList(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Integer> sortFunction)Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order based on a specified comparison function.Observable<java.util.List<T>>toSortedList(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Integer> sortFunction, int initialCapacity)Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order based on a specified comparison function.Observable<java.util.List<T>>toSortedList(int initialCapacity)Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order.static <T> Observable<T>unsafeCreate(Observable.OnSubscribe<T> f)Returns an Observable that executes the given OnSubscribe action for each individual Subscriber that subscribes;unsubscription and backpressure must be implemented manually.SubscriptionunsafeSubscribe(Subscriber<? superT> subscriber)Subscribes to an Observable and invokesObservable.OnSubscribefunction without any contract protection, error handling, unsubscribe, or execution hooks.Observable<T>unsubscribeOn(Scheduler scheduler)Modifies the source Observable so that subscribers will unsubscribe from it on a specifiedScheduler.static <T,Resource>
Observable<T>using(Func0<Resource> resourceFactory,Func1<? super Resource,? extendsObservable<? extends T>> observableFactory,Action1<? super Resource> disposeAction)Constructs an Observable that creates a dependent resource object which is disposed of on unsubscription.static <T,Resource>
Observable<T>using(Func0<Resource> resourceFactory,Func1<? super Resource,? extendsObservable<? extends T>> observableFactory,Action1<? super Resource> disposeAction, boolean disposeEagerly)Constructs an Observable that creates a dependent resource object which is disposed of just before termination if you have setdisposeEagerlytotrueand unsubscription does not occur before termination.<TClosing> Observable<Observable<T>>window(Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> closingSelector)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(int count)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(int count, int skip)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.Observable<Observable<T>>window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.<TOpening,TClosing>
Observable<Observable<T>>window(Observable<? extends TOpening> windowOpenings,Func1<? super TOpening,? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> closingSelector)Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable.<U> Observable<Observable<T>>window(Observable<U> boundary)Returns an Observable that emits non-overlapping windows of items it collects from the source Observable where the boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.<R> Observable<R>withLatestFrom(java.lang.Iterable<Observable<?>> others,FuncN<R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<R> Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<?>[] others,FuncN<R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<U,R> Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<? extends U> other,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector)Merges the specified Observable into this Observable sequence by using theresultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable (this instance) emits an item.<T1,T2,R> Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Func3<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<T1,T2,T3,R>
Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Func4<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<T1,T2,T3,T4,R>
Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Func5<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,R>
Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Func6<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,R>
Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Observable<T6> o6,Func7<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,R>
Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Observable<T6> o6,Observable<T7> o7,Func8<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.<T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,R>
Observable<R>withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Observable<T6> o6,Observable<T7> o7,Observable<T8> o8,Func9<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,R> combiner)Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.static <R> Observable<R>zip(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<?>> ws,FuncN<? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of items emitted, in sequence, by an Iterable of other Observables.static <R> Observable<R>zip(Observable<?>[] ws,FuncN<? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of items emitted, in sequence, by an array of other Observables.static <R> Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extendsObservable<?>> ws,FuncN<? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations ofn items emitted, in sequence, by then Observables emitted by a specified Observable.static <T1,T2,R> Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Func2<? super T1,? super T2,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of two items emitted, in sequence, by two other Observables.static <T1,T2,T3,R>
Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Func3<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of three items emitted, in sequence, by three other Observables.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,R>
Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Func4<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of four items emitted, in sequence, by four other Observables.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,R>
Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Func5<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of five items emitted, in sequence, by five other Observables.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,R>
Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Func6<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of six items emitted, in sequence, by six other Observables.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,R>
Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Func7<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of seven items emitted, in sequence, by seven other Observables.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,R>
Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Func8<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of eight items emitted, in sequence, by eight other Observables.static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,T9,R>
Observable<R>zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Observable<? extends T9> o9,Func9<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? super T9,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of nine items emitted, in sequence, by nine other Observables.<T2,R> Observable<R>zipWith(java.lang.Iterable<? extends T2> other,Func2<? superT,? super T2,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the result of applying a specified function to pairs of values, one each from the source Observable and a specified Iterable sequence.<T2,R> Observable<R>zipWith(Observable<? extends T2> other,Func2<? superT,? super T2,? extends R> zipFunction)Returns an Observable that emits items that are the result of applying a specified function to pairs of values, one each from the source Observable and another specified Observable.
Constructor Detail
Observable
protected Observable(Observable.OnSubscribe<T> f)
Creates an Observable with a Function to execute when it is subscribed to.Note: Use
unsafeCreate(OnSubscribe)to create an Observable, instead of this constructor, unless you specifically have a need for inheritance.- Parameters:
f-Observable.OnSubscribeto be executed whensubscribe(Subscriber)is called
Method Detail
create
@Deprecatedpublic static <T> Observable<T> create(Observable.OnSubscribe<T> f)
Deprecated. 1.2.7 - inherently unsafe, use the other create() methods for basic cases or seeunsafeCreate(OnSubscribe)for advanced cases (such as custom operators)Constructs an Observable in an unsafe manner, that is, unsubscription and backpressure handling is the responsibility of the OnSubscribe implementation.- Type Parameters:
T- the value type emitted- Parameters:
f- the callback to execute for each individual Subscriber that subscribes to the returned Observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- See Also:
create(SyncOnSubscribe),create(AsyncOnSubscribe),create(Action1, rx.Emitter.BackpressureMode)
create
public static <T> Observable<T> create(Action1<Emitter<T>> emitter,Emitter.BackpressureMode backpressure)
Provides an API (via a cold Observable) that bridges the reactive world with the callback-style, generally non-backpressured world.Example:
Observable.<Event>create(emitter -> { Callback listener = new Callback() { @Override public void onEvent(Event e) { emitter.onNext(e); if (e.isLast()) { emitter.onCompleted(); } } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { emitter.onError(e); } }; AutoCloseable c = api.someMethod(listener); emitter.setCancellation(c::close); }, BackpressureMode.BUFFER);You should call the Emitter's onNext, onError and onCompleted methods in a serialized fashion. The rest of its methods are thread-safe.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Type Parameters:
T- the element type- Parameters:
emitter- the emitter that is called when a Subscriber subscribes to the returnedObservablebackpressure- the backpressure mode to apply if the downstream Subscriber doesn't request (fast) enough- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
Emitter,Emitter.BackpressureMode,Cancellable
unsafeCreate
public static <T> Observable<T> unsafeCreate(Observable.OnSubscribe<T> f)
Returns an Observable that executes the given OnSubscribe action for each individual Subscriber that subscribes;unsubscription and backpressure must be implemented manually.
Write the function you pass to
createso that it behaves as an Observable: It should invoke the Subscriber'sonNext,onError, andonCompletedmethods appropriately.A well-formed Observable must invoke either the Subscriber's
onCompletedmethod exactly once or itsonErrormethod exactly once.SeeRx Design Guidelines (PDF) for detailed information.
- Backpressure:
- The
OnSubscribeinstance provided is responsible to be backpressure-aware or document the fact that the consumer of the returnedObservablehas to apply one of theonBackpressureXXXoperators. - Scheduler:
unsafeCreatedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the items that this Observable emits- Parameters:
f- a function that accepts anSubscriber<T>, and invokes itsonNext,onError, andonCompletedmethods as appropriate- Returns:
- an Observable that, when a
Subscribersubscribes to it, will execute the specified function - Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Create
create
public static <S,T> Observable<T> create(SyncOnSubscribe<S,T> syncOnSubscribe)
Returns an Observable that respects the back-pressure semantics. When the returned Observable is subscribed to it will initiate the givenSyncOnSubscribe's life cycle for generating events.Note: the
SyncOnSubscribeprovides a generic way to fulfill data by iterating over a (potentially stateful) function (e.g. reading data off of a channel, a parser, ). If your data comes directly from an asynchronous/potentially concurrent source then consider using theasynchronous overload.
SeeRx Design Guidelines (PDF) for detailed information.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure and generates values on-demand (when requested).
- Scheduler:
createdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the items that this Observable emitsS- the state type- Parameters:
syncOnSubscribe- an implementation ofSyncOnSubscribe. There are many static creation methods on the class for convenience.- Returns:
- an Observable that, when a
Subscribersubscribes to it, will execute the specified function - Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
SyncOnSubscribe.createSingleState(Func0, Action2),SyncOnSubscribe.createSingleState(Func0, Action2, Action1),SyncOnSubscribe.createStateful(Func0, Func2),SyncOnSubscribe.createStateful(Func0, Func2, Action1),SyncOnSubscribe.createStateless(Action1),SyncOnSubscribe.createStateless(Action1, Action0),ReactiveX operators documentation: Create
create
@Betapublic static <S,T> Observable<T> create(AsyncOnSubscribe<S,T> asyncOnSubscribe)
Returns an Observable that respects the back-pressure semantics. When the returned Observable is subscribed to it will initiate the givenAsyncOnSubscribe's life cycle for generating events.Note: the
AsyncOnSubscribeis useful for observable sources of data that are necessarily asynchronous (RPC, external services, etc). Typically most use cases can be solved with thesynchronous overload.
SeeRx Design Guidelines (PDF) for detailed information.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure and generates values on-demand (when requested).
- Scheduler:
createdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the items that this Observable emitsS- the state type- Parameters:
asyncOnSubscribe- an implementation ofAsyncOnSubscribe. There are many static creation methods on the class for convenience.- Returns:
- an Observable that, when a
Subscribersubscribes to it, will execute the specified function - Since:
- 1.3 - beta
- See Also:
AsyncOnSubscribe.createSingleState(Func0, Action3),AsyncOnSubscribe.createSingleState(Func0, Action3, Action1),AsyncOnSubscribe.createStateful(Func0, Func3),AsyncOnSubscribe.createStateful(Func0, Func3, Action1),AsyncOnSubscribe.createStateless(Action2),AsyncOnSubscribe.createStateless(Action2, Action0),ReactiveX operators documentation: Create
lift
public final <R> Observable<R> lift(Observable.Operator<? extends R,? superT> operator)
This method requires advanced knowledge about building operators; please consider other standard composition methods first; Lifts a function to the current Observable and returns a new Observable that when subscribed to will pass the values of the current Observable through the Operator function.In other words, this allows chaining Observers together on an Observable for acting on the values within the Observable.
observable.map(...).filter(...).take(5).lift(new OperatorA()).lift(new OperatorB(...)).subscribe()If the operator you are creating is designed to act on the individual items emitted by a source Observable, use
lift. If your operator is designed to transform the source Observable as a whole (for instance, by applying a particular set of existing RxJava operators to it) usecompose(rx.Observable.Transformer<? super T, ? extends R>).- Backpressure:
- The
Operatorinstance provided is responsible to be backpressure-aware or document the fact that the consumer of the returnedObservablehas to apply one of theonBackpressureXXXoperators. - Scheduler:
liftdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the output value type- Parameters:
operator- the Operator that implements the Observable-operating function to be applied to the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that is the result of applying the lifted Operator to the source Observable
- See Also:
- RxJava wiki: Implementing Your Own Operators
compose
public <R> Observable<R> compose(Observable.Transformer<? superT,? extends R> transformer)
Transform an Observable by applying a particular Transformer function to it.This method operates on the Observable itself whereas
lift(rx.Observable.Operator<? extends R, ? super T>)operates on the Observable's Subscribers or Observers.If the operator you are creating is designed to act on the individual items emitted by a source Observable, use
lift(rx.Observable.Operator<? extends R, ? super T>). If your operator is designed to transform the source Observable as a whole (for instance, by applying a particular set of existing RxJava operators to it) usecompose.- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which only depends on what kind of
Observablethe transformer returns. - Scheduler:
composedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type of the output Observable- Parameters:
transformer- implements the function that transforms the source Observable- Returns:
- the source Observable, transformed by the transformer function
- See Also:
- RxJava wiki: Implementing Your Own Operators
to
public final <R> R to(Func1<? superObservable<T>,R> converter)
Calls the specified converter function during assembly time and returns its resulting value.This allows fluent conversion to any other type.
- Type Parameters:
R- the resulting object type- Parameters:
converter- the function that receives the current Observable instance and returns a value- Returns:
- the value returned by the function
- Since:
- 1.3
toSingle
public Single<T> toSingle()
Returns a Single that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable, if that Observable emits only a single item. If the source Observable emits more than one item or no items, notify of anIllegalArgumentExceptionorNoSuchElementExceptionrespectively.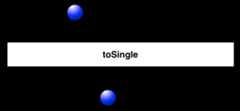
- Backpressure:
- The operator ignores backpressure on the source
Observableand the returnedSingledoes not have a notion of backpressure. - Scheduler:
toSingledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- a Single that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if the source observable emits more than one itemjava.util.NoSuchElementException- if the source observable emits no items- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
- ReactiveX documentation: Single
toCompletable
public Completable toCompletable()
Returns a Completable that discards all onNext emissions (similar toignoreAllElements()) and calls onCompleted when this source observable calls onCompleted. Error terminal events are propagated.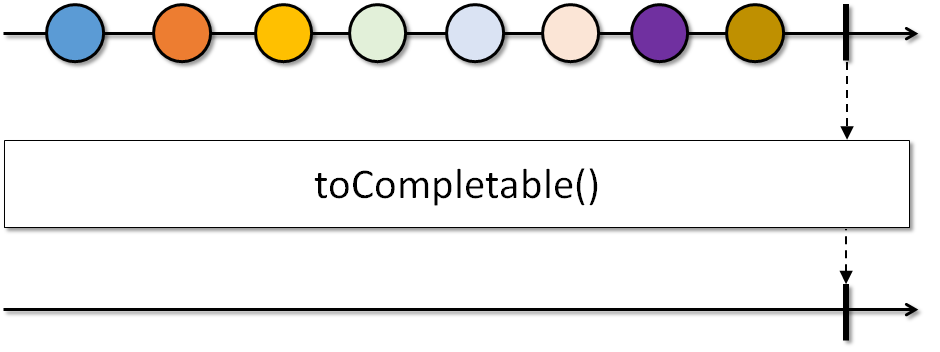
- Backpressure:
- The operator ignores backpressure on the source
Observableand the returnedCompletabledoes not have a notion of backpressure. - Scheduler:
toCompletabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- a Completable that calls onCompleted on it's subscriber when the source Observable calls onCompleted
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX documentation: Completable
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)
Mirrors the one Observable in an Iterable of several Observables that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element type- Parameters:
sources- an Iterable of Observable sources competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2)
Given two Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3)
Given three Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react firsto3- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4)
Given four Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react firsto3- an Observable competing to react firsto4- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5)
Given five Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react firsto3- an Observable competing to react firsto4- an Observable competing to react firsto5- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6)
Given six Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react firsto3- an Observable competing to react firsto4- an Observable competing to react firsto5- an Observable competing to react firsto6- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7)
Given seven Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react firsto3- an Observable competing to react firsto4- an Observable competing to react firsto5- an Observable competing to react firsto6- an Observable competing to react firsto7- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8)
Given eight Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react firsto3- an Observable competing to react firsto4- an Observable competing to react firsto5- an Observable competing to react firsto6- an Observable competing to react firsto7- an Observable competing to react firsto8- an observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
amb
public static <T> Observable<T> amb(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8,Observable<? extends T> o9)
Given nine Observables, mirrors the one that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
o1- an Observable competing to react firsto2- an Observable competing to react firsto3- an Observable competing to react firsto4- an Observable competing to react firsto5- an Observable competing to react firsto6- an Observable competing to react firsto7- an Observable competing to react firsto8- an Observable competing to react firsto9- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Func2<? super T1,? super T2,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines two source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from either of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,T3,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Func3<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines three source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceT3- the element type of the third sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source Observableo3- the third source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Func4<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines four source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceT3- the element type of the third sourceT4- the element type of the fourth sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source Observableo3- the third source Observableo4- the fourth source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Func5<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines five source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceT3- the element type of the third sourceT4- the element type of the fourth sourceT5- the element type of the fifth sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source Observableo3- the third source Observableo4- the fourth source Observableo5- the fifth source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Func6<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines six source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceT3- the element type of the third sourceT4- the element type of the fourth sourceT5- the element type of the fifth sourceT6- the element type of the sixth sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source Observableo3- the third source Observableo4- the fourth source Observableo5- the fifth source Observableo6- the sixth source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Func7<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines seven source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceT3- the element type of the third sourceT4- the element type of the fourth sourceT5- the element type of the fifth sourceT6- the element type of the sixth sourceT7- the element type of the seventh sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source Observableo3- the third source Observableo4- the fourth source Observableo5- the fifth source Observableo6- the sixth source Observableo7- the seventh source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Func8<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines eight source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceT3- the element type of the third sourceT4- the element type of the fourth sourceT5- the element type of the fifth sourceT6- the element type of the sixth sourceT7- the element type of the seventh sourceT8- the element type of the eighth sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source Observableo3- the third source Observableo4- the fourth source Observableo5- the fifth source Observableo6- the sixth source Observableo7- the seventh source Observableo8- the eighth source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,T9,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Observable<? extends T9> o9,Func9<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? super T9,? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines nine source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the element type of the first sourceT2- the element type of the second sourceT3- the element type of the third sourceT4- the element type of the fourth sourceT5- the element type of the fifth sourceT6- the element type of the sixth sourceT7- the element type of the seventh sourceT8- the element type of the eighth sourceT9- the element type of the ninth sourceR- the combined output type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- the second source Observableo3- the third source Observableo4- the fourth source Observableo5- the fifth source Observableo6- the sixth source Observableo7- the seventh source Observableo8- the eighth source Observableo9- the ninth source ObservablecombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(java.util.List<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources,FuncN<? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines a list of source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common base type of source valuesR- the result type- Parameters:
sources- the list of source ObservablescombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatest
public static <T,R> Observable<R> combineLatest(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources,FuncN<? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines a collection of source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function.- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common base type of source valuesR- the result type- Parameters:
sources- the collection of source ObservablescombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
combineLatestDelayError
public static <T,R> Observable<R> combineLatestDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources,FuncN<? extends R> combineFunction)
Combines a collection of source Observables by emitting an item that aggregates the latest values of each of the source Observables each time an item is received from any of the source Observables, where this aggregation is defined by a specified function and delays any error from the sources until all source Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The returned
Observablehonors backpressure from downstream. The sourceObservables are requested in a bounded manner, however, their backpressure is not enforced (the operator won't signalMissingBackpressureException) and may lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
combineLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common base type of source valuesR- the result type- Parameters:
sources- the collection of source ObservablescombineFunction- the aggregation function used to combine the items emitted by the source Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by the source Observables by means of the given aggregation function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences)
Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sequences- the Iterable of Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the items emitted by the Observables in the Iterable, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> observables)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by each of the Observables emitted by the source Observable, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both the outer and inner
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If the outer violates this, aMissingBackpressureExceptionis signalled. If any of the innerObservables violates this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen an innerObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
observables- an Observable that emits Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items all of the items emitted by the Observables emitted by
observables, one after the other, without interleaving them - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by two Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the two source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by three Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the three source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by four Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the four source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by five Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the five source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by six Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the six source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by seven Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenatedt7- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the seven source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by eight Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenatedt7- an Observable to be concatenatedt8- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the eight source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concat
public static <T> Observable<T> concat(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by nine Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenatedt7- an Observable to be concatenatedt8- an Observable to be concatenatedt9- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the nine source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)
Concatenates the Observable sequence of Observables into a single sequence by subscribing to each inner Observable, one after the other, one at a time and delays any errors till the all inner and the outer Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
concatDelayErrorfully supports backpressure.- Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sources- the Observable sequence of Observables- Returns:
- the new Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)
Concatenates the Iterable sequence of Observables into a single sequence by subscribing to each Observable, one after the other, one at a time and delays any errors till the all inner Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both the outer and inner
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If the outer violates this, aMissingBackpressureExceptionis signalled. If any of the innerObservables violates this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen an innerObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sources- the Iterable sequence of Observables- Returns:
- the new Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by two Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by three Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by four Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by five Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by six Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by seven Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenatedt7- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by eight Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenatedt7- an Observable to be concatenatedt8- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> concatDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by nine Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them, and delays any errors till all Observables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenatedt2- an Observable to be concatenatedt3- an Observable to be concatenatedt4- an Observable to be concatenatedt5- an Observable to be concatenatedt6- an Observable to be concatenatedt7- an Observable to be concatenatedt8- an Observable to be concatenatedt9- an Observable to be concatenated- Returns:
- an Observable with the concatenating behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
defer
public static <T> Observable<T> defer(Func0<Observable<T>> observableFactory)
Returns an Observable that calls an Observable factory to create an Observable for each new Observer that subscribes. That is, for each subscriber, the actual Observable that subscriber observes is determined by the factory function.
The defer Observer allows you to defer or delay emitting items from an Observable until such time as an Observer subscribes to the Observable. This allows an
Observerto easily obtain updates or a refreshed version of the sequence.- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the
Observablereturned by theobservableFactory. - Scheduler:
deferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the items emitted by the Observable- Parameters:
observableFactory- the Observable factory function to invoke for eachObserverthat subscribes to the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable whose
Observers' subscriptions trigger an invocation of the given Observable factory function - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Defer
empty
public static <T> Observable<T> empty()
Returns an Observable that emits no items to theObserverand immediately invokes itsonCompletedmethod.
- Backpressure:
- This source doesn't produce any elements and effectively ignores downstream backpressure.
- Scheduler:
emptydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the items (ostensibly) emitted by the Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits no items to the
Observerbut immediately invokes theObserver'sonCompletedmethod - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Empty
error
public static <T> Observable<T> error(java.lang.Throwable exception)
Returns an Observable that invokes anObserver'sonErrormethod when the Observer subscribes to it.
- Backpressure:
- This source doesn't produce any elements and effectively ignores downstream backpressure.
- Scheduler:
errordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the items (ostensibly) emitted by the Observable- Parameters:
exception- the particular Throwable to pass toonError- Returns:
- an Observable that invokes the
Observer'sonErrormethod when the Observer subscribes to it - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Throw
from
public static <T> Observable<T> from(java.util.concurrent.Future<? extends T> future)
Converts aFutureinto an Observable.
You can convert any object that supports the
Futureinterface into an Observable that emits the return value of theFuture.get()method of that object, by passing the object into thefrommethod.Important note: This Observable is blocking; you cannot unsubscribe from it.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream.
- Scheduler:
fromdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of object that theFuturereturns, and also the type of item to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
future- the sourceFuture- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the item from the source
Future - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: From
from
public static <T> Observable<T> from(java.util.concurrent.Future<? extends T> future, long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Converts aFutureinto an Observable, with a timeout on the Future.
You can convert any object that supports the
Futureinterface into an Observable that emits the return value of theFuture.get()method of that object, by passing the object into thefrommethod.Important note: This Observable is blocking; you cannot unsubscribe from it.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream.
- Scheduler:
fromdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of object that theFuturereturns, and also the type of item to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
future- the sourceFuturetimeout- the maximum time to wait before callinggetunit- theTimeUnitof thetimeoutargument- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the item from the source
Future - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: From
from
public static <T> Observable<T> from(java.util.concurrent.Future<? extends T> future,Scheduler scheduler)
Converts aFuture, operating on a specifiedScheduler, into an Observable.
You can convert any object that supports the
Futureinterface into an Observable that emits the return value of theFuture.get()method of that object, by passing the object into thefrommethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of object that theFuturereturns, and also the type of item to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
future- the sourceFuturescheduler- theSchedulerto wait for the Future on. Use a Scheduler such asSchedulers.io()that can block and wait on the Future- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the item from the source
Future - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: From
from
public static <T> Observable<T> from(java.lang.Iterable<? extends T> iterable)
Converts anIterablesequence into an Observable that emits the items in the sequence.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and iterates the given
iterableon demand (i.e., when requested). - Scheduler:
fromdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items in theIterablesequence and the type of items to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
iterable- the sourceIterablesequence- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item in the source
Iterablesequence - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: From
from
public static <T> Observable<T> from(T[] array)
Converts an Array into an Observable that emits the items in the Array.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and iterates the given
arrayon demand (i.e., when requested). - Scheduler:
fromdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items in the Array and the type of items to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
array- the source Array- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item in the source Array
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: From
fromCallable
public static <T> Observable<T> fromCallable(java.util.concurrent.Callable<? extends T> func)
Returns an Observable that, when an observer subscribes to it, invokes a function you specify and then emits the value returned from that function.
This allows you to defer the execution of the function you specify until an observer subscribes to the Observable. That is to say, it makes the function "lazy."
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream.
- Scheduler:
fromCallabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the item emitted by the Observable- Parameters:
func- a function, the execution of which should be deferred;fromCallablewill invoke this function only when an observer subscribes to the Observable thatfromCallablereturns- Returns:
- an Observable whose
Observers' subscriptions trigger an invocation of the given function - Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
defer(Func0)
interval
public static Observable<java.lang.Long> interval(long interval, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits a sequential number every specified interval of time.
- Scheduler:
intervaloperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
interval- interval size in time units (see below)unit- time units to use for the interval size- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a sequential number each time interval
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Interval
interval
public static Observable<java.lang.Long> interval(long interval, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits a sequential number every specified interval of time, on a specified Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator generates values based on time and ignores downstream backpressure which may lead to
MissingBackpressureExceptionat some point in the chain. Consumers should consider applying one of theonBackpressureXXXoperators as well. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
interval- interval size in time units (see below)unit- time units to use for the interval sizescheduler- the Scheduler to use for scheduling the items- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a sequential number each time interval
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Interval
interval
public static Observable<java.lang.Long> interval(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits a0Lafter theinitialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter.
- Backpressure:
- The operator generates values based on time and ignores downstream backpressure which may lead to
MissingBackpressureExceptionat some point in the chain. Consumers should consider applying one of theonBackpressureXXXoperators as well. - Scheduler:
intervaloperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
initialDelay- the initial delay time to wait before emitting the first value of 0Lperiod- the period of time between emissions of the subsequent numbersunit- the time unit for bothinitialDelayandperiod- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a 0L after the
initialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter - Since:
- 1.0.12
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Interval
interval
public static Observable<java.lang.Long> interval(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits a0Lafter theinitialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter, on a specifiedScheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator generates values based on time and ignores downstream backpressure which may lead to
MissingBackpressureExceptionat some point in the chain. Consumers should consider applying one of theonBackpressureXXXoperators as well. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
initialDelay- the initial delay time to wait before emitting the first value of 0Lperiod- the period of time between emissions of the subsequent numbersunit- the time unit for bothinitialDelayandperiodscheduler- the Scheduler on which the waiting happens and items are emitted- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a 0L after the
initialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter, while running on the given Scheduler - Since:
- 1.0.12
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Interval
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T value)
Returns an Observable that emits a single item and then completes.
To convert any object into an Observable that emits that object, pass that object into the
justmethod.This is similar to the
from(java.lang.Object[])method, except thatfromwill convert anIterableobject into an Observable that emits each of the items in the Iterable, one at a time, while thejustmethod converts an Iterable into an Observable that emits the entire Iterable as a single item.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream.
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of that item- Parameters:
value- the item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits
valueas a single item and then completes - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2)
Converts two items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3)
Converts three items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4)
Converts four items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third itemt4- fourth item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5)
Converts five items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third itemt4- fourth itemt5- fifth item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6)
Converts six items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third itemt4- fourth itemt5- fifth itemt6- sixth item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7)
Converts seven items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third itemt4- fourth itemt5- fifth itemt6- sixth itemt7- seventh item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7, T t8)
Converts eight items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third itemt4- fourth itemt5- fifth itemt6- sixth itemt7- seventh itemt8- eighth item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7, T t8, T t9)
Converts nine items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third itemt4- fourth itemt5- fifth itemt6- sixth itemt7- seventh itemt8- eighth itemt9- ninth item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
just
public static <T> Observable<T> just(T t1, T t2, T t3, T t4, T t5, T t6, T t7, T t8, T t9, T t10)
Converts ten items into an Observable that emits those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals each value on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
justdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of these items- Parameters:
t1- first itemt2- second itemt3- third itemt4- fourth itemt5- fifth itemt6- sixth itemt7- seventh itemt8- eighth itemt9- ninth itemt10- tenth item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Just
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences)
Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine the items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sequences- the Iterable of Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the items emitted by the Observables in the Iterable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences, int maxConcurrent)
Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.
You can combine the items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sequences- the Iterable of ObservablesmaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the items emitted by the Observables in the Iterable
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifmaxConcurrentis less than or equal to 0- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source)
Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into a single Observable that emits the items emitted by those Observables, without any transformation.
You can combine the items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in unbounded mode (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). The innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
source- an Observable that emits Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the Observables emitted by the
sourceObservable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source, int maxConcurrent)
Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into a single Observable that emits the items emitted by those Observables, without any transformation, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.
You can combine the items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both the outer and inner
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
source- an Observable that emits ObservablesmaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the Observables emitted by the
sourceObservable - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifmaxConcurrentis less than or equal to 0- Since:
- 1.1.0
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)
Flattens two Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)
Flattens three Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)
Flattens four Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)
Flattens five Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)
Flattens six Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)
Flattens seven Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be mergedt7- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)
Flattens eight Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be mergedt7- an Observable to be mergedt8- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)
Flattens nine Observables into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be mergedt7- an Observable to be mergedt8- an Observable to be mergedt9- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T>[] sequences)
Flattens an Array of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sequences- the Array of Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the Observables in the Array
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
merge
public static <T> Observable<T> merge(Observable<? extends T>[] sequences, int maxConcurrent)
Flattens an Array of Observables into one Observable, without any transformation, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergemethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sequences- the Array of ObservablesmaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the Observables in the Array
- Since:
- 1.1.0
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source)
Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in unbounded mode (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). The innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
source- an Observable that emits Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the Observables emitted by the
sourceObservable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> source, int maxConcurrent)
Flattens an Observable that emits Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.This behaves like
merge(Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both the outer and inner
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
source- an Observable that emits ObservablesmaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the Observables emitted by the
sourceObservable - Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences)
Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from each of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sequences- the Iterable of Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the items emitted by the Observables in the Iterable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequences, int maxConcurrent)
Flattens an Iterable of Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from each of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.This behaves like
merge(Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
sequences- the Iterable of ObservablesmaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the items emitted by the Observables in the Iterable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2)
Flattens two Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from each of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if both merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the two source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3)
Flattens three Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4)
Flattens four Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5)
Flattens five Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6)
Flattens six Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7)
Flattens seven Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be mergedt7- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8)
Flattens eight Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be mergedt7- an Observable to be mergedt8- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
mergeDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> mergeDelayError(Observable<? extends T> t1,Observable<? extends T> t2,Observable<? extends T> t3,Observable<? extends T> t4,Observable<? extends T> t5,Observable<? extends T> t6,Observable<? extends T> t7,Observable<? extends T> t8,Observable<? extends T> t9)
Flattens nine Observables into one Observable, in a way that allows an Observer to receive all successfully emitted items from all of the source Observables without being interrupted by an error notification from one of them.This behaves like
merge(Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable, Observable)except that if any of the merged Observables notify of an error viaonError,mergeDelayErrorwill refrain from propagating that error notification until all of the merged Observables have finished emitting items.
Even if multiple merged Observables send
onErrornotifications,mergeDelayErrorwill only invoke theonErrormethod of its Observers once.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the common element base type- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be mergedt2- an Observable to be mergedt3- an Observable to be mergedt4- an Observable to be mergedt5- an Observable to be mergedt6- an Observable to be mergedt7- an Observable to be mergedt8- an Observable to be mergedt9- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items that are emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
nest
public final Observable<Observable<T>> nest()
Converts the sourceObservable<T>into anObservable<Observable<T>>that emits the source Observable as its single emission.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream.
- Scheduler:
nestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
never
public static <T> Observable<T> never()
Returns an Observable that never sends any items or notifications to anObserver.
This Observable is useful primarily for testing purposes.
- Backpressure:
- This source doesn't produce any elements and effectively ignores downstream backpressure.
- Scheduler:
neverdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items (not) emitted by the Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that never emits any items or sends any notifications to an
Observer - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Never
range
public static Observable<java.lang.Integer> range(int start, int count)
Returns an Observable that emits a sequence of Integers within a specified range.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals values on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
rangedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
start- the value of the first Integer in the sequencecount- the number of sequential Integers to generate- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a range of sequential Integers
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifcountis less than zero, or ifstart+count− 1 exceedsInteger.MAX_VALUE- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Range
range
public static Observable<java.lang.Integer> range(int start, int count,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits a sequence of Integers within a specified range, on a specified Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and signals values on-demand (i.e., when requested).
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
start- the value of the first Integer in the sequencecount- the number of sequential Integers to generatescheduler- the Scheduler to run the generator loop on- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a range of sequential Integers
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Range
sequenceEqual
public static <T> Observable<java.lang.Boolean> sequenceEqual(Observable<? extends T> first,Observable<? extends T> second)
Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean value that indicates whether two Observable sequences are the same by comparing the items emitted by each Observable pairwise.
- Scheduler:
sequenceEqualdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items emitted by each Observable- Parameters:
first- the first Observable to comparesecond- the second Observable to compare- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a Boolean value that indicates whether the two sequences are the same
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SequenceEqual
sequenceEqual
public static <T> Observable<java.lang.Boolean> sequenceEqual(Observable<? extends T> first,Observable<? extends T> second,Func2<? super T,? super T,java.lang.Boolean> equality)
Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean value that indicates whether two Observable sequences are the same by comparing the items emitted by each Observable pairwise based on the results of a specified equality function.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operator signals aMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
sequenceEqualdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the type of items emitted by each Observable- Parameters:
first- the first Observable to comparesecond- the second Observable to compareequality- a function used to compare items emitted by each Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a Boolean value that indicates whether the two Observable two sequences are the same according to the specified function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SequenceEqual
switchOnNext
public static <T> Observable<T> switchOnNext(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequenceOfSequences)
Converts an Observable that emits Observables into an Observable that emits the items emitted by the most recently emitted of those Observables.
switchOnNextsubscribes to an Observable that emits Observables. Each time it observes one of these emitted Observables, the Observable returned byswitchOnNextbegins emitting the items emitted by that Observable. When a new Observable is emitted,switchOnNextstops emitting items from the earlier-emitted Observable and begins emitting items from the new one.The resulting Observable completes if both the outer Observable and the last inner Observable, if any, complete. If the outer Observable signals an onError, the inner Observable is unsubscribed and the error delivered in-sequence.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., without backpressure) and the innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure but it is not enforced; the operator won't signal aMissingBackpressureExceptionbut the violationmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
switchOnNextdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the item type- Parameters:
sequenceOfSequences- the source Observable that emits Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the Observable most recently emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Switch
switchOnNextDelayError
public static <T> Observable<T> switchOnNextDelayError(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sequenceOfSequences)
Converts an Observable that emits Observables into an Observable that emits the items emitted by the most recently emitted of those Observables and delays any exception until all Observables terminate.
switchOnNextsubscribes to an Observable that emits Observables. Each time it observes one of these emitted Observables, the Observable returned byswitchOnNextbegins emitting the items emitted by that Observable. When a new Observable is emitted,switchOnNextstops emitting items from the earlier-emitted Observable and begins emitting items from the new one.The resulting Observable completes if both the main Observable and the last inner Observable, if any, complete. If the main Observable signals an onError, the termination of the last inner Observable will emit that error as is or wrapped into a CompositeException along with the other possible errors the former inner Observables signalled.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., without backpressure) and the innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure but it is not enforced; the operator won't signal aMissingBackpressureExceptionbut the violationmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
switchOnNextdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the item type- Parameters:
sequenceOfSequences- the source Observable that emits Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the Observable most recently emitted by the source Observable
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Switch
timer
@Deprecatedpublic static Observable<java.lang.Long> timer(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Deprecated. useinterval(long, long, TimeUnit)insteadReturns an Observable that emits a0Lafter theinitialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. If the downstream needs a slower rate it should slow the timer or use something like
onBackpressureDrop(rx.functions.Action1<? super T>). - Scheduler:
timeroperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
initialDelay- the initial delay time to wait before emitting the first value of 0Lperiod- the period of time between emissions of the subsequent numbersunit- the time unit for bothinitialDelayandperiod- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a 0L after the
initialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timer
timer
@Deprecatedpublic static Observable<java.lang.Long> timer(long initialDelay, long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Deprecated. useinterval(long, long, TimeUnit, Scheduler)insteadReturns an Observable that emits a0Lafter theinitialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter, on a specifiedScheduler.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. If the downstream needs a slower rate it should slow the timer or use something like
onBackpressureDrop(rx.functions.Action1<? super T>). - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
initialDelay- the initial delay time to wait before emitting the first value of 0Lperiod- the period of time between emissions of the subsequent numbersunit- the time unit for bothinitialDelayandperiodscheduler- the Scheduler on which the waiting happens and items are emitted- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a 0L after the
initialDelayand ever increasing numbers after eachperiodof time thereafter, while running on the given Scheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timer
timer
public static Observable<java.lang.Long> timer(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits0Lafter a specified delay, and then completes.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. If the downstream needs a slower rate it should slow the timer or use something like
onBackpressureDrop(rx.functions.Action1<? super T>). - Scheduler:
timeroperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
delay- the initial delay before emitting a single0Lunit- time units to use fordelay- Returns:
- an Observable that emits one item after a specified delay, and then completes
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timer
timer
public static Observable<java.lang.Long> timer(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits0Lafter a specified delay, on a specified Scheduler, and then completes.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. If the downstream needs a slower rate it should slow the timer or use something like
onBackpressureDrop(rx.functions.Action1<? super T>). - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
delay- the initial delay before emitting a single 0Lunit- time units to use fordelayscheduler- theSchedulerto use for scheduling the item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits one item after a specified delay, on a specified Scheduler, and then completes
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timer
using
public static <T,Resource> Observable<T> using(Func0<Resource> resourceFactory,Func1<? super Resource,? extendsObservable<? extends T>> observableFactory,Action1<? super Resource> disposeAction)
Constructs an Observable that creates a dependent resource object which is disposed of on unsubscription.
- Backpressure:
- The operator is a pass-through for backpressure and otherwise depends on the backpressure support of the Observable returned by the
resourceFactory. - Scheduler:
usingdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the element type of the generated ObservableResource- the type of the resource associated with the output sequence- Parameters:
resourceFactory- the factory function to create a resource object that depends on the ObservableobservableFactory- the factory function to create an ObservabledisposeAction- the function that will dispose of the resource- Returns:
- the Observable whose lifetime controls the lifetime of the dependent resource object
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Using
using
public static <T,Resource> Observable<T> using(Func0<Resource> resourceFactory,Func1<? super Resource,? extendsObservable<? extends T>> observableFactory,Action1<? super Resource> disposeAction, boolean disposeEagerly)
Constructs an Observable that creates a dependent resource object which is disposed of just before termination if you have setdisposeEagerlytotrueand unsubscription does not occur before termination. Otherwise resource disposal will occur on unsubscription. Eager disposal is particularly appropriate for a synchronous Observable that reuses resources.disposeActionwill only be called once per subscription.
- Backpressure:
- The operator is a pass-through for backpressure and otherwise depends on the backpressure support of the Observable returned by the
resourceFactory. - Scheduler:
usingdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the element type of the generated ObservableResource- the type of the resource associated with the output sequence- Parameters:
resourceFactory- the factory function to create a resource object that depends on the ObservableobservableFactory- the factory function to create an ObservabledisposeAction- the function that will dispose of the resourcedisposeEagerly- iftruethen disposal will happen either on unsubscription or just before emission of a terminal event (onCompleteoronError).- Returns:
- the Observable whose lifetime controls the lifetime of the dependent resource object
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Using
zip
public static <R> Observable<R> zip(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<?>> ws,FuncN<? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of items emitted, in sequence, by an Iterable of other Observables.zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted by each of the source Observables; the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables; and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(Arrays.asList(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2)), (a) -> a)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.
- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the zipped result type- Parameters:
ws- an Iterable of source ObservableszipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<?>[] ws,FuncN<? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of items emitted, in sequence, by an array of other Observables.zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted by each of the source Observables; the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables; and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(new Observable[]{range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2)}, (a) -> a)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.
- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the result type- Parameters:
ws- an array of source ObservableszipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extendsObservable<?>> ws,FuncN<? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations ofn items emitted, in sequence, by then Observables emitted by a specified Observable.zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted by each of the Observables emitted by the source Observable; the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables; and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(just(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2)), (a) -> a)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.
- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the zipped result type- Parameters:
ws- an Observable of source ObservableszipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the Observables emitted byws, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Func2<? super T1,? super T2,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of two items emitted, in sequence, by two other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted byo1and the first item emitted byo2; the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted byo1and the second item emitted byo2; and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), (a, b) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,T3,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Func3<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of three items emitted, in sequence, by three other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted byo1, the first item emitted byo2, and the first item emitted byo3; the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted byo1, the second item emitted byo2, and the second item emitted byo3; and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), ..., (a, b, c) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceT3- the value type of the third sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source Observableo3- a third source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Func4<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of four items emitted, in sequence, by four other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted byo1, the first item emitted byo2, the first item emitted byo3, and the first item emitted by04; the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables; and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), ..., (a, b, c, d) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceT3- the value type of the third sourceT4- the value type of the fourth sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source Observableo3- a third source Observableo4- a fourth source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Func5<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of five items emitted, in sequence, by five other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted byo1, the first item emitted byo2, the first item emitted byo3, the first item emitted byo4, and the first item emitted byo5; the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables; and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), ..., (a, b, c, d, e) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceT3- the value type of the third sourceT4- the value type of the fourth sourceT5- the value type of the fifth sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source Observableo3- a third source Observableo4- a fourth source Observableo5- a fifth source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Func6<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of six items emitted, in sequence, by six other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted by each source Observable, the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables, and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), ..., (a, b, c, d, e, f) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceT3- the value type of the third sourceT4- the value type of the fourth sourceT5- the value type of the fifth sourceT6- the value type of the sixth sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source Observableo3- a third source Observableo4- a fourth source Observableo5- a fifth source Observableo6- a sixth source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Func7<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of seven items emitted, in sequence, by seven other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted by each source Observable, the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables, and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), ..., (a, b, c, d, e, f, g) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceT3- the value type of the third sourceT4- the value type of the fourth sourceT5- the value type of the fifth sourceT6- the value type of the sixth sourceT7- the value type of the seventh sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source Observableo3- a third source Observableo4- a fourth source Observableo5- a fifth source Observableo6- a sixth source Observableo7- a seventh source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Func8<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of eight items emitted, in sequence, by eight other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted by each source Observable, the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables, and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), ..., (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceT3- the value type of the third sourceT4- the value type of the fourth sourceT5- the value type of the fifth sourceT6- the value type of the sixth sourceT7- the value type of the seventh sourceT8- the value type of the eighth sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source Observableo3- a third source Observableo4- a fourth source Observableo5- a fifth source Observableo6- a sixth source Observableo7- a seventh source Observableo8- an eighth source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zip
public static <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,T9,R> Observable<R> zip(Observable<? extends T1> o1,Observable<? extends T2> o2,Observable<? extends T3> o3,Observable<? extends T4> o4,Observable<? extends T5> o5,Observable<? extends T6> o6,Observable<? extends T7> o7,Observable<? extends T8> o8,Observable<? extends T9> o9,Func9<? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,? super T9,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified combiner function applied to combinations of nine items emitted, in sequence, by nine other Observables.
zipapplies this function in strict sequence, so the first item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the first item emitted by each source Observable, the second item emitted by the new Observable will be the result of the function applied to the second item emitted by each of those Observables, and so forth.The resulting
Observable<R>returned fromzipwill invokeonNextas many times as the number ofonNextinvocations of the source Observable that emits the fewest items.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:zip(range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1), range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), ..., (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the value type of the first sourceT2- the value type of the second sourceT3- the value type of the third sourceT4- the value type of the fourth sourceT5- the value type of the fifth sourceT6- the value type of the sixth sourceT7- the value type of the seventh sourceT8- the value type of the eighth sourceT9- the value type of the ninth sourceR- the zipped result type- Parameters:
o1- the first source Observableo2- a second source Observableo3- a third source Observableo4- a fourth source Observableo5- a fifth source Observableo6- a sixth source Observableo7- a seventh source Observableo8- an eighth source Observableo9- a ninth source ObservablezipFunction- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by each of the source Observables, results in an item that will be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the zipped results
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
all
public final Observable<java.lang.Boolean> all(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean that indicates whether all of the items emitted by the source Observable satisfy a condition.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
alldoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- a function that evaluates an item and returns a Boolean- Returns:
- an Observable that emits
trueif all items emitted by the source Observable satisfy the predicate; otherwise,false - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: All
ambWith
public final Observable<T> ambWith(Observable<? extendsT> t1)
Mirrors the Observable (current or provided) that first either emits an item or sends a termination notification.
- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the winning
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ambdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- an Observable competing to react first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same sequence as whichever of the source Observables first emitted an item or sent a termination notification
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Amb
asObservable
public final Observable<T> asObservable()
Portrays a object of an Observable subclass as a simple Observable object. This is useful, for instance, when you have an implementation of a subclass of Observable but you want to hide the properties and methods of this subclass from whomever you are passing the Observable to.- Backpressure:
- The operator itself doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by this
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
asObservabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that hides the identity of this Observable
buffer
public final <TClosing> Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> bufferClosingSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping buffers. It emits the current buffer and replaces it with a new buffer whenever the Observable produced by the specifiedbufferClosingSelectoremits an item.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it is instead controlled by the given Observables and buffers data. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
TClosing- the value type of the boundary-providing Observable- Parameters:
bufferClosingSelector- aFunc0that produces an Observable that governs the boundary between buffers. Whenever the sourceObservableemits an item,bufferemits the current buffer and begins to fill a new one- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a connected, non-overlapping buffer of items from the source Observable each time the Observable created with the
bufferClosingSelectorargument emits an item - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(int count)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping buffers, each containingcountitems. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and expects the source
Observableto honor it as well, although not enforced; violationmay lead toMissingBackpressureExceptionsomewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items in each buffer before it should be emitted- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping buffers, each containing at most
countitems from the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(int count, int skip)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits buffers everyskipitems, each containingcountitems. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and expects the source
Observableto honor it as well, although not enforced; violationmay lead toMissingBackpressureExceptionsomewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum size of each buffer before it should be emittedskip- how many items emitted by the source Observable should be skipped before starting a new buffer. Note that whenskipandcountare equal, this is the same operation asbuffer(int).- Returns:
- an Observable that emits buffers for every
skipitem from the source Observable and containing at mostcountitems - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable starts a new buffer periodically, as determined by thetimeshiftargument. It emits each buffer after a fixed timespan, specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each buffer collects items before it is emittedtimeshift- the period of time after which a new buffer will be createdunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanandtimeshiftarguments- Returns:
- an Observable that emits new buffers of items emitted by the source Observable periodically after a fixed timespan has elapsed
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable starts a new buffer periodically, as determined by thetimeshiftargument, and on the specifiedscheduler. It emits each buffer after a fixed timespan, specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each buffer collects items before it is emittedtimeshift- the period of time after which a new buffer will be createdunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanandtimeshiftargumentsscheduler- theSchedulerto use when determining the end and start of a buffer- Returns:
- an Observable that emits new buffers of items emitted by the source Observable periodically after a fixed timespan has elapsed
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping buffers, each of a fixed duration specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each buffer collects items before it is emitted and replaced with a new bufferunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanargument- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping buffers of items emitted by the source Observable within a fixed duration
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping buffers, each of a fixed duration specified by thetimespanargument or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (whichever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each buffer collects items before it is emitted and replaced with a new bufferunit- the unit of time which applies to thetimespanargumentcount- the maximum size of each buffer before it is emitted- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping buffers of items emitted by the source Observable, after a fixed duration or when the buffer reaches maximum capacity (whichever occurs first)
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping buffers, each of a fixed duration specified by thetimespanargument as measured on the specifiedscheduler, or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (whichever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each buffer collects items before it is emitted and replaced with a new bufferunit- the unit of time which applies to thetimespanargumentcount- the maximum size of each buffer before it is emittedscheduler- theSchedulerto use when determining the end and start of a buffer- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping buffers of items emitted by the source Observable after a fixed duration or when the buffer reaches maximum capacity (whichever occurs first)
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping buffers, each of a fixed duration specified by thetimespanargument and on the specifiedscheduler. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current buffer and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each buffer collects items before it is emitted and replaced with a new bufferunit- the unit of time which applies to thetimespanargumentscheduler- theSchedulerto use when determining the end and start of a buffer- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping buffers of items emitted by the source Observable within a fixed duration
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final <TOpening,TClosing> Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(Observable<? extends TOpening> bufferOpenings,Func1<? super TOpening,? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> bufferClosingSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits buffers of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits buffers that it creates when the specifiedbufferOpeningsObservable emits an item, and closes when the Observable returned frombufferClosingSelectoremits an item.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it is instead controlled by the given Observables and buffers data. It requests
Long.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
TOpening- the element type of the buffer-opening ObservableTClosing- the element type of the individual buffer-closing Observables- Parameters:
bufferOpenings- the Observable that, when it emits an item, causes a new buffer to be createdbufferClosingSelector- theFunc1that is used to produce an Observable for every buffer created. When this Observable emits an item, the associated buffer is emitted.- Returns:
- an Observable that emits buffers, containing items from the source Observable, that are created and closed when the specified Observables emit items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final <B> Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(Observable<B> boundary)
Returns an Observable that emits non-overlapping buffered items from the source Observable each time the specified boundary Observable emits an item.
Completion of either the source or the boundary Observable causes the returned Observable to emit the latest buffer and complete.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it is instead controlled by the
Observableboundaryand buffers data. It requestsLong.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
B- the boundary value type (ignored)- Parameters:
boundary- the boundary Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits buffered items from the source Observable when the boundary Observable emits an item
- See Also:
buffer(rx.Observable, int),ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer
buffer
public final <B> Observable<java.util.List<T>> buffer(Observable<B> boundary, int initialCapacity)
Returns an Observable that emits non-overlapping buffered items from the source Observable each time the specified boundary Observable emits an item.
Completion of either the source or the boundary Observable causes the returned Observable to emit the latest buffer and complete.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it is instead controlled by the
Observableboundaryand buffers data. It requestsLong.MAX_VALUEupstream and does not obey downstream requests. - Scheduler:
- This version of
bufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
B- the boundary value type (ignored)- Parameters:
boundary- the boundary ObservableinitialCapacity- the initial capacity of each buffer chunk- Returns:
- an Observable that emits buffered items from the source Observable when the boundary Observable emits an item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Buffer,
buffer(rx.Observable, int)
cache
public final Observable<T> cache()
Returns an Observable that subscribes to this Observable lazily, caches all of its events and replays them, in the same order as received, to all the downstream subscribers.
This is useful when you want an Observable to cache responses and you can't control the subscribe/unsubscribe behavior of all the
Subscribers.The operator subscribes only when the first downstream subscriber subscribes and maintains a single subscription towards this Observable. In contrast, the operator family of
replay()that return aConnectableObservablerequire an explicit call toConnectableObservable.connect().Note: You sacrifice the ability to unsubscribe from the origin when you use the
cacheObserver so be careful not to use this Observer on Observables that emit an infinite or very large number of items that will use up memory. A possible workaround is to apply `takeUntil` with a predicate or another source before (and perhaps after) the application of cache().
Since the operator doesn't allow clearing the cached values either, the possible workaround is to forget all references to it viaAtomicBoolean shouldStop = new AtomicBoolean(); source.takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .cache() .takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .subscribe(...);onTerminateDetach()applied along with the previous workaround:AtomicBoolean shouldStop = new AtomicBoolean(); source.takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .onTerminateDetach() .cache() .takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .onTerminateDetach() .subscribe(...);- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes this Observable in an unbounded fashion but respects the backpressure of each downstream Subscriber individually.
- Scheduler:
cachedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that, when first subscribed to, caches all of its items and notifications for the benefit of subsequent subscribers
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
cache
@Deprecatedpublic final Observable<T> cache(int initialCapacity)
Deprecated. UsecacheWithInitialCapacity(int)instead.Caches and shares everything from this Observable and uses the initialCapacity to reduce the number of times the internal buffer needs resizing.- Parameters:
initialCapacity- the capacity to start with- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specific behavior.
- See Also:
cacheWithInitialCapacity(int)
cacheWithInitialCapacity
public final Observable<T> cacheWithInitialCapacity(int initialCapacity)
Returns an Observable that subscribes to this Observable lazily, caches all of its events and replays them, in the same order as received, to all the downstream subscribers.
This is useful when you want an Observable to cache responses and you can't control the subscribe/unsubscribe behavior of all the
Subscribers.The operator subscribes only when the first downstream subscriber subscribes and maintains a single subscription towards this Observable. In contrast, the operator family of
replay()that return aConnectableObservablerequire an explicit call toConnectableObservable.connect().Note: You sacrifice the ability to unsubscribe from the origin when you use the
cacheObserver so be careful not to use this Observer on Observables that emit an infinite or very large number of items that will use up memory. A possible workaround is to apply `takeUntil` with a predicate or another source before (and perhaps after) the application of cache().
Since the operator doesn't allow clearing the cached values either, the possible workaround is to forget all references to it viaAtomicBoolean shouldStop = new AtomicBoolean(); source.takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .cache() .takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .subscribe(...);onTerminateDetach()applied along with the previous workaround:AtomicBoolean shouldStop = new AtomicBoolean(); source.takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .onTerminateDetach() .cache() .takeUntil(v -> shouldStop.get()) .onTerminateDetach() .subscribe(...);- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes this Observable in an unbounded fashion but respects the backpressure of each downstream Subscriber individually.
- Scheduler:
cachedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
Note: The capacity hint is not an upper bound on cache size. For that, consider
replay(int)in combination withConnectableObservable.autoConnect()or similar.- Parameters:
initialCapacity- hint for number of items to cache (for optimizing underlying data structure)- Returns:
- an Observable that, when first subscribed to, caches all of its items and notifications for the benefit of subsequent subscribers
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
cast
public final <R> Observable<R> cast(java.lang.Class<R> klass)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable, converted to the specified type.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
castdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the output value type cast to- Parameters:
klass- the target class type thatcastwill cast the items emitted by the source Observable into before emitting them from the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits each item from the source Observable after converting it to the specified type
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Map
collect
public final <R> Observable<R> collect(Func0<R> stateFactory,Action2<R,? superT> collector)
Collects items emitted by the source Observable into a single mutable data structure and returns an Observable that emits this structure.
This is a simplified version of
reducethat does not need to return the state on each pass.- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure because by intent it will receive all values and reduce them to a single
onNext. - Scheduler:
collectdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the accumulator and output type- Parameters:
stateFactory- the mutable data structure that will collect the itemscollector- a function that accepts thestateand an emitted item, and modifiesstateaccordingly- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the result of collecting the values emitted by the source Observable into a single mutable data structure
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Reduce
concatMap
public final <R> Observable<R> concatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)
Returns a new Observable that emits items resulting from applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then emitting the items that result from concatenating those resulting Observables.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both this and the inner
Observables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If the sourceObservableviolates the rule, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureException. If any of the innerObservables doesn't honor backpressure, thatmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen thatObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of the inner Observable sources and thus the output type- Parameters:
func- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the result of applying the transformation function to each item emitted by the source Observable and concatenating the Observables obtained from this transformation
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
concatMapDelayError
public final <R> Observable<R> concatMapDelayError(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)
Maps each of the items into an Observable, subscribes to them one after the other, one at a time and emits their values in order while delaying any error from either this or any of the inner Observables till all of them terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both this and the inner
Observables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If the sourceObservableviolates the rule, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureException. If any of the innerObservables doesn't honor backpressure, thatmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen thatObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatMapDelayErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the result value type- Parameters:
func- the function that maps the items of this Observable into the inner Observables.- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatMapIterable
public final <R> Observable<R> concatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends R>> collectionSelector)
Returns an Observable that concatenate each item emitted by the source Observable with the values in an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables is expected to honor backpressure as well. If the sourceObservableviolates the rule, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
concatMapIterabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of item emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
collectionSelector- a function that returns an Iterable sequence of values for when given an item emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of concatenating the items emitted by the source Observable with the values in the Iterables corresponding to those items, as generated by
collectionSelector - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
concatWith
public final Observable<T> concatWith(Observable<? extendsT> t1)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted from the current Observable, then the next, one after the other, without interleaving them.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both this and the
otherObservables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of then violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
concatdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be concatenated after the current- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items emitted by the two source Observables, one after the other, without interleaving them
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Concat
contains
public final Observable<java.lang.Boolean> contains(java.lang.Object element)
Returns an Observable that emits a Boolean that indicates whether the source Observable emitted a specified item.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
containsdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
element- the item to search for in the emissions from the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits
trueif the specified item is emitted by the source Observable, orfalseif the source Observable completes without emitting that item - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Contains
count
public final Observable<java.lang.Integer> count()
Returns an Observable that emits the count of the total number of items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
countdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: the number of elements emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Count,
countLong()
countLong
public final Observable<java.lang.Long> countLong()
Returns an Observable that counts the total number of items emitted by the source Observable and emits this count as a 64-bit Long.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
countLongdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: the number of items emitted by the source Observable as a 64-bit Long item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Count,
count()
debounce
public final <U> Observable<T> debounce(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<U>> debounceSelector)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by another item within a computed debounce duration.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses the
debounceSelectorto mark boundaries. - Scheduler:
- This version of
debouncedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the debounce value type (ignored)- Parameters:
debounceSelector- function to retrieve a sequence that indicates the throttle duration for each item- Returns:
- an Observable that omits items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by another item within a computed debounce duration
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Debounce,RxJava wiki: Backpressure
debounce
public final Observable<T> debounce(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by newer items before a timeout value expires. The timer resets on each emission.Note: If items keep being emitted by the source Observable faster than the timeout then no items will be emitted by the resulting Observable.

Information on debounce vs throttle:
- Debounce and Throttle: visual explanation
- Debouncing: javascript methods
- Javascript - don't spam your server: debounce and throttle
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
debounceoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timeout- the time each item has to be "the most recent" of those emitted by the source Observable to ensure that it's not droppedunit- theTimeUnitfor the timeout- Returns:
- an Observable that filters out items from the source Observable that are too quickly followed by newer items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Debounce,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
throttleWithTimeout(long, TimeUnit)
debounce
public final Observable<T> debounce(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by newer items before a timeout value expires on a specified Scheduler. The timer resets on each emission.Note: If items keep being emitted by the source Observable faster than the timeout then no items will be emitted by the resulting Observable.

Information on debounce vs throttle:
- Debounce and Throttle: visual explanation
- Debouncing: javascript methods
- Javascript - don't spam your server: debounce and throttle
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timeout- the time each item has to be "the most recent" of those emitted by the source Observable to ensure that it's not droppedunit- the unit of time for the specified timeoutscheduler- theSchedulerto use internally to manage the timers that handle the timeout for each item- Returns:
- an Observable that filters out items from the source Observable that are too quickly followed by newer items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Debounce,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
throttleWithTimeout(long, TimeUnit, Scheduler)
defaultIfEmpty
public final Observable<T> defaultIfEmpty(T defaultValue)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or a specified default item if the source Observable is empty.
- Backpressure:
- If the source
Observableis empty, this operator is guaranteed to honor backpressure from downstream. If the sourceObservableis non-empty, it is expected to honor backpressure as well; if the rule is violated, aMissingBackpressureExceptionmay get signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
defaultIfEmptydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
defaultValue- the item to emit if the source Observable emits no items- Returns:
- an Observable that emits either the specified default item if the source Observable emits no items, or the items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: DefaultIfEmpty
switchIfEmpty
public final Observable<T> switchIfEmpty(Observable<? extendsT> alternate)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or the items of an alternate Observable if the source Observable is empty.
- Backpressure:
- If the source
Observableis empty, the alternateObservableis expected to honor backpressure. If the sourceObservableis non-empty, it is expected to honor backpressure as instead. In either case, if violated, aMissingBackpressureExceptionmay get signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
switchIfEmptydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
alternate- the alternate Observable to subscribe to if the source does not emit any items- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or the items of an alternate Observable if the source Observable is empty.
- Throws:
java.lang.NullPointerException- ifalternateis null- Since:
- 1.1.0
delay
public final <U,V> Observable<T> delay(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> subscriptionDelay,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> itemDelay)
Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to and emissions from the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.
Note: the resulting Observable will immediately propagate any
onErrornotification from the source Observable.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which is determined by the source
Observable. All of the otherObservables supplied by the functions are consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to them). - Scheduler:
- This version of
delaydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the subscription delay value type (ignored)V- the item delay value type (ignored)- Parameters:
subscriptionDelay- a function that returns an Observable that triggers the subscription to the source Observable once it emits any itemitemDelay- a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source Observable, which is then used to delay the emission of that item by the resulting Observable until the Observable returned fromitemDelayemits an item- Returns:
- an Observable that delays the subscription and emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Delay
delay
public final <U> Observable<T> delay(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<U>> itemDelay)
Returns an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.
Note: the resulting Observable will immediately propagate any
onErrornotification from the source Observable.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which is determined by the source
Observable. All of the otherObservables supplied by the function are consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to them). - Scheduler:
- This version of
delaydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the item delay value type (ignored)- Parameters:
itemDelay- a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source Observable, which is then used to delay the emission of that item by the resulting Observable until the Observable returned fromitemDelayemits an item- Returns:
- an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Delay
delay
public final Observable<T> delay(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay. Error notifications from the source Observable are not delayed.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which is determined by the source
Observable. - Scheduler:
- This version of
delayoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
delay- the delay to shift the source byunit- theTimeUnitin whichperiodis defined- Returns:
- the source Observable shifted in time by the specified delay
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Delay
delay
public final Observable<T> delay(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay. Error notifications from the source Observable are not delayed.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which is determined by the source
Observable. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
delay- the delay to shift the source byunit- the time unit ofdelayscheduler- theSchedulerto use for delaying- Returns:
- the source Observable shifted in time by the specified delay
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Delay
delaySubscription
public final Observable<T> delaySubscription(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable by a given amount of time.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which is determined by the source
Observable. - Scheduler:
- This version of
delayoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
delay- the time to delay the subscriptionunit- the time unit ofdelay- Returns:
- an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable by the given amount
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Delay
delaySubscription
public final Observable<T> delaySubscription(long delay, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable by a given amount of time, both waiting and subscribing on a given Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which is determined by the source
Observable. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
delay- the time to delay the subscriptionunit- the time unit ofdelayscheduler- the Scheduler on which the waiting and subscription will happen- Returns:
- an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable by a given amount, waiting and subscribing on the given Scheduler
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Delay
delaySubscription
public final <U> Observable<T> delaySubscription(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> subscriptionDelay)
Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with the backpressure behavior which is determined by the source
Observable. The otherObservables supplied by the function is consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the element type of the delaying Observable- Parameters:
subscriptionDelay- a function that returns an Observable that triggers the subscription to the source Observable once it emits any item- Returns:
- an Observable that delays the subscription to the source Observable until the Observable returned by
subscriptionDelayemits an item - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Delay
delaySubscription
public final <U> Observable<T> delaySubscription(Observable<U> other)
Returns an Observable that delays the subscription to this Observable until the other Observable emits an element or completes normally.- Backpressure:
- The operator forwards the backpressure requests to this Observable once the subscription happens and requests Long.MAX_VALUE from the other Observable
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the value type of the other Observable, irrelevant- Parameters:
other- the other Observable that should trigger the subscription to this Observable.- Returns:
- an Observable that delays the subscription to this Observable until the other Observable emits an element or completes normally.
- Since:
- 1.3
dematerialize
public final <T2> Observable<T2> dematerialize()
Returns an Observable that reverses the effect ofmaterializeby transforming theNotificationobjects emitted by the source Observable into the items or notifications they represent.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
dematerializedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T2- the output value type- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items and notifications embedded in the
Notificationobjects emitted by the source Observable - Throws:
OnErrorNotImplementedException- if the source Observable is not of typeObservable<Notification<T>>- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Dematerialize
distinct
public final Observable<T> distinct()
Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
distinctdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only those items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct from each other
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Distinct
distinct
public final <U> Observable<T> distinct(Func1<? superT,? extends U> keySelector)
Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
distinctdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the key type- Parameters:
keySelector- a function that projects an emitted item to a key value that is used to decide whether an item is distinct from another one or not- Returns:
- an Observable that emits those items emitted by the source Observable that have distinct keys
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Distinct
distinctUntilChanged
public final Observable<T> distinctUntilChanged()
Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
distinctUntilChangeddoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits those items from the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Distinct
distinctUntilChanged
public final <U> Observable<T> distinctUntilChanged(Func1<? superT,? extends U> keySelector)
Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors, according to a key selector function.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
distinctUntilChangeddoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the key type- Parameters:
keySelector- a function that projects an emitted item to a key value that is used to decide whether an item is distinct from another one or not- Returns:
- an Observable that emits those items from the source Observable whose keys are distinct from those of their immediate predecessors
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Distinct
distinctUntilChanged
public final Observable<T> distinctUntilChanged(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Boolean> comparator)
Returns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors when compared with each other via the provided comparator function.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
distinctUntilChangeddoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
comparator- the function that receives the previous item and the current item and is expected to return true if the two are equal, thus skipping the current value.- Returns:
- an Observable that emits those items from the source Observable that are distinct from their immediate predecessors
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Distinct
doOnCompleted
public final Observable<T> doOnCompleted(Action0 onCompleted)
Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action when it callsonCompleted.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnCompleteddoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onCompleted- the action to invoke when the source Observable callsonCompleted- Returns:
- the source Observable with the side-effecting behavior applied
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
doOnEach
public final Observable<T> doOnEach(Action1<Notification<? superT>> onNotification)
Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action for each item and terminal event it emits.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnEachdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNotification- the action to invoke for each item emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- the source Observable with the side-effecting behavior applied
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
doOnEach
public final Observable<T> doOnEach(Observer<? superT> observer)
Modifies the source Observable so that it notifies an Observer for each item and terminal event it emits.In case the
onErrorof the supplied observer throws, the downstream will receive a composite exception containing the original exception and the exception thrown byonError. If either theonNextor theonCompletedmethod of the supplied observer throws, the downstream will be terminated and will receive this thrown exception.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnEachdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
observer- the observer to be notified about onNext, onError and onCompleted events on its respective methods before the actual downstream Subscriber gets notified.- Returns:
- the source Observable with the side-effecting behavior applied
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
doOnError
public final Observable<T> doOnError(Action1<? super java.lang.Throwable> onError)
Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action if it callsonError.In case the
onErroraction throws, the downstream will receive a composite exception containing the original exception and the exception thrown byonError.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnErrordoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onError- the action to invoke if the source Observable callsonError- Returns:
- the source Observable with the side-effecting behavior applied
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
doOnNext
public final Observable<T> doOnNext(Action1<? superT> onNext)
Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action when it callsonNext.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnNextdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNext- the action to invoke when the source Observable callsonNext- Returns:
- the source Observable with the side-effecting behavior applied
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
doOnRequest
public final Observable<T> doOnRequest(Action1<? super java.lang.Long> onRequest)
Modifies the sourceObservableso that it invokes the given action when it receives a request for more items.Note: This operator is for tracing the internal behavior of back-pressure request patterns and generally intended for debugging use.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnRequestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onRequest- the action that gets called when an observer requests items from thisObservable- Returns:
- the source
Observablemodified so as to call this Action when appropriate - Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
doOnSubscribe
public final Observable<T> doOnSubscribe(Action0 subscribe)
Modifies the sourceObservableso that it invokes the given action when it is subscribed from its subscribers. Each subscription will result in an invocation of the given action except when the sourceObservableis reference counted, in which case the sourceObservablewill invoke the given action for the first subscription.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnSubscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
subscribe- the action that gets called when an observer subscribes to the sourceObservable- Returns:
- the source
Observablemodified so as to call this Action when appropriate - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
doOnTerminate
public final Observable<T> doOnTerminate(Action0 onTerminate)
Modifies the source Observable so that it invokes an action when it callsonCompletedoronError.
This differs from
finallyDoin that this happensbefore theonCompletedoronErrornotification.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doOnTerminatedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onTerminate- the action to invoke when the source Observable callsonCompletedoronError- Returns:
- the source Observable with the side-effecting behavior applied
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do,
finallyDo(Action0)
doOnUnsubscribe
public final Observable<T> doOnUnsubscribe(Action0 unsubscribe)
Calls the unsubscribeAction0if the downstream unsubscribes the sequence.The action is shared between subscriptions and thus may be called concurrently from multiple threads; the action must be thread safe.
If the action throws a runtime exception, that exception is rethrown by the
unsubscribe()call, sometimes as aCompositeExceptionif there were multiple exceptions along the way.Note that terminal events trigger the action unless the
Observableis subscribed to viaunsafeSubscribe().
- Backpressure:
doOnUnsubscribedoes not interact with backpressure requests or value delivery; backpressure behavior is preserved between its upstream and its downstream.- Scheduler:
doOnUnsubscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
unsubscribe- the action that gets called when the sourceObservableis unsubscribed- Returns:
- the source
Observablemodified so as to call this Action when appropriate - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2)
Concatenates two source Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3)
Concatenates three sources eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second sourceo3- the third source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4)
Concatenates four sources eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second sourceo3- the third sourceo4- the fourth source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5)
Concatenates five sources eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second sourceo3- the third sourceo4- the fourth sourceo5- the fifth source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6)
Concatenates six sources eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second sourceo3- the third sourceo4- the fourth sourceo5- the fifth sourceo6- the sixth source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7)
Concatenates seven sources eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second sourceo3- the third sourceo4- the fourth sourceo5- the fifth sourceo6- the sixth sourceo7- the seventh source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8)
Concatenates eight sources eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second sourceo3- the third sourceo4- the fourth sourceo5- the fifth sourceo6- the sixth sourceo7- the seventh sourceo8- the eighth source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extends T> o1,Observable<? extends T> o2,Observable<? extends T> o3,Observable<? extends T> o4,Observable<? extends T> o5,Observable<? extends T> o6,Observable<? extends T> o7,Observable<? extends T> o8,Observable<? extends T> o9)
Concatenates nine sources eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
o1- the first sourceo2- the second sourceo3- the third sourceo4- the fourth sourceo5- the fifth sourceo6- the sixth sourceo7- the seventh sourceo8- the eighth sourceo9- the ninth source- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)
Concatenates a sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
sources- a sequence of Observables that need to be eagerly concatenated- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(java.lang.Iterable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources, int capacityHint)
Concatenates a sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
sources- a sequence of Observables that need to be eagerly concatenatedcapacityHint- hints about the number of expected source sequence values- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources)
Concatenates an Observable sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the emitted source Observables as they are observed. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
sources- a sequence of Observables that need to be eagerly concatenated- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatEager
public static <T> Observable<T> concatEager(Observable<? extendsObservable<? extends T>> sources, int capacityHint)
Concatenates an Observable sequence of Observables eagerly into a single stream of values.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the emitted source Observables as they are observed. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T- the value type- Parameters:
sources- a sequence of Observables that need to be eagerly concatenatedcapacityHint- hints about the number of expected source sequence values- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatMapEager
public final <R> Observable<R> concatMapEager(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> mapper)
Maps a sequence of values into Observables and concatenates these Observables eagerly into a single Observable.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type- Parameters:
mapper- the function that maps a sequence of values into a sequence of Observables that will be eagerly concatenated- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatMapEager
public final <R> Observable<R> concatMapEager(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> mapper, int capacityHint)
Maps a sequence of values into Observables and concatenates these Observables eagerly into a single Observable.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type- Parameters:
mapper- the function that maps a sequence of values into a sequence of Observables that will be eagerly concatenatedcapacityHint- hints about the number of expected source sequence values- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
concatMapEager
public final <R> Observable<R> concatMapEager(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> mapper, int capacityHint, int maxConcurrent)
Maps a sequence of values into Observables and concatenates these Observables eagerly into a single Observable.Eager concatenation means that once a subscriber subscribes, this operator subscribes to all of the source Observables. The operator buffers the values emitted by these Observables and then drains them in order, each one after the previous one completes.
- Backpressure:
- Backpressure is honored towards the downstream, however, due to the eagerness requirement, sources are subscribed to in unbounded mode and their values are queued up in an unbounded buffer.
- Scheduler:
- This method does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type- Parameters:
mapper- the function that maps a sequence of values into a sequence of Observables that will be eagerly concatenatedcapacityHint- hints about the number of expected source sequence valuesmaxConcurrent- the maximum number of concurrent subscribed observables- Returns:
- the new Observable instance with the specified concatenation behavior
- Since:
- 1.3
elementAt
public final Observable<T> elementAt(int index)
Returns an Observable that emits the single item at a specified index in a sequence of emissions from a source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
elementAtdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
index- the zero-based index of the item to retrieve- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: the item at the specified position in the sequence of those emitted by the source Observable
- Throws:
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifindexis greater than or equal to the number of items emitted by the source Observable, or ifindexis less than 0- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: ElementAt
elementAtOrDefault
public final Observable<T> elementAtOrDefault(int index,T defaultValue)
Returns an Observable that emits the item found at a specified index in a sequence of emissions from a source Observable, or a default item if that index is out of range.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
elementAtOrDefaultdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
index- the zero-based index of the item to retrievedefaultValue- the default item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the item at the specified position in the sequence emitted by the source Observable, or the default item if that index is outside the bounds of the source sequence
- Throws:
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifindexis less than 0- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: ElementAt
exists
public final Observable<java.lang.Boolean> exists(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emitstrueif any item emitted by the source Observable satisfies a specified condition, otherwisefalse.Note: this always emitsfalseif the source Observable is empty.
In Rx.Net this is the
anyObserver but we renamed it in RxJava to better match Java naming idioms.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
existsdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- the condition to test items emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a Boolean that indicates whether any item emitted by the source Observable satisfies the
predicate - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Contains
filter
public final Observable<T> filter(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Filters items emitted by an Observable by only emitting those that satisfy a specified predicate.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
filterdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- a function that evaluates each item emitted by the source Observable, returningtrueif it passes the filter- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only those items emitted by the source Observable that the filter evaluates as
true - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Filter
finallyDo
@Deprecatedpublic final Observable<T> finallyDo(Action0 action)
Deprecated. usedoAfterTerminate(Action0)instead.Registers anAction0to be called when this Observable invokes eitheronCompletedoronError.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
finallyDodoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
action- anAction0to be invoked when the source Observable finishes- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same items as the source Observable, then invokes the
Action0 - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do,
doOnTerminate(Action0)
doAfterTerminate
public final Observable<T> doAfterTerminate(Action0 action)
Registers anAction0to be called when this Observable invokes eitheronCompletedoronError.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
doAfterTerminatedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
action- anAction0to be invoked when the source Observable finishes- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the same items as the source Observable, then invokes the
Action0 - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Do,
doOnTerminate(Action0)
first
public final Observable<T> first()
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or notifies of anNoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
firstdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or raises an
NoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
first
public final Observable<T> first(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition, or notifies of anNoSuchElementExceptionif no such items are emitted.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
firstdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- the condition that an item emitted by the source Observable has to satisfy- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies the
predicate, or raises anNoSuchElementExceptionif no such items are emitted - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
firstOrDefault
public final Observable<T> firstOrDefault(T defaultValue)
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable completes without emitting anything.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
firstOrDefaultdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
defaultValue- the default item to emit if the source Observable doesn't emit anything- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the very first item from the source, or a default item if the source Observable completes without emitting any items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
firstOrDefault
public final Observable<T> firstOrDefault(T defaultValue,Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition, or a default item if the source Observable emits no such items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
firstOrDefaultdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- the condition any item emitted by the source Observable has to satisfydefaultValue- the default item to emit if the source Observable doesn't emit anything that satisfies thepredicate- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies the
predicate, or a default item if the source Observable emits no such items - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
flatMap
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)
Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in unbounded mode (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). The innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type of the inner Observables and the output type- Parameters:
func- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the result of applying the transformation function to each item emitted by the source Observable and merging the results of the Observables obtained from this transformation
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMap
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func, int maxConcurrent)
Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both the outer and inner
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type of the inner Observables and the output type- Parameters:
func- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an ObservablemaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the result of applying the transformation function to each item emitted by the source Observable and merging the results of the Observables obtained from this transformation
- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMap
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onNext,Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onError,Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onCompleted)
Returns an Observable that applies a function to each item emitted or notification raised by the source Observable and then flattens the Observables returned from these functions and emits the resulting items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in unbounded mode (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). The innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the result type- Parameters:
onNext- a function that returns an Observable to merge for each item emitted by the source ObservableonError- a function that returns an Observable to merge for an onError notification from the source ObservableonCompleted- a function that returns an Observable to merge for an onCompleted notification from the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of merging the Observables returned from applying the specified functions to the emissions and notifications of the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMap
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onNext,Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onError,Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends R>> onCompleted, int maxConcurrent)
Returns an Observable that applies a function to each item emitted or notification raised by the source Observable and then flattens the Observables returned from these functions and emits the resulting items, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both the outer and inner
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the result type- Parameters:
onNext- a function that returns an Observable to merge for each item emitted by the source ObservableonError- a function that returns an Observable to merge for an onError notification from the source ObservableonCompleted- a function that returns an Observable to merge for an onCompleted notification from the source ObservablemaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of merging the Observables returned from applying the specified functions to the emissions and notifications of the source Observable
- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMap
public final <U,R> Observable<R> flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified function to the pair of values emitted by the source Observable and a specified collection Observable.
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in unbounded mode (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). The innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the type of items emitted by the collection ObservableR- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
collectionSelector- a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source ObservableresultSelector- a function that combines one item emitted by each of the source and collection Observables and returns an item to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of applying a function to a pair of values emitted by the source Observable and the collection Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
flatMap
public final <U,R> Observable<R> flatMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector, int maxConcurrent)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of a specified function to the pair of values emitted by the source Observable and a specified collection Observable, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both the outer and inner
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the type of items emitted by the collection ObservableR- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
collectionSelector- a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source ObservableresultSelector- a function that combines one item emitted by each of the source and collection Observables and returns an item to be emitted by the resulting ObservablemaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of applying a function to a pair of values emitted by the source Observable and the collection Observable
- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMapCompletable
public final Observable<T> flatMapCompletable(Func1<? superT,? extendsCompletable> mapper)
Maps all upstream values to Completables and runs them together until the upstream and all inner Completables complete normally.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes items from upstream in an unbounded manner and ignores downstream backpressure as it doesn't emit items but only terminal event.
- Scheduler:
flatMapCompletabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Parameters:
mapper- the function that receives an upstream value and turns it into a Completable to be merged.- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
flatMapCompletable(Func1, boolean, int)
flatMapCompletable
public final Observable<T> flatMapCompletable(Func1<? superT,? extendsCompletable> mapper, boolean delayErrors)
Maps all upstream values to Completables and runs them together, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Completables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes items from upstream in an unbounded manner and ignores downstream backpressure as it doesn't emit items but only terminal event.
- Scheduler:
flatMapCompletabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Parameters:
mapper- the function that receives an upstream value and turns it into a Completable to be merged.delayErrors- if true, errors from the upstream and from the inner Completables get delayed till the all of them terminate.- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
flatMapCompletable(Func1, boolean, int)
flatMapCompletable
public final Observable<T> flatMapCompletable(Func1<? superT,? extendsCompletable> mapper, boolean delayErrors, int maxConcurrency)
Maps upstream values to Completables and runs up to the given number of them together at a time, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Completables terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes at most maxConcurrent items from upstream and one-by-one after as the inner Completables terminate. The operator ignores downstream backpressure as it doesn't emit items but only the terminal event.
- Scheduler:
flatMapCompletabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Parameters:
mapper- the function that receives an upstream value and turns it into a Completable to be merged.delayErrors- if true, errors from the upstream and from the inner Completables get delayed till the all of them terminate.maxConcurrency- the maximum number of inner Completables to run at a time- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
flatMapIterable
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends R>> collectionSelector)
Returns an Observable that merges each item emitted by the source Observable with the values in an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables is expected to honor backpressure as well. If the sourceObservableviolates the rule, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapIterabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of item emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
collectionSelector- a function that returns an Iterable sequence of values for when given an item emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of merging the items emitted by the source Observable with the values in the Iterables corresponding to those items, as generated by
collectionSelector - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMapIterable
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends R>> collectionSelector, int maxConcurrent)
Returns an Observable that merges each item emitted by the source Observable with the values in an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables is expected to honor backpressure as well. If the sourceObservableviolates the rule, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapIterabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of item emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
collectionSelector- a function that returns an Iterable sequence of values for when given an item emitted by the source ObservablemaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of merging the items emitted by the source Observable with the values in the Iterables corresponding to those items, as generated by
collectionSelector - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifmaxConcurrentis less than or equal to 0- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMapIterable
public final <U,R> Observable<R> flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of applying a function to the pair of values from the source Observable and an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and the source
Observables is consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
flatMapIterabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the collection element typeR- the type of item emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
collectionSelector- a function that returns an Iterable sequence of values for each item emitted by the source ObservableresultSelector- a function that returns an item based on the item emitted by the source Observable and the Iterable returned for that item by thecollectionSelector- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items returned by
resultSelectorfor each item in the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMapIterable
public final <U,R> Observable<R> flatMapIterable(Func1<? superT,? extends java.lang.Iterable<? extends U>> collectionSelector,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector, int maxConcurrent)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of applying a function to the pair of values from the source Observable and an Iterable corresponding to that item that is generated by a selector, while limiting the number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables is expected to honor backpressure as well. If the sourceObservableviolates the rule, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
flatMapIterabledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the collection element typeR- the type of item emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
collectionSelector- a function that returns an Iterable sequence of values for each item emitted by the source ObservableresultSelector- a function that returns an item based on the item emitted by the source Observable and the Iterable returned for that item by thecollectionSelectormaxConcurrent- the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items returned by
resultSelectorfor each item in the source Observable - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifmaxConcurrentis less than or equal to 0- Since:
- 1.2
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
flatMapSingle
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMapSingle(Func1<? superT,? extendsSingle<? extends R>> mapper)
Maps all upstream values to Singles and runs them together until the upstream and all inner Singles complete normally.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes items from upstream in an unbounded manner and honors downstream backpressure.
- Scheduler:
flatMapSingledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type of the inner Singles and the resulting Observable- Parameters:
mapper- the function that receives an upstream value and turns it into a Single to be merged.- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
flatMapSingle(Func1, boolean, int)
flatMapSingle
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMapSingle(Func1<? superT,? extendsSingle<? extends R>> mapper, boolean delayErrors)
Maps all upstream values to Singles and runs them together, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Singles terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes items from upstream in an unbounded manner and honors downstream backpressure.
- Scheduler:
flatMapSingledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type of the inner Singles and the resulting Observable- Parameters:
mapper- the function that receives an upstream value and turns it into a Single to be merged.delayErrors- if true, errors from the upstream and from the inner Singles get delayed till the all of them terminate.- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
flatMapSingle(Func1, boolean, int)
flatMapSingle
public final <R> Observable<R> flatMapSingle(Func1<? superT,? extendsSingle<? extends R>> mapper, boolean delayErrors, int maxConcurrency)
Maps upstream values to Singles and runs up to the given number of them together at a time, optionally delaying any errors, until the upstream and all inner Singles terminate.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes at most maxConcurrent items from upstream and one-by-one after as the inner Singles terminate. The operator honors downstream backpressure.
- Scheduler:
flatMapSingledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Type Parameters:
R- the value type of the inner Singles and the resulting Observable- Parameters:
mapper- the function that receives an upstream value and turns it into a Single to be merged.delayErrors- if true, errors from the upstream and from the inner Singles get delayed till the all of them terminate.maxConcurrency- the maximum number of inner Singles to run at a time- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
forEach
public final void forEach(Action1<? superT> onNext)
Subscribes to theObservableand receives notifications for each element.Alias to
subscribe(Action1)- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
forEachdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNext-Action1to execute for each item.- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifonNextis nullOnErrorNotImplementedException- if the Observable callsonError- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
forEach
public final void forEach(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError)
Subscribes to theObservableand receives notifications for each element and error events.Alias to
subscribe(Action1, Action1)- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
forEachdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNext-Action1to execute for each item.onError-Action1to execute when an error is emitted.- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifonNextis null, or ifonErroris nullOnErrorNotImplementedException- if the Observable callsonError- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
forEach
public final void forEach(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError,Action0 onComplete)
Subscribes to theObservableand receives notifications for each element and the terminal events.Alias to
subscribe(Action1, Action1, Action0)- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
forEachdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNext-Action1to execute for each item.onError-Action1to execute when an error is emitted.onComplete-Action0to execute when completion is signalled.- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifonNextis null, or ifonErroris null, or ifonCompleteis nullOnErrorNotImplementedException- if the Observable callsonError- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
groupBy
public final <K,R> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,R>> groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends R> elementSelector)
Groups the items emitted by anObservableaccording to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items asGroupedObservables. The emittedGroupedObservableallows only a singleSubscriberduring its lifetime and if thisSubscriberunsubscribes before the source terminates, the next emission by the source having the same key will trigger a newGroupedObservableemission.
Note: A
GroupedObservablewill cache the items it is to emit until such time as it is subscribed to. For this reason, in order to avoid memory leaks, you should not simply ignore thoseGroupedObservables that do not concern you. Instead, you can signal to them that they may discard their buffers by applying an operator likeignoreElements()to them.- Backpressure:
- Both the returned and its inner
Observables honor backpressure and the sourceObservableis consumed in a bounded mode (i.e., requested a fixed amount upfront and replenished based on downstream consumption). Note that both the returned and its innerObservables use unbounded internal buffers and if the sourceObservabledoesn't honor backpressure, thatmay lead toOutOfMemoryError. - Scheduler:
groupBydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key typeR- the element type- Parameters:
keySelector- a function that extracts the key for each itemelementSelector- a function that extracts the return element for each item- Returns:
- an
Observablethat emitsGroupedObservables, each of which corresponds to a unique key value and each of which emits those items from the source Observable that share that key value - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: GroupBy
groupBy
@Deprecatedpublic final <K,R> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,R>> groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends R> elementSelector,Func1<Action1<K>,java.util.Map<K,java.lang.Object>> evictingMapFactory)
Deprecated. since 1.3.7, usegroupBy(Func1, Func1, int, boolean, Func1)instead which uses much less memory. Please take note of the usage difference involving the evicting action which now expects the value from the map instead of the key.Groups the items emitted by anObservableaccording to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items asGroupedObservables. The emittedGroupedObservableallows only a singleSubscriberduring its lifetime and if thisSubscriberunsubscribes before the source terminates, the next emission by the source having the same key will trigger a newGroupedObservableemission.
Note: A
GroupedObservablewill cache the items it is to emit until such time as it is subscribed to. For this reason, in order to avoid memory leaks, you should not simply ignore thoseGroupedObservables that do not concern you. Instead, you can signal to them that they may discard their buffers by applying an operator likeignoreElements()to them.- Backpressure:
- Both the returned and its inner
Observables honor backpressure and the sourceObservableis consumed in a bounded mode (i.e., requested a fixed amount upfront and replenished based on downstream consumption). Note that both the returned and its innerObservables use unbounded internal buffers and if the sourceObservabledoesn't honor backpressure, thatmay lead toOutOfMemoryError. - Scheduler:
groupBydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key typeR- the element type- Parameters:
keySelector- a function that extracts the key for each itemelementSelector- a function that extracts the return element for each itemevictingMapFactory- a function that given an eviction action returns aMapinstance that will be used to assign items to the appropriateGroupedObservables. TheMapinstance must be thread-safe and any eviction must trigger a call to the supplied action (synchronously or asynchronously). This can be used to limit the size of the map by evicting keys by maximum size or access time for instance. Here's an example using Guava'sCacheBuilderfrom v19.0:Func1<Action1<K>, Map<K, Object>> mapFactory = action -> CacheBuilder.newBuilder() .maximumSize(1000) .expireAfterAccess(12, TimeUnit.HOURS) .removalListener(notification -> action.call(notification.getKey())) .<K, Object> build().asMap();- Returns:
- an
Observablethat emitsGroupedObservables, each of which corresponds to a unique key value and each of which emits those items from the source Observable that share that key value - Throws:
java.lang.NullPointerException- ifevictingMapFactoryis null- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: GroupBy
groupBy
@Experimentalpublic final <K,R> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,R>> groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends R> elementSelector, int bufferSize, boolean delayError,Func1<Action1<java.lang.Object>,java.util.Map<K,java.lang.Object>> evictingMapFactory)
Groups the items emitted by anObservableaccording to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items asGroupedObservables. The emittedGroupedObservableallows only a singleSubscriberduring its lifetime and if thisSubscriberunsubscribes before the source terminates, the next emission by the source having the same key will trigger a newGroupedObservableemission.
Note: A
GroupedObservablewill cache the items it is to emit until such time as it is subscribed to. For this reason, in order to avoid memory leaks, you should not simply ignore thoseGroupedObservables that do not concern you. Instead, you can signal to them that they may discard their buffers by applying an operator likeignoreElements()to them.- Backpressure:
- Both the returned and its inner
Observables honor backpressure and the sourceObservableis consumed in a bounded mode (i.e., requested a fixed amount upfront and replenished based on downstream consumption). Note that both the returned and its innerObservables use unbounded internal buffers and if the sourceObservabledoesn't honor backpressure, thatmay lead toOutOfMemoryError. - Scheduler:
groupBydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key typeR- the element type- Parameters:
keySelector- a function that extracts the key for each itemelementSelector- a function that extracts the return element for each itembufferSize- the size of the buffer (RxRingBuffer.SIZEmay be suitable).delayError- if and only if false then onError emissions can shortcut onNext emissions (emissions may be buffered)evictingMapFactory- a function that given an eviction action returns aMapinstance that will be used to assign items to the appropriateGroupedObservables. TheMapinstance must be thread-safe and any eviction must trigger a call to the supplied action (synchronously or asynchronously). This can be used to limit the size of the map by evicting entries by map maximum size or access time for instance. Here's an example using Guava'sCacheBuilderfrom v24.0:Func1<Action1<Object>, Map<K, Object>> mapFactory = action -> CacheBuilder.newBuilder() .maximumSize(1000) .expireAfterAccess(12, TimeUnit.HOURS) .removalListener(entry -> action.call(entry.getValue())) .<K, Object> build().asMap();- Returns:
- an
Observablethat emitsGroupedObservables, each of which corresponds to a unique key value and each of which emits those items from the source Observable that share that key value - Throws:
java.lang.NullPointerException- ifevictingMapFactoryis null- Since:
- 1.3.7
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: GroupBy
groupBy
public final <K> Observable<GroupedObservable<K,T>> groupBy(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector)
Groups the items emitted by anObservableaccording to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items asGroupedObservables. The emittedGroupedObservableallows only a singleSubscriberduring its lifetime and if thisSubscriberunsubscribes before the source terminates, the next emission by the source having the same key will trigger a newGroupedObservableemission.
Note: A
GroupedObservablewill cache the items it is to emit until such time as it is subscribed to. For this reason, in order to avoid memory leaks, you should not simply ignore thoseGroupedObservables that do not concern you. Instead, you can signal to them that they may discard their buffers by applying an operator likeignoreElements()to them.- Scheduler:
groupBydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type- Parameters:
keySelector- a function that extracts the key for each item- Returns:
- an
Observablethat emitsGroupedObservables, each of which corresponds to a unique key value and each of which emits those items from the source Observable that share that key value - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: GroupBy
groupJoin
public final <T2,D1,D2,R> Observable<R> groupJoin(Observable<T2> right,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<D1>> leftDuration,Func1<? super T2,? extendsObservable<D2>> rightDuration,Func2<? superT,? superObservable<T2>,? extends R> resultSelector)
Returns an Observable that correlates two Observables when they overlap in time and groups the results.There are no guarantees in what order the items get combined when multiple items from one or both source Observables overlap.

- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't support backpressure and consumes all participating
Observables in an unbounded mode (i.e., not applying any backpressure to them). - Scheduler:
groupJoindoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T2- the value type of the right Observable sourceD1- the element type of the left duration ObservablesD2- the element type of the right duration ObservablesR- the result type- Parameters:
right- the other Observable to correlate items from the source Observable withleftDuration- a function that returns an Observable whose emissions indicate the duration of the values of the source ObservablerightDuration- a function that returns an Observable whose emissions indicate the duration of the values of therightObservableresultSelector- a function that takes an item emitted by each Observable and returns the value to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items based on combining those items emitted by the source Observables whose durations overlap
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Join
ignoreElements
public final Observable<T> ignoreElements()
Ignores all items emitted by the source Observable and only callsonCompletedoronError.
- Backpressure:
- This operator ignores backpressure as it doesn't emit any elements and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
ignoreElementsdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an empty Observable that only calls
onCompletedoronError, based on which one is called by the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: IgnoreElements
isEmpty
public final Observable<java.lang.Boolean> isEmpty()
Returns an Observable that emitstrueif the source Observable is empty, otherwisefalse.In Rx.Net this is negated as the
anyObserver but we renamed this in RxJava to better match Java naming idioms.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
isEmptydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a Boolean
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Contains
join
public final <TRight,TLeftDuration,TRightDuration,R> Observable<R> join(Observable<TRight> right,Func1<T,Observable<TLeftDuration>> leftDurationSelector,Func1<TRight,Observable<TRightDuration>> rightDurationSelector,Func2<T,TRight,R> resultSelector)
Correlates the items emitted by two Observables based on overlapping durations.There are no guarantees in what order the items get combined when multiple items from one or both source Observables overlap.

- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't support backpressure and consumes all participating
Observables in an unbounded mode (i.e., not applying any backpressure to them). - Scheduler:
joindoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
TRight- the value type of the right Observable sourceTLeftDuration- the element type of the left duration ObservablesTRightDuration- the element type of the right duration ObservablesR- the result type- Parameters:
right- the second Observable to join items fromleftDurationSelector- a function to select a duration for each item emitted by the source Observable, used to determine overlaprightDurationSelector- a function to select a duration for each item emitted by therightObservable, used to determine overlapresultSelector- a function that computes an item to be emitted by the resulting Observable for any two overlapping items emitted by the two Observables- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items correlating to items emitted by the source Observables that have overlapping durations
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Join
last
public final Observable<T> last()
Returns an Observable that emits the last item emitted by the source Observable or notifies observers of aNoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
lastdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the last item from the source Observable or notifies observers of an error
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Last
last
public final Observable<T> last(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a given condition, or notifies of aNoSuchElementExceptionif no such items are emitted.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
lastdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- the condition any source emitted item has to satisfy- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the last item satisfying the given condition from the source, or an
NoSuchElementExceptionif no such items are emitted - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if no items that match the predicate are emitted by the source Observable- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Last
lastOrDefault
public final Observable<T> lastOrDefault(T defaultValue)
Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable completes without emitting any items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
lastOrDefaultdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
defaultValue- the default item to emit if the source Observable is empty- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable is empty
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Last
lastOrDefault
public final Observable<T> lastOrDefault(T defaultValue,Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition, or a default item if no such item is emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
lastOrDefaultdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
defaultValue- the default item to emit if the source Observable doesn't emit anything that satisfies the specifiedpredicatepredicate- the condition any item emitted by the source Observable has to satisfy- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies the given condition, or a default item if no such item is emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Last
limit
public final Observable<T> limit(int count)
Returns an Observable that emits only the firstcountitems emitted by the source Observable.Alias of
take(int)to match Java 8 Stream API naming convention.
This method returns an Observable that will invoke a subscribing
Observer'sonNextfunction a maximum ofcounttimes before invokingonCompleted.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior in case the first request is smaller than thecount. Otherwise, the sourceObservableis consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
limitdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the first
countitems emitted by the source Observable, or all of the items from the source Observable if that Observable emits fewer thancountitems - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Take
map
public final <R> Observable<R> map(Func1<? superT,? extends R> func)
Returns an Observable that applies a specified function to each item emitted by the source Observable and emits the results of these function applications.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
mapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the output type- Parameters:
func- a function to apply to each item emitted by the Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable, transformed by the specified function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Map
materialize
public final Observable<Notification<T>> materialize()
Returns an Observable that represents all of the emissionsand notifications from the source Observable into emissions marked with their original types withinNotificationobjects.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and expects it from the source
Observable. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
materializedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the result of materializing the items and notifications of the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Materialize
mergeWith
public final Observable<T> mergeWith(Observable<? extendsT> t1)
Flattens this and another Observable into a single Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine items emitted by multiple Observables so that they appear as a single Observable, by using the
mergeWithmethod.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. This and the other
Observables are expected to honor backpressure; if violated, the operatormay signalMissingBackpressureException. - Scheduler:
mergeWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- an Observable to be merged- Returns:
- an Observable that emits all of the items emitted by the source Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Merge
observeOn
public final Observable<T> observeOn(Scheduler scheduler)
Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer ofRxRingBuffer.SIZEslots.Note that onError notifications will cut ahead of onNext notifications on the emission thread if Scheduler is truly asynchronous. If strict event ordering is required, consider using the
observeOn(Scheduler, boolean)overload.
- Backpressure:
- This operator honors backpressure from downstream and expects it from the source
Observable. Violating this expectation will lead toMissingBackpressureException. This is the most common operator where the exception pops up; look for sources up the chain that don't support backpressure, such asinterval,timer, {code PublishSubject} orBehaviorSubjectand apply any of theonBackpressureXXXoperatorsbefore applyingobserveOnitself. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto notifyObservers on- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that its
Observers are notified on the specifiedScheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: ObserveOn,RxJava Threading Examples,
subscribeOn(rx.Scheduler),observeOn(Scheduler, int),observeOn(Scheduler, boolean),observeOn(Scheduler, boolean, int)
observeOn
public final Observable<T> observeOn(Scheduler scheduler, int bufferSize)
Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer of configurable size.Note that onError notifications will cut ahead of onNext notifications on the emission thread if Scheduler is truly asynchronous. If strict event ordering is required, consider using the
observeOn(Scheduler, boolean)overload.
- Backpressure:
- This operator honors backpressure from downstream and expects it from the source
Observable. Violating this expectation will lead toMissingBackpressureException. This is the most common operator where the exception pops up; look for sources up the chain that don't support backpressure, such asinterval,timer, {code PublishSubject} orBehaviorSubjectand apply any of theonBackpressureXXXoperatorsbefore applyingobserveOnitself. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto notifyObservers onbufferSize- the size of the buffer.- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that its
Observers are notified on the specifiedScheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: ObserveOn,RxJava Threading Examples,
subscribeOn(rx.Scheduler),observeOn(Scheduler),observeOn(Scheduler, boolean),observeOn(Scheduler, boolean, int)
observeOn
public final Observable<T> observeOn(Scheduler scheduler, boolean delayError)
Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer and optionally delays onError notifications.
- Backpressure:
- This operator honors backpressure from downstream and expects it from the source
Observable. Violating this expectation will lead toMissingBackpressureException. This is the most common operator where the exception pops up; look for sources up the chain that don't support backpressure, such asinterval,timer, {code PublishSubject} orBehaviorSubjectand apply any of theonBackpressureXXXoperatorsbefore applyingobserveOnitself. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto notifyObservers ondelayError- indicates if the onError notification may not cut ahead of onNext notification on the other side of the scheduling boundary. If true a sequence ending in onError will be replayed in the same order as was received from upstream- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that its
Observers are notified on the specifiedScheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: ObserveOn,RxJava Threading Examples,
subscribeOn(rx.Scheduler),observeOn(Scheduler),observeOn(Scheduler, int),observeOn(Scheduler, boolean, int)
observeOn
public final Observable<T> observeOn(Scheduler scheduler, boolean delayError, int bufferSize)
Modifies an Observable to perform its emissions and notifications on a specifiedScheduler, asynchronously with a bounded buffer of configurable size and optionally delays onError notifications.
- Backpressure:
- This operator honors backpressure from downstream and expects it from the source
Observable. Violating this expectation will lead toMissingBackpressureException. This is the most common operator where the exception pops up; look for sources up the chain that don't support backpressure, such asinterval,timer, {code PublishSubject} orBehaviorSubjectand apply any of theonBackpressureXXXoperatorsbefore applyingobserveOnitself. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto notifyObservers ondelayError- indicates if the onError notification may not cut ahead of onNext notification on the other side of the scheduling boundary. If true a sequence ending in onError will be replayed in the same order as was received from upstreambufferSize- the size of the buffer.- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that its
Observers are notified on the specifiedScheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: ObserveOn,RxJava Threading Examples,
subscribeOn(rx.Scheduler),observeOn(Scheduler),observeOn(Scheduler, int),observeOn(Scheduler, boolean)
ofType
public final <R> Observable<R> ofType(java.lang.Class<R> klass)
Filters the items emitted by an Observable, only emitting those of the specified type.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
ofTypedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the output type- Parameters:
klass- the class type to filter the items emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items from the source Observable of type
klass - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Filter
onBackpressureBuffer
public final Observable<T> onBackpressureBuffer()
Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer these items indefinitely until they can be emitted.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., not applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
onBackpressureBufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- the source Observable modified to buffer items to the extent system resources allow
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: backpressure operators
onBackpressureBuffer
public final Observable<T> onBackpressureBuffer(long capacity)
Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer up to a given amount of items until they can be emitted. The resulting Observable willonErroremitting aBufferOverflowExceptionas soon as the buffer's capacity is exceeded, dropping all undelivered items, and unsubscribing from the source.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., not applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
onBackpressureBufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
capacity- number of slots available in the buffer.- Returns:
- the source
Observablemodified to buffer items up to the given capacity. - Since:
- 1.1.0
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: backpressure operators
onBackpressureBuffer
public final Observable<T> onBackpressureBuffer(long capacity,Action0 onOverflow)
Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer up to a given amount of items until they can be emitted. The resulting Observable willonErroremitting aBufferOverflowExceptionas soon as the buffer's capacity is exceeded, dropping all undelivered items, unsubscribing from the source, and notifying the producer withonOverflow.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., not applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
onBackpressureBufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
capacity- number of slots available in the buffer.onOverflow- action to execute if an item needs to be buffered, but there are no available slots. Null is allowed.- Returns:
- the source
Observablemodified to buffer items up to the given capacity - Since:
- 1.1.0
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: backpressure operators
onBackpressureBuffer
public final Observable<T> onBackpressureBuffer(long capacity,Action0 onOverflow,BackpressureOverflow.Strategy overflowStrategy)
Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to buffer up to a given amount of items until they can be emitted. The resulting Observable will behave as determined byoverflowStrategyif the buffer capacity is exceeded.BackpressureOverflow.Strategy.ON_OVERFLOW_ERROR(default) willonErrordropping all undelivered items, unsubscribing from the source, and notifying the producer withonOverflow.BackpressureOverflow.Strategy.ON_OVERFLOW_DROP_LATESTwill drop any new items emitted by the producer while the buffer is full, without generating anyonError. Each drop will however invokeonOverflowto signal the overflow to the producer. jBackpressureOverflow.Strategy.ON_OVERFLOW_DROP_OLDESTwill drop the oldest items in the buffer in order to make room for newly emitted ones. Overflow will not generate anonError, but each drop will invokeonOverflowto signal the overflow to the producer.

- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., not applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
onBackpressureBufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
capacity- number of slots available in the buffer.onOverflow- action to execute if an item needs to be buffered, but there are no available slots. Null is allowed.overflowStrategy- how should theObservablereact to buffer overflows. Null is not allowed.- Returns:
- the source
Observablemodified to buffer items up to the given capacity - Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: backpressure operators
onBackpressureDrop
public final Observable<T> onBackpressureDrop(Action1<? superT> onDrop)
Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to discard, rather than emit, those items that its observer is not prepared to observe.
If the downstream request count hits 0 then the Observable will refrain from calling
onNextuntil the observer invokesrequest(n)again to increase the request count.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., not applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
onBackpressureDropdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onDrop- the action to invoke for each item dropped. onDrop action should be fast and should never block.- Returns:
- the source Observable modified to drop
onNextnotifications on overflow - Since:
- 1.1.0
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: backpressure operators
onBackpressureDrop
public final Observable<T> onBackpressureDrop()
Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to discard, rather than emit, those items that its observer is not prepared to observe.
If the downstream request count hits 0 then the Observable will refrain from calling
onNextuntil the observer invokesrequest(n)again to increase the request count.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., not applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
onBackpressureDropdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- the source Observable modified to drop
onNextnotifications on overflow - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: backpressure operators
onBackpressureLatest
public final Observable<T> onBackpressureLatest()
Instructs an Observable that is emitting items faster than its observer can consume them to hold onto the latest value and emit that on request.
Its behavior is logically equivalent to
toBlocking().latest()with the exception that the downstream is not blocking while requesting more values.Note that if the upstream Observable does support backpressure, this operator ignores that capability and doesn't propagate any backpressure requests from downstream.
Note that due to the nature of how backpressure requests are propagated through subscribeOn/observeOn, requesting more than 1 from downstream doesn't guarantee a continuous delivery of onNext events.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., not applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
onBackpressureLatestdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that it emits the most recently-received item upon request
- Since:
- 1.1.0
onErrorResumeNext
public final Observable<T> onErrorResumeNext(Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsObservable<? extendsT>> resumeFunction)
Instructs an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters an error.
By default, when an Observable encounters an error that prevents it from emitting the expected item to its
Observer, the Observable invokes its Observer'sonErrormethod, and then quits without invoking any more of its Observer's methods. TheonErrorResumeNextmethod changes this behavior. If you pass a function that returns an Observable (resumeFunction) toonErrorResumeNext, if the original Observable encounters an error, instead of invoking its Observer'sonErrormethod, it will instead relinquish control to the Observable returned fromresumeFunction, which will invoke the Observer'sonNextmethod if it is able to do so. In such a case, because no Observable necessarily invokesonError, the Observer may never know that an error happened.You can use this to prevent errors from propagating or to supply fallback data should errors be encountered.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. This and the resuming
Observables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of them violate this expectation, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes or aMissingBackpressureExceptionis signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
onErrorResumeNextdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
resumeFunction- a function that returns an Observable that will take over if the source Observable encounters an error- Returns:
- the original Observable, with appropriately modified behavior
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Catch
onErrorResumeNext
public final Observable<T> onErrorResumeNext(Observable<? extendsT> resumeSequence)
Instructs an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters an error.
By default, when an Observable encounters an error that prevents it from emitting the expected item to its
Observer, the Observable invokes its Observer'sonErrormethod, and then quits without invoking any more of its Observer's methods. TheonErrorResumeNextmethod changes this behavior. If you pass another Observable (resumeSequence) to an Observable'sonErrorResumeNextmethod, if the original Observable encounters an error, instead of invoking its Observer'sonErrormethod, it will instead relinquish control toresumeSequencewhich will invoke the Observer'sonNextmethod if it is able to do so. In such a case, because no Observable necessarily invokesonError, the Observer may never know that an error happened.You can use this to prevent errors from propagating or to supply fallback data should errors be encountered.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. This and the resuming
Observables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of them violate this expectation, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes orMissingBackpressureExceptionis signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
onErrorResumeNextdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
resumeSequence- a function that returns an Observable that will take over if the source Observable encounters an error- Returns:
- the original Observable, with appropriately modified behavior
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Catch
onErrorReturn
public final Observable<T> onErrorReturn(Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable,? extendsT> resumeFunction)
Instructs an Observable to emit an item (returned by a specified function) rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters an error.
By default, when an Observable encounters an error that prevents it from emitting the expected item to its
Observer, the Observable invokes its Observer'sonErrormethod, and then quits without invoking any more of its Observer's methods. TheonErrorReturnmethod changes this behavior. If you pass a function (resumeFunction) to an Observable'sonErrorReturnmethod, if the original Observable encounters an error, instead of invoking its Observer'sonErrormethod, it will instead emit the return value ofresumeFunction.You can use this to prevent errors from propagating or to supply fallback data should errors be encountered.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observables is expected to honor backpressure as well. If it this expectation is violated, the operatormay throwIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes orMissingBackpressureExceptionis signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
onErrorReturndoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
resumeFunction- a function that returns an item that the new Observable will emit if the source Observable encounters an error- Returns:
- the original Observable with appropriately modified behavior
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Catch
onExceptionResumeNext
public final Observable<T> onExceptionResumeNext(Observable<? extendsT> resumeSequence)
Instructs an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invokingonErrorif it encounters anException.This differs from
onErrorResumeNext(rx.functions.Func1<? super java.lang.Throwable, ? extends rx.Observable<? extends T>>)in that this one does not handleThrowableorErrorbut lets those continue through.
By default, when an Observable encounters an exception that prevents it from emitting the expected item to its
Observer, the Observable invokes its Observer'sonErrormethod, and then quits without invoking any more of its Observer's methods. TheonExceptionResumeNextmethod changes this behavior. If you pass another Observable (resumeSequence) to an Observable'sonExceptionResumeNextmethod, if the original Observable encounters an exception, instead of invoking its Observer'sonErrormethod, it will instead relinquish control toresumeSequencewhich will invoke the Observer'sonNextmethod if it is able to do so. In such a case, because no Observable necessarily invokesonError, the Observer may never know that an exception happened.You can use this to prevent exceptions from propagating or to supply fallback data should exceptions be encountered.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. This and the resuming
Observables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of them violate this expectation, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes orMissingBackpressureExceptionis signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
onExceptionResumeNextdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
resumeSequence- a function that returns an Observable that will take over if the source Observable encounters an exception- Returns:
- the original Observable, with appropriately modified behavior
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Catch
onTerminateDetach
public final Observable<T> onTerminateDetach()
Nulls out references to the upstream producer and downstream Subscriber if the sequence is terminated or downstream unsubscribes.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
onTerminateDetachdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable which out references to the upstream producer and downstream Subscriber if the sequence is terminated or downstream unsubscribes
- Since:
- 1.3
publish
public final ConnectableObservable<T> publish()
Returns aConnectableObservable, which is a variety of Observable that waits until itsconnectmethod is called before it begins emitting items to thoseObservers that have subscribed to it.
- Backpressure:
- The returned
ConnectableObservablehonors backpressure for each of itsSubscribers and expects the sourceObservableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureExceptionto itsSubscribers and disconnect. - Scheduler:
publishdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat upon connection causes the source Observable to emit items to itsObservers - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Publish
publish
public final <R> Observable<R> publish(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector)
Returns an Observable that emits the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the underlying sequence.
- Backpressure:
- The operator expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure and if this expectation is violated, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureExceptionthrough theObservableprovided to the function. Since theObservablereturned by theselectormay be independent from the providedObservableto the function, the output's backpressure behavior is determined by this returnedObservable. - Scheduler:
publishdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- a function that can use the multicasted source sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the source sequence. Subscribers to the given source will receive all notifications of the source from the time of the subscription forward.- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of invoking the selector on the items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the underlying sequence - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Publish
rebatchRequests
public final Observable<T> rebatchRequests(int n)
Requestsninitially from the upstream and then 75% ofnsubsequently after 75% ofnvalues have been emitted to the downstream.This operator allows preventing the downstream to trigger unbounded mode via
request(Long.MAX_VALUE)or compensate for the per-item overhead of small and frequent requests.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from upstream and honors backpressure from downstream.
- Scheduler:
rebatchRequestsdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
n- the initial request amount, further request will happen after 75% of this value- Returns:
- the Observable that rebatches request amounts from downstream
- Since:
- 1.3
reduce
public final Observable<T> reduce(Func2<T,T,T> accumulator)
Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, and emits the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.
This technique, which is called "reduce" here, is sometimes called "aggregate," "fold," "accumulate," "compress," or "inject" in other programming contexts. Groovy, for instance, has an
injectmethod that does a similar operation on lists.- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure of its downstream consumer and consumes the upstream source in unbounded mode.
- Scheduler:
reducedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
accumulator- an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, whose result will be used in the next accumulator call- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item that is the result of accumulating the items emitted by the source Observable
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if the source Observable emits no items- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Reduce,Wikipedia: Fold (higher-order function)
reduce
public final <R> Observable<R> reduce(R initialValue,Func2<R,? superT,R> accumulator)
Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable and a specified seed value, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.
This technique, which is called "reduce" here, is sometimes called "aggregate," "fold," "accumulate," "compress," or "inject" in other programming contexts. Groovy, for instance, has an
injectmethod that does a similar operation on lists.Note that the
initialValueis shared among all subscribers to the resulting Observable and may cause problems if it is mutable. To make sure each subscriber gets its own value, defer the application of this operator viadefer(Func0):Observable<T> source = ... Observable.defer(() -> source.reduce(new ArrayList<>(), (list, item) -> list.add(item))); // alternatively, by using compose to stay fluent source.compose(o -> Observable.defer(() -> o.reduce(new ArrayList<>(), (list, item) -> list.add(item))) );- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure of its downstream consumer and consumes the upstream source in unbounded mode.
- Scheduler:
reducedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the accumulator and output value type- Parameters:
initialValue- the initial (seed) accumulator valueaccumulator- an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, the result of which will be used in the next accumulator call- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item that is the result of accumulating the output from the items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Reduce,Wikipedia: Fold (higher-order function)
repeat
public final Observable<T> repeat()
Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable indefinitely.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
repeatoperates by default on thetrampolineScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable repeatedly and in sequence
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Repeat
repeat
public final Observable<T> repeat(Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable indefinitely, on a particular Scheduler.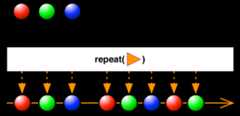
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- the Scheduler to emit the items on- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable repeatedly and in sequence
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Repeat
repeat
public final Observable<T> repeat(long count)
Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at mostcounttimes.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
repeatoperates by default on thetrampolineScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the number of times the source Observable items are repeated, a count of 0 will yield an empty sequence- Returns:
- an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at most
counttimes - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifcountis less than zero- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Repeat
repeat
public final Observable<T> repeat(long count,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at mostcounttimes, on a particular Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
count- the number of times the source Observable items are repeated, a count of 0 will yield an empty sequencescheduler- theSchedulerto emit the items on- Returns:
- an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at most
counttimes on a particular Scheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Repeat
repeatWhen
public final Observable<T> repeatWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Void>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source Observable with the exception of anonCompleted. AnonCompletednotification from the source will result in the emission of avoiditem to the Observable provided as an argument to thenotificationHandlerfunction. If that Observable callsonCompleteoronErrorthenrepeatWhenwill callonCompletedoronErroron the child subscription. Otherwise, this Observable will resubscribe to the source Observable, on a particular Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
notificationHandler- receives an Observable of notifications with which a user can complete or error, aborting the repeat.scheduler- theSchedulerto emit the items on- Returns:
- the source Observable modified with repeat logic
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Repeat
repeatWhen
public final Observable<T> repeatWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Void>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler)
Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source Observable with the exception of anonCompleted. AnonCompletednotification from the source will result in the emission of avoiditem to the Observable provided as an argument to thenotificationHandlerfunction. If that Observable callsonCompleteoronErrorthenrepeatWhenwill callonCompletedoronErroron the child subscription. Otherwise, this Observable will resubscribe to the source observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
repeatWhenoperates by default on thetrampolineScheduler.
- Parameters:
notificationHandler- receives an Observable of notifications with which a user can complete or error, aborting the repeat.- Returns:
- the source Observable modified with repeat logic
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Repeat
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay()
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the underlying Observable that will replay all of its items and notifications to any futureObserver. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replaydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat upon connection causes the source Observable to emit its items to itsObservers - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on the items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replaydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- the selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replayingbufferSizenotifications.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replaydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- the selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the ObservablebufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items the connectable observable can replay- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable replaying no more thanbufferSizeitems - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying no more thanbufferSizeitems that were emitted within a specified time window.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replayoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- a selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the ObservablebufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items the connectable observable can replaytime- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, and replays no more thanbufferSizeitems that were emitted within the window defined bytime - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying no more thanbufferSizeitems that were emitted within a specified time window.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- a selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the ObservablebufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items the connectable observable can replaytime- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the Scheduler that is the time source for the window- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, and replays no more thanbufferSizeitems that were emitted within the window defined bytime - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifbufferSizeis less than zero- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, int bufferSize,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying a maximum ofbufferSizeitems.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- a selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the ObservablebufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items the connectable observable can replayscheduler- the Scheduler on which the replay is observed- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying no more thanbufferSizenotifications - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying all items that were emitted within a specified time window.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replayoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- a selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the Observabletime- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying all items that were emitted within the window defined bytime - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying all items that were emitted within a specified time window.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- a selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the Observabletime- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the scheduler that is the time source for the window- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying all items that were emitted within the window defined bytime - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final <R> Observable<R> replay(Func1<? superObservable<T>,? extendsObservable<R>> selector,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking a specified selector on items emitted by aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Type Parameters:
R- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
selector- a selector function, which can use the multicasted sequence as many times as needed, without causing multiple subscriptions to the Observablescheduler- the Scheduler where the replay is observed- Returns:
- an Observable that emits items that are the results of invoking the selector on items emitted by a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable, replaying all items - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay(int bufferSize)
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable that replays at mostbufferSizeitems emitted by that Observable. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replaydoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
bufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items that can be replayed- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems emitted by that Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay(int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems that were emitted during a specified time window. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replayoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
bufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items that can be replayedtime- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems that were emitted during the window defined bytime - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay(int bufferSize, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and that replays a maximum ofbufferSizeitems that are emitted within a specified time window. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
bufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items that can be replayedtime- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the scheduler that is used as a time source for the window- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems that were emitted during the window defined bytime - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifbufferSizeis less than zero- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay(int bufferSize,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems emitted by that Observable. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
bufferSize- the buffer size that limits the number of items that can be replayedscheduler- the scheduler on which the Observers will observe the emitted items- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays at mostbufferSizeitems that were emitted by the Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays all items emitted by that Observable within a specified time window. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- This version of
replayoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
time- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays the items that were emitted during the window defined bytime - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays all items emitted by that Observable within a specified time window. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
time- the duration of the window in which the replayed items must have been emittedunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the Scheduler that is the time source for the window- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable and replays the items that were emitted during the window defined bytime - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
replay
public final ConnectableObservable<T> replay(Scheduler scheduler)
Returns aConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable that will replay all of its items and notifications to any futureObserveron the givenScheduler. A Connectable Observable resembles an ordinary Observable, except that it does not begin emitting items when it is subscribed to, but only when itsconnectmethod is called.
- Backpressure:
- This operator supports backpressure. Note that the upstream requests are determined by the child Subscriber which requests the largest amount: i.e., two child Subscribers with requests of 10 and 100 will request 100 elements from the underlying Observable sequence.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- the Scheduler on which the Observers will observe the emitted items- Returns:
- a
ConnectableObservablethat shares a single subscription to the source Observable that will replay all of its items and notifications to any futureObserveron the givenScheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Replay
retry
public final Observable<T> retry()
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, resubscribing to it if it callsonError(infinite retry count).
If the source Observable calls
Observer.onError(java.lang.Throwable), this method will resubscribe to the source Observable rather than propagating theonErrorcall.Any and all items emitted by the source Observable will be emitted by the resulting Observable, even those emitted during failed subscriptions. For example, if an Observable fails at first but emits
[1, 2]then succeeds the second time and emits[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]then the complete sequence of emissions and notifications would be[1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, onCompleted].- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
retryoperates by default on thetrampolineScheduler.
- Returns:
- the source Observable modified with retry logic
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Retry
retry
public final Observable<T> retry(long count)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, resubscribing to it if it callsonErrorup to a specified number of retries.
If the source Observable calls
Observer.onError(java.lang.Throwable), this method will resubscribe to the source Observable for a maximum ofcountresubscriptions rather than propagating theonErrorcall.Any and all items emitted by the source Observable will be emitted by the resulting Observable, even those emitted during failed subscriptions. For example, if an Observable fails at first but emits
[1, 2]then succeeds the second time and emits[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]then the complete sequence of emissions and notifications would be[1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, onCompleted].- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
retryoperates by default on thetrampolineScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- number of retry attempts before failing- Returns:
- the source Observable modified with retry logic
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Retry
retry
public final Observable<T> retry(Func2<java.lang.Integer,java.lang.Throwable,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, resubscribing to it if it callsonErrorand the predicate returns true for that specific exception and retry count.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
retryoperates by default on thetrampolineScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- the predicate that determines if a resubscription may happen in case of a specific exception and retry count- Returns:
- the source Observable modified with retry logic
- See Also:
retry(),ReactiveX operators documentation: Retry
retryWhen
public final Observable<T> retryWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Throwable>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler)
Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source observable with the exception of anonError. AnonErrornotification from the source will result in the emission of aThrowableitem to the Observable provided as an argument to thenotificationHandlerfunction. If that Observable callsonCompleteoronErrorthenretrywill callonCompletedoronErroron the child subscription. Otherwise, this Observable will resubscribe to the source Observable. Example: This retries 3 times, each time incrementing the number of seconds it waits.
Example: This retries 3 times, each time incrementing the number of seconds it waits.
Output is:Observable.create((Subscriber s) -> { System.out.println("subscribing"); s.onError(new RuntimeException("always fails")); }).retryWhen(attempts -> { return attempts.zipWith(Observable.range(1, 3), (n, i) -> i).flatMap(i -> { System.out.println("delay retry by " + i + " second(s)"); return Observable.timer(i, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }); }).toBlocking().forEach(System.out::println);subscribing delay retry by 1 second(s) subscribing delay retry by 2 second(s) subscribing delay retry by 3 second(s) subscribing- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
retryWhenoperates by default on thetrampolineScheduler.
- Parameters:
notificationHandler- receives an Observable of notifications with which a user can complete or error, aborting the retry- Returns:
- the source Observable modified with retry logic
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Retry
retryWhen
public final Observable<T> retryWhen(Func1<? superObservable<? extends java.lang.Throwable>,? extendsObservable<?>> notificationHandler,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source observable with the exception of anonError. AnonErrorwill cause the emission of theThrowablethat cause the error to the Observable returned fromnotificationHandler. If that Observable callsonCompleteoronErrorthenretrywill callonCompletedoronErroron the child subscription. Otherwise, this Observable will resubscribe to the source observable, on a particular Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operatormay throw anIllegalStateException. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
notificationHandler- receives an Observable of notifications with which a user can complete or error, aborting the retryscheduler- theScheduleron which to subscribe to the source Observable- Returns:
- the source Observable modified with retry logic
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Retry
sample
public final Observable<T> sample(long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits the most recently emitted item (if any) emitted by the source Observable within periodic time intervals.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
sampleoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
period- the sampling rateunit- theTimeUnitin whichperiodis defined- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at the specified time interval
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Sample,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
throttleLast(long, TimeUnit)
sample
public final Observable<T> sample(long period, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits the most recently emitted item (if any) emitted by the source Observable within periodic time intervals, where the intervals are defined on a particular Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
period- the sampling rateunit- theTimeUnitin whichperiodis definedscheduler- theSchedulerto use when sampling- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at the specified time interval
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Sample,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
throttleLast(long, TimeUnit, Scheduler)
sample
public final <U> Observable<T> sample(Observable<U> sampler)
Returns an Observable that, when the specifiedsamplerObservable emits an item or completes, emits the most recently emitted item (if any) emitted by the source Observable since the previous emission from thesamplerObservable.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses the emissions of the
samplerObservable to control data flow. - Scheduler:
- This version of
sampledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the element type of the sampler Observable- Parameters:
sampler- the Observable to use for sampling the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by this Observable whenever the
samplerObservable emits an item or completes - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Sample,RxJava wiki: Backpressure
scan
public final Observable<T> scan(Func2<T,T,T> accumulator)
Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.
This sort of function is sometimes called an accumulator.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. Violating this expectation, aMissingBackpressureExceptionmay get signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
scandoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
accumulator- an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, whose result will be emitted toObservers viaonNextand used in the next accumulator call- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the results of each call to the accumulator function
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Scan
scan
public final <R> Observable<R> scan(R initialValue,Func2<R,? superT,R> accumulator)
Returns an Observable that applies a specified accumulator function to the first item emitted by a source Observable and a seed value, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.
This sort of function is sometimes called an accumulator.
Note that the Observable that results from this method will emit
initialValueas its first emitted item.Note that the
initialValueis shared among all subscribers to the resulting Observable and may cause problems if it is mutable. To make sure each subscriber gets its own value, defer the application of this operator viadefer(Func0):Observable<T> source = ... Observable.defer(() -> source.scan(new ArrayList<>(), (list, item) -> list.add(item))); // alternatively, by using compose to stay fluent source.compose(o -> Observable.defer(() -> o.scan(new ArrayList<>(), (list, item) -> list.add(item))) );- Backpressure:
- The operator honors downstream backpressure and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. Violating this expectation, aMissingBackpressureExceptionmay get signalled somewhere downstream. - Scheduler:
scandoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the initial, accumulator and result type- Parameters:
initialValue- the initial (seed) accumulator itemaccumulator- an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, whose result will be emitted toObservers viaonNextand used in the next accumulator call- Returns:
- an Observable that emits
initialValuefollowed by the results of each call to the accumulator function - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Scan
serialize
public final Observable<T> serialize()
Forces an Observable's emissions and notifications to be serialized and for it to obeythe Observable contract in other ways.It is possible for an Observable to invoke its Subscribers' methods asynchronously, perhaps from different threads. This could make such an Observable poorly-behaved, in that it might try to invoke
onCompletedoronErrorbefore one of itsonNextinvocations, or it might callonNextfrom two different threads concurrently. You can force such an Observable to be well-behaved and sequential by applying theserializemethod to it.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
serializedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an
Observablethat is guaranteed to be well-behaved and to make only serialized calls to its observers - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Serialize
share
public final Observable<T> share()
Returns a newObservablethat multicasts (shares) the originalObservable. As long as there is at least oneSubscriberthisObservablewill be subscribed and emitting data. When all subscribers have unsubscribed it will unsubscribe from the sourceObservable.This is an alias for
publish().ConnectableObservable.refCount().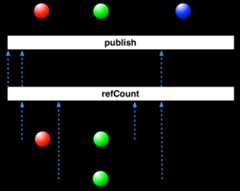
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure and and expects the source
Observableto honor backpressure as well. If this expectation is violated, the operator will signal aMissingBackpressureExceptionto itsSubscribers. - Scheduler:
sharedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an
Observablethat upon connection causes the sourceObservableto emit items to itsObservers - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: RefCount
single
public final Observable<T> single()
Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable, if that Observable emits only a single item. If the source Observable emits more than one item or no items, notify of anIllegalArgumentExceptionorNoSuchElementExceptionrespectively.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
singledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if the source emits more than one itemjava.util.NoSuchElementException- if the source emits no items- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
single
public final Observable<T> single(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable that matches a specified predicate, if that Observable emits one such item. If the source Observable emits more than one such item or no such items, notify of anIllegalArgumentExceptionorNoSuchElementExceptionrespectively.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
singledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- a predicate function to evaluate items emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable that matches the predicate
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if the source Observable emits more than one item that matches the predicatejava.util.NoSuchElementException- if the source Observable emits no item that matches the predicate- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
singleOrDefault
public final Observable<T> singleOrDefault(T defaultValue)
Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable, if that Observable emits only a single item, or a default item if the source Observable emits no items. If the source Observable emits more than one item, throw anIllegalArgumentException.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
singleOrDefaultdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
defaultValue- a default value to emit if the source Observable emits no item- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable is empty
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if the source Observable emits more than one item- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
singleOrDefault
public final Observable<T> singleOrDefault(T defaultValue,Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable that matches a predicate, if that Observable emits only one such item, or a default item if the source Observable emits no such items. If the source Observable emits more than one such item, throw anIllegalArgumentException.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure). - Scheduler:
singleOrDefaultdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
defaultValue- a default item to emit if the source Observable emits no matching itemspredicate- a predicate function to evaluate items emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable that matches the predicate, or the default item if no emitted item matches the predicate
- Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if the source Observable emits more than one item that matches the predicate- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
skip
public final Observable<T> skip(int count)
Returns an Observable that skips the firstcountitems emitted by the source Observable and emits the remainder.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- This version of
skipdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the number of items to skip- Returns:
- an Observable that is identical to the source Observable except that it does not emit the first
countitems that the source Observable emits - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Skip
skip
public final Observable<T> skip(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that skips values emitted by the source Observable before a specified time window elapses.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't support backpressure as it uses time to skip arbitrary number of elements and thus has to consume the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
- This version of
skipoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time window to skipunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that skips values emitted by the source Observable before the time window defined by
timeelapses and the emits the remainder - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Skip
skip
public final Observable<T> skip(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that skips values emitted by the source Observable before a specified time window on a specifiedSchedulerelapses.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't support backpressure as it uses time to skip arbitrary number of elements and thus has to consume the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time window to skipunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- theScheduleron which the timed wait happens- Returns:
- an Observable that skips values emitted by the source Observable before the time window defined by
timeandschedulerelapses, and then emits the remainder - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Skip
skipLast
public final Observable<T> skipLast(int count)
Returns an Observable that drops a specified number of items from the end of the sequence emitted by the source Observable.
This Observer accumulates a queue long enough to store the first
countitems. As more items are received, items are taken from the front of the queue and emitted by the returned Observable. This causes such items to be delayed.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- This version of
skipLastdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- number of items to drop from the end of the source sequence- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable except for the dropped ones at the end
- Throws:
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifcountis less than zero- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SkipLast
skipLast
public final Observable<T> skipLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that drops items emitted by the source Observable during a specified time window before the source completes.
Note: this action will cache the latest items arriving in the specified time window.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't support backpressure as it uses time to skip arbitrary number of elements and thus has to consume the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
- This version of
skipLastoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that drops those items emitted by the source Observable in a time window before the source completes defined by
time - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SkipLast
skipLast
public final Observable<T> skipLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that drops items emitted by the source Observable during a specified time window (defined on a specified scheduler) before the source completes.
Note: this action will cache the latest items arriving in the specified time window.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't support backpressure as it uses time to skip arbitrary number of elements and thus has to consume the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure applied to it). - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the scheduler used as the time source- Returns:
- an Observable that drops those items emitted by the source Observable in a time window before the source completes defined by
timeandscheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SkipLast
skipUntil
public final <U> Observable<T> skipUntil(Observable<U> other)
Returns an Observable that skips items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
skipUntildoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the element type of the other Observable- Parameters:
other- the second Observable that has to emit an item before the source Observable's elements begin to be mirrored by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that skips items from the source Observable until the second Observable emits an item, then emits the remaining items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SkipUntil
skipWhile
public final Observable<T> skipWhile(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that skips all items emitted by the source Observable as long as a specified condition holds true, but emits all further source items as soon as the condition becomes false.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
skipWhiledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- a function to test each item emitted from the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that begins emitting items emitted by the source Observable when the specified predicate becomes false
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SkipWhile
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(Observable<T> values)
Returns an Observable that emits the items in a specifiedObservablebefore it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both this and the
otherObservables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of then violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
values- an Observable that contains the items you want the modified Observable to emit first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items in the specified
Observableand then emits the items emitted by the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(java.lang.Iterable<T> values)
Returns an Observable that emits the items in a specifiedIterablebefore it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
values- an Iterable that contains the items you want the modified Observable to emit first- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items in the specified
Iterableand then emits the items emitted by the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1)
Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emitt3- the third item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emitt3- the third item to emitt4- the fourth item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emitt3- the third item to emitt4- the fourth item to emitt5- the fifth item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emitt3- the third item to emitt4- the fourth item to emitt5- the fifth item to emitt6- the sixth item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6,T t7)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emitt3- the third item to emitt4- the fourth item to emitt5- the fifth item to emitt6- the sixth item to emitt7- the seventh item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6,T t7,T t8)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emitt3- the third item to emitt4- the fourth item to emitt5- the fifth item to emitt6- the sixth item to emitt7- the seventh item to emitt8- the eighth item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
startWith
public final Observable<T> startWith(T t1,T t2,T t3,T t4,T t5,T t6,T t7,T t8,T t9)
Returns an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The source
Observableis expected to honor backpressure as well. If it violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
startWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
t1- the first item to emitt2- the second item to emitt3- the third item to emitt4- the fourth item to emitt5- the fifth item to emitt6- the sixth item to emitt7- the seventh item to emitt8- the eighth item to emitt9- the ninth item to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the specified items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: StartWith
subscribe
public final Subscription subscribe()
Subscribes to an Observable and ignoresonNextandonCompletedemissions. If anonErroremission arrives thenOnErrorNotImplementedExceptionis thrown.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
subscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- a
Subscriptionreference with which theObservercan stop receiving items before the Observable has finished sending them - Throws:
OnErrorNotImplementedException- if the Observable tries to callonError- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
subscribe
public final Subscription subscribe(Action1<? superT> onNext)
Subscribes to an Observable and provides a callback to handle the items it emits.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
subscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNext- theAction1<T>you have designed to accept emissions from the Observable- Returns:
- a
Subscriptionreference with which theObservercan stop receiving items before the Observable has finished sending them - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifonNextis nullOnErrorNotImplementedException- if the Observable callsonError- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
subscribe
public final Subscription subscribe(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError)
Subscribes to an Observable and provides callbacks to handle the items it emits and any error notification it issues.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
subscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNext- theAction1<T>you have designed to accept emissions from the ObservableonError- theAction1<Throwable>you have designed to accept any error notification from the Observable- Returns:
- a
Subscriptionreference with which theObservercan stop receiving items before the Observable has finished sending them - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifonNextis null, or ifonErroris null- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
subscribe
public final Subscription subscribe(Action1<? superT> onNext,Action1<java.lang.Throwable> onError,Action0 onCompleted)
Subscribes to an Observable and provides callbacks to handle the items it emits and any error or completion notification it issues.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
subscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
onNext- theAction1<T>you have designed to accept emissions from the ObservableonError- theAction1<Throwable>you have designed to accept any error notification from the ObservableonCompleted- theAction0you have designed to accept a completion notification from the Observable- Returns:
- a
Subscriptionreference with which theObservercan stop receiving items before the Observable has finished sending them - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- ifonNextis null, or ifonErroris null, or ifonCompleteis null- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
subscribe
public final Subscription subscribe(Observer<? superT> observer)
Subscribes to an Observable and provides an Observer that implements functions to handle the items the Observable emits and any error or completion notification it issues.- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
subscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
observer- the Observer that will handle emissions and notifications from the Observable- Returns:
- a
Subscriptionreference with which theObservercan stop receiving items before the Observable has completed - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
unsafeSubscribe
public final Subscription unsafeSubscribe(Subscriber<? superT> subscriber)
Subscribes to an Observable and invokesObservable.OnSubscribefunction without any contract protection, error handling, unsubscribe, or execution hooks.Use this only for implementing an
Observable.Operatorthat requires nested subscriptions. For other purposes, usesubscribe(Subscriber)which ensuresthe Observable contract and other functionality.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
unsafeSubscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
subscriber- the Subscriber that will handle emissions and notifications from the Observable- Returns:
- a
Subscriptionreference with which theSubscribercan stop receiving items before the Observable has completed
subscribe
public final Subscription subscribe(Subscriber<? superT> subscriber)
Subscribes to an Observable and provides a Subscriber that implements functions to handle the items the Observable emits and any error or completion notification it issues.A typical implementation of
subscribedoes the following:- It stores a reference to the Subscriber in a collection object, such as a
List<T>object. - It returns a reference to the
Subscriptioninterface. This enables Subscribers to unsubscribe, that is, to stop receiving items and notifications before the Observable completes, which also invokes the Subscriber'sonCompletedmethod.
An
Observable<T>instance is responsible for accepting all subscriptions and notifying all Subscribers. Unless the documentation for a particularObservable<T>implementation indicates otherwise, Subscriber should make no assumptions about the order in which multiple Subscribers will receive their notifications.For more information see theReactiveX documentation.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
subscribedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
subscriber- theSubscriberthat will handle emissions and notifications from the Observable- Returns:
- a
Subscriptionreference with which Subscribers that areObservers can unsubscribe from the Observable - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalStateException- ifsubscribeis unable to obtain anOnSubscribe<>functionjava.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if theSubscriberprovided as the argument tosubscribeisnullOnErrorNotImplementedException- if theSubscriber'sonErrormethod is nulljava.lang.RuntimeException- if theSubscriber'sonErrormethod itself threw aThrowable- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Subscribe
- It stores a reference to the Subscriber in a collection object, such as a
subscribeOn
public final Observable<T> subscribeOn(Scheduler scheduler)
Asynchronously subscribes Observers to this Observable on the specifiedScheduler.If there is a
create(Action1, rx.Emitter.BackpressureMode)type source up in the chain, it is recommended to usesubscribeOn(scheduler, false)instead to avoid same-pool deadlock because requests pile up behind a eager/blocking emitter.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure amount which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. However, the upstream is requested from the given scheduler thread. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto perform subscription actions on- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that its subscriptions happen on the specified
Scheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SubscribeOn,RxJava Threading Examples,
observeOn(rx.Scheduler),subscribeOn(Scheduler, boolean)
subscribeOn
public final Observable<T> subscribeOn(Scheduler scheduler, boolean requestOn)
Asynchronously subscribes Observers to this Observable on the specifiedSchedulerand optionally reroutes requests from other threads to the sameSchedulerthread.If there is a
create(Action1, rx.Emitter.BackpressureMode)type source up in the chain, it is recommended to haverequestOnfalse to avoid same-pool deadlock because requests pile up behind a eager/blocking emitter.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure amount which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. However, the upstream is requested from the given scheduler if requestOn is true. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
History: 1.2.7 - experimental
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto perform subscription actions onrequestOn- if true, requests are rerouted to the given Scheduler as well (strong pipelining) if false, requests coming from any thread are simply forwarded to the upstream on the same thread (weak pipelining)- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that its subscriptions happen on the specified
Scheduler - Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SubscribeOn,RxJava Threading Examples,
observeOn(rx.Scheduler),subscribeOn(Scheduler)
switchMap
public final <R> Observable<R> switchMap(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)
Returns a new Observable by applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable that returns an Observable, and then emitting the items emitted by the most recently emitted of these Observables.The resulting Observable completes if both the upstream Observable and the last inner Observable, if any, complete. If the upstream Observable signals an onError, the inner Observable is unsubscribed and the error delivered in-sequence.

- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., without backpressure) and the innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure but it is not enforced; the operator won't signal aMissingBackpressureExceptionbut the violationmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
switchMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the element type of the inner Observables and the output- Parameters:
func- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the Observable returned from applying
functo the most recently emitted item emitted by the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
switchMapDelayError
public final <R> Observable<R> switchMapDelayError(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<? extends R>> func)
Returns a new Observable by applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable that returns an Observable, and then emitting the items emitted by the most recently emitted of these Observables and delays any error until all Observables terminate.The resulting Observable completes if both the upstream Observable and the last inner Observable, if any, complete. If the upstream Observable signals an onError, the termination of the last inner Observable will emit that error as is or wrapped into a CompositeException along with the other possible errors the former inner Observables signalled.

- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The outer
Observableis consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., without backpressure) and the innerObservables are expected to honor backpressure but it is not enforced; the operator won't signal aMissingBackpressureExceptionbut the violationmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. - Scheduler:
switchMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the element type of the inner Observables and the output- Parameters:
func- a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the Observable returned from applying
functo the most recently emitted item emitted by the source Observable - Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: FlatMap
take
public final Observable<T> take(int count)
Returns an Observable that emits only the firstcountitems emitted by the source Observable. If the source emits fewer thancountitems then all of its items are emitted.
This method returns an Observable that will invoke a subscribing
Observer'sonNextfunction a maximum ofcounttimes before invokingonCompleted.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior in case the first request is smaller than thecount. Otherwise, the sourceObservableis consumed in an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
- This version of
takedoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emit- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the first
countitems emitted by the source Observable, or all of the items from the source Observable if that Observable emits fewer thancountitems - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Take
take
public final Observable<T> take(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits those items emitted by source Observable before a specified time runs out.If time runs out before the
Observablecompletes normally, theonCompleteevent will be signaled on the defaultcomputationScheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- This version of
takeoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that emits those items emitted by the source Observable before the time runs out
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Take
take
public final Observable<T> take(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits those items emitted by source Observable before a specified time (on a specified Scheduler) runs out.If time runs out before the
Observablecompletes normally, theonCompleteevent will be signaled on the providedScheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the Scheduler used for time source- Returns:
- an Observable that emits those items emitted by the source Observable before the time runs out, according to the specified Scheduler
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Take
takeFirst
public final Observable<T> takeFirst(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies a specified condition.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
takeFirstdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- the condition any item emitted by the source Observable has to satisfy- Returns:
- an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies the given condition, or that completes without emitting anything if the source Observable completes without emitting a single condition-satisfying item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: First
takeLast
public final Observable<T> takeLast(int count)
Returns an Observable that emits at most the lastcountitems emitted by the source Observable. If the source emits fewer thancountitems then all of its items are emitted.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream if the
countis non-zero; ignores backpressure if thecountis zero as it doesn't signal any values. - Scheduler:
- This version of
takeLastdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emit from the end of the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits at most the last
countitems emitted by the source Observable - Throws:
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifcountis less than zero- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLast
public final Observable<T> takeLast(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits at most a specified number of items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
- This version of
takeLastoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emittime- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that emits at most
countitems from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLast
public final Observable<T> takeLast(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits at most a specified number of items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed, where the timing information is provided by a given Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it). - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emittime- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- theSchedulerthat provides the timestamps for the observed items- Returns:
- an Observable that emits at most
countitems from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed, where the timing information is provided by the givenscheduler - Throws:
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException- ifcountis less than zero- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLast
public final Observable<T> takeLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it) but note that thismay lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. Consider usingtakeLast(int, long, TimeUnit)in this case. behavior. - Scheduler:
- This version of
takeLastoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable that were emitted in the window of time before the Observable completed specified by
time - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLast
public final Observable<T> takeLast(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable that were emitted in a specified window of time before the Observable completed, where the timing information is provided by a specified Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., no backpressure is applied to it) but note that thismay lead toOutOfMemoryErrordue to internal buffer bloat. Consider usingtakeLast(int, long, TimeUnit, Scheduler)in this case. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the Scheduler that provides the timestamps for the Observed items- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable that were emitted in the window of time before the Observable completed specified by
time, where the timing information is provided byscheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLastBuffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> takeLastBuffer(int count)
Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing at most the lastcountelements emitted by the source Observable. If the source emits fewer thancountitems then the emitted List will contain all of the source emissions.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
- This version of
takeLastBufferdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emit in the list- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single list containing at most the last
countelements emitted by the source Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLastBuffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> takeLastBuffer(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing at mostcountitems from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time before the source Observable completed.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
- This version of
takeLastBufferoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emittime- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single List containing at most
countitems emitted by the source Observable during the time window defined bytimebefore the source Observable completed - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLastBuffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> takeLastBuffer(int count, long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing at mostcountitems from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time (on a specified Scheduler) before the source Observable completed.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
count- the maximum number of items to emittime- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the Scheduler that provides the timestamps for the observed items- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single List containing at most
countitems emitted by the source Observable during the time window defined bytimebefore the source Observable completed - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLastBuffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> takeLastBuffer(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing those items from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time before the source Observable completed.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
- This version of
takeLastBufferoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftime- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single List containing the items emitted by the source Observable during the time window defined by
timebefore the source Observable completed - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeLastBuffer
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> takeLastBuffer(long time, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits a single List containing those items from the source Observable that were emitted during a specified window of time before the source Observable completed, where the timing information is provided by the given Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
time- the length of the time windowunit- the time unit oftimescheduler- the Scheduler that provides the timestamps for the observed items- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single List containing the items emitted by the source Observable during the time window defined by
timebefore the source Observable completed, where the timing information is provided byscheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeLast
takeUntil
public final <E> Observable<T> takeUntil(Observable<? extends E> other)
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
takeUntildoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
E- the type of items emitted byother- Parameters:
other- the Observable whose first emitted item will causetakeUntilto stop emitting items from the source Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable until such time as
otheremits its first item - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeUntil
takeWhile
public final Observable<T> takeWhile(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> predicate)
Returns an Observable that emits items emitted by the source Observable so long as each item satisfied a specified condition, and then completes as soon as this condition is not satisfied.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
takeWhiledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
predicate- a function that evaluates an item emitted by the source Observable and returns a Boolean- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable so long as each item satisfies the condition defined by
predicate, then completes - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeWhile,
takeUntil(Func1)
takeUntil
public final Observable<T> takeUntil(Func1<? superT,java.lang.Boolean> stopPredicate)
Returns an Observable that emits items emitted by the source Observable, checks the specified predicate for each item, and then completes when the condition is satisfied.
The difference between this operator and
takeWhile(Func1)is that here, the condition is evaluatedafter the item is emitted.- Backpressure:
- The operator is a pass-through for backpressure; the backpressure behavior is determined by the upstream source and the downstream consumer.
- Scheduler:
takeWhiledoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
stopPredicate- a function that evaluates an item emitted by the source Observable and returns a Boolean- Returns:
- an Observable that first emits items emitted by the source Observable, checks the specified condition after each item, and then completes when the condition is satisfied.
- Since:
- 1.1.0
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TakeUntil,
takeWhile(Func1)
throttleFirst
public final Observable<T> throttleFirst(long windowDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits only the first item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration.This differs from
throttleLast(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)in that this only tracks passage of time whereasthrottleLast(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)ticks at scheduled intervals.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
throttleFirstoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
windowDuration- time to wait before emitting another item after emitting the last itemunit- the unit of time ofwindowDuration- Returns:
- an Observable that performs the throttle operation
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Sample,RxJava wiki: Backpressure
throttleFirst
public final Observable<T> throttleFirst(long skipDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits only the first item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration, where the windows are managed by a specified Scheduler.This differs from
throttleLast(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)in that this only tracks passage of time whereasthrottleLast(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)ticks at scheduled intervals.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
skipDuration- time to wait before emitting another item after emitting the last itemunit- the unit of time ofskipDurationscheduler- theSchedulerto use internally to manage the timers that handle timeout for each event- Returns:
- an Observable that performs the throttle operation
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Sample,RxJava wiki: Backpressure
throttleLast
public final Observable<T> throttleLast(long intervalDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration.This differs from
throttleFirst(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)in that this ticks along at a scheduled interval whereasthrottleFirst(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)does not tick, it just tracks passage of time.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
throttleLastoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
intervalDuration- duration of windows within which the last item emitted by the source Observable will be emittedunit- the unit of time ofintervalDuration- Returns:
- an Observable that performs the throttle operation
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Sample,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
sample(long, TimeUnit)
throttleLast
public final Observable<T> throttleLast(long intervalDuration, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable during sequential time windows of a specified duration, where the duration is governed by a specified Scheduler.This differs from
throttleFirst(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)in that this ticks along at a scheduled interval whereasthrottleFirst(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)does not tick, it just tracks passage of time.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
intervalDuration- duration of windows within which the last item emitted by the source Observable will be emittedunit- the unit of time ofintervalDurationscheduler- theSchedulerto use internally to manage the timers that handle timeout for each event- Returns:
- an Observable that performs the throttle operation
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Sample,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
sample(long, TimeUnit, Scheduler)
throttleWithTimeout
public final Observable<T> throttleWithTimeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that only emits those items emitted by the source Observable that are not followed by another emitted item within a specified time window.Note: If the source Observable keeps emitting items more frequently than the length of the time window then no items will be emitted by the resulting Observable.

Information on debounce vs throttle:
- Debounce and Throttle: visual explanation
- Debouncing: javascript methods
- Javascript - don't spam your server: debounce and throttle
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
throttleWithTimeoutoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timeout- the length of the window of time that must pass after the emission of an item from the source Observable in which that Observable emits no items in order for the item to be emitted by the resulting Observableunit- theTimeUnitoftimeout- Returns:
- an Observable that filters out items that are too quickly followed by newer items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Debounce,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
debounce(long, TimeUnit)
throttleWithTimeout
public final Observable<T> throttleWithTimeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that only emits those items emitted by the source Observable that are not followed by another emitted item within a specified time window, where the time window is governed by a specified Scheduler.Note: If the source Observable keeps emitting items more frequently than the length of the time window then no items will be emitted by the resulting Observable.

Information on debounce vs throttle:
- Debounce and Throttle: visual explanation
- Debouncing: javascript methods
- Javascript - don't spam your server: debounce and throttle
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as it uses time to control data flow.
- Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timeout- the length of the window of time that must pass after the emission of an item from the source Observable in which that Observable emits no items in order for the item to be emitted by the resulting Observableunit- theTimeUnitoftimeoutscheduler- theSchedulerto use internally to manage the timers that handle the timeout for each item- Returns:
- an Observable that filters out items that are too quickly followed by newer items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Debounce,RxJava wiki: Backpressure,
debounce(long, TimeUnit, Scheduler)
timeInterval
public final Observable<TimeInterval<T>> timeInterval()
Returns an Observable that emits records of the time interval between consecutive items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
timeIntervaldoes not operate on any particular scheduler but uses the current time from thecomputationScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits time interval information items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TimeInterval
timeInterval
public final Observable<TimeInterval<T>> timeInterval(Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits records of the time interval between consecutive items emitted by the source Observable, where this interval is computed on a specified Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- The operator does not operate on any particular scheduler but uses the current time from the specified
Scheduler.
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerused to compute time intervals- Returns:
- an Observable that emits time interval information items
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: TimeInterval
timeout
public final <U,V> Observable<T> timeout(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> firstTimeoutSelector,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but notifies observers of aTimeoutExceptionif either the first item emitted by the source Observable or any subsequent item doesn't arrive within time windows defined by other Observables.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. Both this and the returned
Observables are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of then violates this rule, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen theObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
- This version of
timeoutoperates by default on theimmediateScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the first timeout value type (ignored)V- the subsequent timeout value type (ignored)- Parameters:
firstTimeoutSelector- a function that returns an Observable that determines the timeout window for the first source itemtimeoutSelector- a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source Observable and that determines the timeout window in which the subsequent source item must arrive in order to continue the sequence- Returns:
- an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but notifies observers of a
TimeoutExceptionif either the first item or any subsequent item doesn't arrive within the time windows specified by the timeout selectors - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timeout
public final <U,V> Observable<T> timeout(Func0<? extendsObservable<U>> firstTimeoutSelector,Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector,Observable<? extendsT> other)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but switches to a fallback Observable if either the first item emitted by the source Observable or any subsequent item doesn't arrive within time windows defined by other Observables.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
- This version of
timeoutoperates by default on theimmediateScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the first timeout value type (ignored)V- the subsequent timeout value type (ignored)- Parameters:
firstTimeoutSelector- a function that returns an Observable which determines the timeout window for the first source itemtimeoutSelector- a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source Observable and that determines the timeout window in which the subsequent source item must arrive in order to continue the sequenceother- the fallback Observable to switch to if the source Observable times out- Returns:
- an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but switches to the
otherObservable if either the first item emitted by the source Observable or any subsequent item doesn't arrive within time windows defined by the timeout selectors - Throws:
java.lang.NullPointerException- iftimeoutSelectoris null- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timeout
public final <V> Observable<T> timeout(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but notifies observers of aTimeoutExceptionif an item emitted by the source Observable doesn't arrive within a window of time after the emission of the previous item, where that period of time is measured by an Observable that is a function of the previous item.
Note: The arrival of the first source item is never timed out.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
- This version of
timeoutoperates by default on theimmediateScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
V- the timeout value type (ignored)- Parameters:
timeoutSelector- a function that returns an observable for each item emitted by the source Observable and that determines the timeout window for the subsequent item- Returns:
- an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but notifies observers of a
TimeoutExceptionif an item emitted by the source Observable takes longer to arrive than the time window defined by the selector for the previously emitted item - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timeout
public final <V> Observable<T> timeout(Func1<? superT,? extendsObservable<V>> timeoutSelector,Observable<? extendsT> other)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but that switches to a fallback Observable if an item emitted by the source Observable doesn't arrive within a window of time after the emission of the previous item, where that period of time is measured by an Observable that is a function of the previous item.
Note: The arrival of the first source item is never timed out.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
- This version of
timeoutoperates by default on theimmediateScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
V- the timeout value type (ignored)- Parameters:
timeoutSelector- a function that returns an Observable, for each item emitted by the source Observable, that determines the timeout window for the subsequent itemother- the fallback Observable to switch to if the source Observable times out- Returns:
- an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, but switches to mirroring a fallback Observable if an item emitted by the source Observable takes longer to arrive than the time window defined by the selector for the previously emitted item
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timeout
public final Observable<T> timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item. If the next item isn't emitted within the specified timeout duration starting from its predecessor, the resulting Observable terminates and notifies observers of aTimeoutException.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- This version of
timeoutoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timeout- maximum duration between emitted items before a timeout occurstimeUnit- the unit of time that applies to thetimeoutargument.- Returns:
- the source Observable modified to notify observers of a
TimeoutExceptionin case of a timeout - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timeout
public final Observable<T> timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit,Observable<? extendsT> other)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item. If the next item isn't emitted within the specified timeout duration starting from its predecessor, the resulting Observable begins instead to mirror a fallback Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
- This version of
timeoutoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timeout- maximum duration between items before a timeout occurstimeUnit- the unit of time that applies to thetimeoutargumentother- the fallback Observable to use in case of a timeout- Returns:
- the source Observable modified to switch to the fallback Observable in case of a timeout
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timeout
public final Observable<T> timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit,Observable<? extendsT> other,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item using a specified Scheduler. If the next item isn't emitted within the specified timeout duration starting from its predecessor, the resulting Observable begins instead to mirror a fallback Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream. The
Observablesources are expected to honor backpressure as well. If any of the sourceObservables violate this, itmay throw anIllegalStateExceptionwhen the sourceObservablecompletes. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timeout- maximum duration between items before a timeout occurstimeUnit- the unit of time that applies to thetimeoutargumentother- the Observable to use as the fallback in case of a timeoutscheduler- theSchedulerto run the timeout timers on- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that it will switch to the fallback Observable in case of a timeout
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timeout
public final Observable<T> timeout(long timeout, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit timeUnit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that mirrors the source Observable but applies a timeout policy for each emitted item, where this policy is governed on a specified Scheduler. If the next item isn't emitted within the specified timeout duration starting from its predecessor, the resulting Observable terminates and notifies observers of aTimeoutException.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timeout- maximum duration between items before a timeout occurstimeUnit- the unit of time that applies to thetimeoutargumentscheduler- the Scheduler to run the timeout timers on- Returns:
- the source Observable modified to notify observers of a
TimeoutExceptionin case of a timeout - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timeout
timestamp
public final Observable<Timestamped<T>> timestamp()
Returns an Observable that emits each item emitted by the source Observable, wrapped in aTimestampedobject.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
timestampdoes not operate on any particular scheduler but uses the current time from thecomputationScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits timestamped items from the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timestamp
timestamp
public final Observable<Timestamped<T>> timestamp(Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits each item emitted by the source Observable, wrapped in aTimestampedobject whose timestamps are provided by a specified Scheduler.
- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- The operator does not operate on any particular scheduler but uses the current time from the specified
Scheduler.
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto use as a time source- Returns:
- an Observable that emits timestamped items from the source Observable with timestamps provided by the
scheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Timestamp
toBlocking
public final BlockingObservable<T> toBlocking()
Converts an Observable into aBlockingObservable(an Observable with blocking operators).- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
toBlockingdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- a
BlockingObservableversion of this Observable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toList
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> toList()
Returns an Observable that emits a single item, a list composed of all the items emitted by the source Observable.
Normally, an Observable that returns multiple items will do so by invoking its
Observer'sonNextmethod for each such item. You can change this behavior, instructing the Observable to compose a list of all of these items and then to invoke the Observer'sonNextfunction once, passing it the entire list, by calling the Observable'stoListmethod prior to calling itssubscribe()method.Be careful not to use this operator on Observables that emit infinite or very large numbers of items, as you do not have the option to unsubscribe.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toListdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a List containing all of the items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toMap
public final <K> Observable<java.util.Map<K,T>> toMap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector)
Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap containing all items emitted by the source Observable, mapped by the keys returned by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.
If more than one source item maps to the same key, the HashMap will contain the latest of those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type of the Map- Parameters:
keySelector- the function that extracts the key from a source item to be used in the HashMap- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a HashMap containing the mapped items from the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toMap
public final <K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,V>> toMap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap containing values corresponding to items emitted by the source Observable, mapped by the keys returned by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.
If more than one source item maps to the same key, the HashMap will contain a single entry that corresponds to the latest of those items.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type of the MapV- the value type of the Map- Parameters:
keySelector- the function that extracts the key from a source item to be used in the HashMapvalueSelector- the function that extracts the value from a source item to be used in the HashMap- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a HashMap containing the mapped items from the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toMap
public final <K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,V>> toMap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector,Func0<? extends java.util.Map<K,V>> mapFactory)
Returns an Observable that emits a single Map, returned by a specifiedmapFactoryfunction, that contains keys and values extracted from the items emitted by the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type of the MapV- the value type of the Map- Parameters:
keySelector- the function that extracts the key from a source item to be used in the MapvalueSelector- the function that extracts the value from the source items to be used as value in the MapmapFactory- the function that returns a Map instance to be used- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a Map that contains the mapped items emitted by the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toMultimap
public final <K> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<T>>> toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector)
Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap that contains an ArrayList of items emitted by the source Observable keyed by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.
- Backpressure:
- This operator does not support backpressure as by intent it is requesting and buffering everything.
- Scheduler:
toMultiMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type of the Map- Parameters:
keySelector- the function that extracts the key from the source items to be used as key in the HashMap- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a HashMap that contains an ArrayList of items mapped from the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toMultimap
public final <K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>> toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits a single HashMap that contains an ArrayList of values extracted by a specifiedvalueSelectorfunction from items emitted by the source Observable, keyed by a specifiedkeySelectorfunction.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toMultiMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type of the MapV- the value type of the Map- Parameters:
keySelector- the function that extracts a key from the source items to be used as key in the HashMapvalueSelector- the function that extracts a value from the source items to be used as value in the HashMap- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a HashMap that contains an ArrayList of items mapped from the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toMultimap
public final <K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>> toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector,Func0<? extends java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>> mapFactory)
Returns an Observable that emits a single Map, returned by a specifiedmapFactoryfunction, that contains an ArrayList of values, extracted by a specifiedvalueSelectorfunction from items emitted by the source Observable and keyed by thekeySelectorfunction.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toMultiMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type of the MapV- the value type of the Map- Parameters:
keySelector- the function that extracts a key from the source items to be used as the key in the MapvalueSelector- the function that extracts a value from the source items to be used as the value in the MapmapFactory- the function that returns a Map instance to be used- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a Map that contains a list items mapped from the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toMultimap
public final <K,V> Observable<java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>> toMultimap(Func1<? superT,? extends K> keySelector,Func1<? superT,? extends V> valueSelector,Func0<? extends java.util.Map<K,java.util.Collection<V>>> mapFactory,Func1<? super K,? extends java.util.Collection<V>> collectionFactory)
Returns an Observable that emits a single Map, returned by a specifiedmapFactoryfunction, that contains a custom collection of values, extracted by a specifiedvalueSelectorfunction from items emitted by the source Observable, and keyed by thekeySelectorfunction.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toMultiMapdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
K- the key type of the MapV- the value type of the Map- Parameters:
keySelector- the function that extracts a key from the source items to be used as the key in the MapvalueSelector- the function that extracts a value from the source items to be used as the value in the MapmapFactory- the function that returns a Map instance to be usedcollectionFactory- the function that returns a Collection instance for a particular key to be used in the Map- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a single item: a Map that contains the collection of mapped items from the source Observable
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toSortedList
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> toSortedList()
Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order. Each item emitted by the Observable must implementComparablewith respect to all other items in the sequence.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toSortedListdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable in sorted order
- Throws:
java.lang.ClassCastException- if any item emitted by the Observable does not implementComparablewith respect to all other items emitted by the Observable- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toSortedList
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> toSortedList(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Integer> sortFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order based on a specified comparison function.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toSortedListdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
sortFunction- a function that compares two items emitted by the source Observable and returns an Integer that indicates their sort order- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable in sorted order
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toSortedList
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> toSortedList(int initialCapacity)
Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order. Each item emitted by the Observable must implementComparablewith respect to all other items in the sequence.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toSortedListdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
initialCapacity- the initial capacity of the ArrayList used to accumulate items before sorting- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable in sorted order
- Throws:
java.lang.ClassCastException- if any item emitted by the Observable does not implementComparablewith respect to all other items emitted by the Observable- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
toSortedList
public final Observable<java.util.List<T>> toSortedList(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Integer> sortFunction, int initialCapacity)
Returns an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable, in a sorted order based on a specified comparison function.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
toSortedListdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
sortFunction- a function that compares two items emitted by the source Observable and returns an Integer that indicates their sort orderinitialCapacity- the initial capacity of the ArrayList used to accumulate items before sorting- Returns:
- an Observable that emits a list that contains the items emitted by the source Observable in sorted order
- Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: To
sorted
public final Observable<T> sorted()
Returns an Observable that emits the events emitted by source Observable, in a sorted order. Each item emitted by the Observable must implementComparablewith respect to all other items in the sequence.Note that calling
sortedwith long, non-terminating or infinite sources might causeOutOfMemoryError- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
sorteddoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable in sorted order
- Throws:
java.lang.ClassCastException- if any item emitted by the Observable does not implementComparablewith respect to all other items emitted by the Observable- Since:
- 1.3
sorted
public final Observable<T> sorted(Func2<? superT,? superT,java.lang.Integer> sortFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits the events emitted by source Observable, in a sorted order based on a specified comparison function.Note that calling
sortedwith long, non-terminating or infinite sources might causeOutOfMemoryError- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure from downstream and consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner (i.e., without applying backpressure to it). - Scheduler:
sorteddoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
sortFunction- a function that compares two items emitted by the source Observable and returns an Integer that indicates their sort order- Returns:
- an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable in sorted order
- Since:
- 1.3
unsubscribeOn
public final Observable<T> unsubscribeOn(Scheduler scheduler)
Modifies the source Observable so that subscribers will unsubscribe from it on a specifiedScheduler.- Backpressure:
- The operator doesn't interfere with backpressure which is determined by the source
Observable's backpressure behavior. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
scheduler- theSchedulerto perform unsubscription actions on- Returns:
- the source Observable modified so that its unsubscriptions happen on the specified
Scheduler - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: SubscribeOn
withLatestFrom
public final <U,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<? extends U> other,Func2<? superT,? super U,? extends R> resultSelector)
Merges the specified Observable into this Observable sequence by using theresultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable (this instance) emits an item.
- Backpressure:
- The operator is a pass-through for backpressure: the backpressure support depends on the upstream and downstream's backpressure behavior. The other Observable is consumed in an unbounded fashion.
- Scheduler:
- This operator, by default, doesn't run any particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the element type of the other ObservableR- the result type of the combination- Parameters:
other- the other ObservableresultSelector- the function to call when this Observable emits an item and the other Observable has already emitted an item, to generate the item to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that merges the specified Observable into this Observable by using the
resultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable sequence (this instance) emits an item - Since:
- 1.3
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: CombineLatest
withLatestFrom
public final <T1,T2,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Func3<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the first other source's value typeT2- the second other source's value typeR- the result value type- Parameters:
o1- the first other Observableo2- the second other Observablecombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <T1,T2,T3,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Func4<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the first other source's value typeT2- the second other source's value typeT3- the third other source's value typeR- the result value type- Parameters:
o1- the first other Observableo2- the second other Observableo3- the third other Observablecombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <T1,T2,T3,T4,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Func5<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the first other source's value typeT2- the second other source's value typeT3- the third other source's value typeT4- the fourth other source's value typeR- the result value type- Parameters:
o1- the first other Observableo2- the second other Observableo3- the third other Observableo4- the fourth other Observablecombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Func6<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the first other source's value typeT2- the second other source's value typeT3- the third other source's value typeT4- the fourth other source's value typeT5- the fifth other source's value typeR- the result value type- Parameters:
o1- the first other Observableo2- the second other Observableo3- the third other Observableo4- the fourth other Observableo5- the fifth other Observablecombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Observable<T6> o6,Func7<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the first other source's value typeT2- the second other source's value typeT3- the third other source's value typeT4- the fourth other source's value typeT5- the fifth other source's value typeT6- the sixth other source's value typeR- the result value type- Parameters:
o1- the first other Observableo2- the second other Observableo3- the third other Observableo4- the fourth other Observableo5- the fifth other Observableo6- the sixth other Observablecombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Observable<T6> o6,Observable<T7> o7,Func8<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the first other source's value typeT2- the second other source's value typeT3- the third other source's value typeT4- the fourth other source's value typeT5- the fifth other source's value typeT6- the sixth other source's value typeT7- the seventh other source's value typeR- the result value type- Parameters:
o1- the first other Observableo2- the second other Observableo3- the third other Observableo4- the fourth other Observableo5- the fifth other Observableo6- the sixth other Observableo7- the seventh other Observablecombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<T1> o1,Observable<T2> o2,Observable<T3> o3,Observable<T4> o4,Observable<T5> o5,Observable<T6> o6,Observable<T7> o7,Observable<T8> o8,Func9<? superT,? super T1,? super T2,? super T3,? super T4,? super T5,? super T6,? super T7,? super T8,R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T1- the first other source's value typeT2- the second other source's value typeT3- the third other source's value typeT4- the fourth other source's value typeT5- the fifth other source's value typeT6- the sixth other source's value typeT7- the seventh other source's value typeT8- the eighth other source's value typeR- the result value type- Parameters:
o1- the first other Observableo2- the second other Observableo3- the third other Observableo4- the fourth other Observableo5- the fifth other Observableo6- the sixth other Observableo7- the seventh other Observableo8- the eighth other Observablecombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(Observable<?>[] others,FuncN<R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the result value type- Parameters:
others- the array of other sourcescombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
withLatestFrom
public final <R> Observable<R> withLatestFrom(java.lang.Iterable<Observable<?>> others,FuncN<R> combiner)
Combines the value emission from this Observable with the latest emissions from the other Observables via a function to produce the output item.Note that this operator doesn't emit anything until all other sources have produced at least one value. The resulting emission only happens when this Observable emits (and not when any of the other sources emit, unlike combineLatest). If a source doesn't produce any value and just completes, the sequence is completed immediately.
- Backpressure:
- This operator is a pass-through for backpressure behavior between the source
Observableand the downstream Subscriber. The otherObservables are consumed in an unbounded manner. - Scheduler:
- This operator does not operate by default on a particular
Scheduler.
- Type Parameters:
R- the result value type- Parameters:
others- the iterable of other sourcescombiner- the function called with an array of values from each participating observable- Returns:
- the new Observable instance
- Since:
- 1.3
window
public final <TClosing> Observable<Observable<T>> window(Func0<? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> closingSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping windows. It emits the current window and opens a new one whenever the Observable produced by the specifiedclosingSelectoremits an item.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses theclosingSelectorto control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure but have an unbounded inner buffer thatmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrorif left unconsumed. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
TClosing- the element type of the boundary Observable- Parameters:
closingSelector- aFunc0that returns anObservablethat governs the boundary between windows. When the sourceObservableemits an item,windowemits the current window and begins a new one.- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping windows of items from the source Observable whenever
closingSelectoremits an item - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(int count)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping windows, each containingcountitems. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure of its inner and outer subscribers, however, the inner Observable uses an unbounded buffer that may hold at most
countelements. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum size of each window before it should be emitted- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping windows, each containing at most
countitems from the source Observable - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if either count is non-positive- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(int count, int skip)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits windows everyskipitems, each containing no more thancountitems. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator honors backpressure of its inner and outer subscribers, however, the inner Observable uses an unbounded buffer that may hold at most
countelements. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Parameters:
count- the maximum size of each window before it should be emittedskip- how many items need to be skipped before starting a new window. Note that ifskipandcountare equal this is the same operation aswindow(int).- Returns:
- an Observable that emits windows every
skipitems containing at mostcountitems from the source Observable - Throws:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException- if either count or skip is non-positive- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable starts a new window periodically, as determined by thetimeshiftargument. It emits each window after a fixed timespan, specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses time to control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure but have an unbounded inner buffer thatmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrorif left unconsumed. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each window collects items before it should be emittedtimeshift- the period of time after which a new window will be createdunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanandtimeshiftarguments- Returns:
- an Observable that emits new windows periodically as a fixed timespan elapses
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable starts a new window periodically, as determined by thetimeshiftargument. It emits each window after a fixed timespan, specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses time to control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure but have an unbounded inner buffer thatmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrorif left unconsumed. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each window collects items before it should be emittedtimeshift- the period of time after which a new window will be createdunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanandtimeshiftargumentsscheduler- theSchedulerto use when determining the end and start of a window- Returns:
- an Observable that emits new windows periodically as a fixed timespan elapses
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(long timespan, long timeshift, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable starts a new window periodically, as determined by thetimeshiftargument or a maximum size as specified by thecountargument (whichever is reached first). It emits each window after a fixed timespan, specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses time to control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure and may hold up tocountelements at most. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each window collects items before it should be emittedtimeshift- the period of time after which a new window will be createdunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanandtimeshiftargumentscount- the maximum size of each window before it should be emittedscheduler- theSchedulerto use when determining the end and start of a window- Returns:
- an Observable that emits new windows periodically as a fixed timespan elapses
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses time to control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure and may hold up tocountelements at most. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each window collects items before it should be emitted and replaced with a new windowunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanargument- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping windows representing items emitted by the source Observable during fixed, consecutive durations
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration as specified by thetimespanargument or a maximum size as specified by thecountargument (whichever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses time to control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure and may hold up tocountelements at most. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowoperates by default on thecomputationScheduler.
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each window collects items before it should be emitted and replaced with a new windowunit- the unit of time that applies to thetimespanargumentcount- the maximum size of each window before it should be emitted- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping windows of items from the source Observable that were emitted during a fixed duration of time or when the window has reached maximum capacity (whichever occurs first)
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit, int count,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration specified by thetimespanargument or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (whichever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses time to control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure and may hold up tocountelements at most. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each window collects items before it should be emitted and replaced with a new windowunit- the unit of time which applies to thetimespanargumentcount- the maximum size of each window before it should be emittedscheduler- theSchedulerto use when determining the end and start of a window- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping windows of items from the source Observable that were emitted during a fixed duration of time or when the window has reached maximum capacity (whichever occurs first)
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final Observable<Observable<T>> window(long timespan, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit unit,Scheduler scheduler)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits connected, non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration as specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the resulting Observable emits the current window and propagates the notification from the source Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The operator consumes the source
Observablein an unbounded manner. The returnedObservabledoesn't support backpressure as it uses time to control the creation of windows. The returned innerObservables honor backpressure but have an unbounded inner buffer thatmay lead toOutOfMemoryErrorif left unconsumed. - Scheduler:
- you specify which
Schedulerthis operator will use
- Parameters:
timespan- the period of time each window collects items before it should be emitted and replaced with a new windowunit- the unit of time which applies to thetimespanargumentscheduler- theSchedulerto use when determining the end and start of a window- Returns:
- an Observable that emits connected, non-overlapping windows containing items emitted by the source Observable within a fixed duration
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final <TOpening,TClosing> Observable<Observable<T>> window(Observable<? extends TOpening> windowOpenings,Func1<? super TOpening,? extendsObservable<? extends TClosing>> closingSelector)
Returns an Observable that emits windows of items it collects from the source Observable. The resulting Observable emits windows that contain those items emitted by the source Observable between the time when thewindowOpeningsObservable emits an item and when the Observable returned byclosingSelectoremits an item.
- Backpressure:
- The outer Observable of this operator doesn't support backpressure because the emission of new inner Observables are controlled by the
windowOpeningsObservable. The inner Observables honor backpressure and buffer everything until the associated closing Observable signals or completes. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
TOpening- the element type of the window-opening ObservableTClosing- the element type of the window-closing Observables- Parameters:
windowOpenings- an Observable that, when it emits an item, causes another window to be createdclosingSelector- aFunc1that produces an Observable for every window created. When this Observable emits an item, the associated window is closed and emitted- Returns:
- an Observable that emits windows of items emitted by the source Observable that are governed by the specified window-governing Observables
- See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
window
public final <U> Observable<Observable<T>> window(Observable<U> boundary)
Returns an Observable that emits non-overlapping windows of items it collects from the source Observable where the boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.
- Backpressure:
- The outer Observable of this operator does not support backpressure as it uses a
boundaryObservable to control data flow. The inner Observables honor backpressure and buffer everything until the boundary signals the next element. - Scheduler:
- This version of
windowdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
U- the window element type (ignored)- Parameters:
boundary- an Observable whose emitted items close and open windows- Returns:
- an Observable that emits non-overlapping windows of items it collects from the source Observable where the boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from the
boundaryObservable - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Window
zipWith
public final <T2,R> Observable<R> zipWith(java.lang.Iterable<? extends T2> other,Func2<? superT,? super T2,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the result of applying a specified function to pairs of values, one each from the source Observable and a specified Iterable sequence.
Note that the
otherIterable is evaluated as items are observed from the source Observable; it is not pre-consumed. This allows you to zip infinite streams on either side.- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T2- the type of items in theotherIterableR- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
other- the Iterable sequencezipFunction- a function that combines the pairs of items from the Observable and the Iterable to generate the items to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that pairs up values from the source Observable and the
otherIterable sequence and emits the results ofzipFunctionapplied to these pairs - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
zipWith
public final <T2,R> Observable<R> zipWith(Observable<? extends T2> other,Func2<? superT,? super T2,? extends R> zipFunction)
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the result of applying a specified function to pairs of values, one each from the source Observable and another specified Observable.The operator subscribes to its sources in order they are specified and completes eagerly if one of the sources is shorter than the rest while unsubscribing the other sources. Therefore, it is possible those other sources will never be able to run to completion (and thus not calling
doOnCompleted()). This can also happen if the sources are exactly the same length; if source A completes and B has been consumed and is about to complete, the operator detects A won't be sending further values and it will unsubscribe B immediately. For example:range(1, 5).doOnCompleted(action1).zipWith(range(6, 5).doOnCompleted(action2), (a, b) -> a + b)action1will be called butaction2won't.
To work around this termination property, usedoOnUnsubscribed()as well or useusing()to do cleanup in case of completion or unsubscription.
- Backpressure:
- The operator expects backpressure from the sources and honors backpressure from the downstream. (I.e., zipping with
interval(long, TimeUnit)may result in MissingBackpressureException, use one of theonBackpressureXto handle similar, backpressure-ignoring sources. - Scheduler:
zipWithdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
- Type Parameters:
T2- the type of items emitted by theotherObservableR- the type of items emitted by the resulting Observable- Parameters:
other- the other ObservablezipFunction- a function that combines the pairs of items from the two Observables to generate the items to be emitted by the resulting Observable- Returns:
- an Observable that pairs up values from the source Observable and the
otherObservable and emits the results ofzipFunctionapplied to these pairs - See Also:
- ReactiveX operators documentation: Zip
test
public final AssertableSubscriber<T> test()
Creates a AssertableSubscriber that requestsLong.MAX_VALUEand subscribes it to this Observable.- Backpressure:
- The returned AssertableSubscriber consumes this Observable in an unbounded fashion.
- Scheduler:
testdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.3 - experimental
- Returns:
- the new AssertableSubscriber instance
- Since:
- 1.3
test
public final AssertableSubscriber<T> test(long initialRequestAmount)
Creates an AssertableSubscriber with the initial request amount and subscribes it to this Observable.- Backpressure:
- The returned AssertableSubscriber requests the given
initialRequestamount upfront. - Scheduler:
testdoes not operate by default on a particularScheduler.
History: 1.2.3 - experimental
- Parameters:
initialRequestAmount- the amount to request from upstream upfront, non-negative (not verified)- Returns:
- the new AssertableSubscriber instance
- Since:
- 1.3