Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork554
3D U-Net model for volumetric semantic segmentation written in pytorch
License
wolny/pytorch-3dunet
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
PyTorch implementation of 3D U-Net and its variants:
UNet3DStandard 3D U-Net based on3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse AnnotationResidualUNet3DResidual 3D U-Net based onSuperhuman Accuracy on the SNEMI3D Connectomics ChallengeResidualUNetSE3DSimilar toResidualUNet3Dwith the addition of Squeeze and Excitation blocks based onDeep Learning Semantic Segmentation for High-Resolution Medical Volumes. Original squeeze and excite paper:Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
The code allows for training the U-Net for both:semantic segmentation (binary and multi-class) andregression problems (e.g. de-noising, learning deconvolutions).
2D U-Net is also supported, see2DUnet_confocal or2DUnet_dsb2018 for example configuration.Just make sure to keep the singleton z-dimension in your H5 dataset (i.e.(1, Y, X) instead of(Y, X)) , because data loading / data augmentation requires tensors of rank 3.The 2D U-Net itself uses the standard 2D convolutional layers instead of 3D convolutions with kernel size(1, 3, 3) for performance reasons.
The input data should be stored in HDF5 files. The HDF5 files for training should contain two datasets:raw andlabel.Theraw dataset contains the input data, while thelabel dataset contains the ground truth labels.The format of the raw and label datasets depends on whether the problem is 2D or 3D, as well as whether the data is single-channel or multi-channel. Please refer to the table below:
| 2D | 3D | |
|---|---|---|
| single-channel | (1, Y, X) | (Z, Y, X) |
| multi-channel | (C, 1, Y, X) | (C, Z, Y, X) |
- Miniconda
- Python 3.11+
- NVIDIA GPU (optional but recommended for training/prediction speedup)
pytorch-3dunet is a cross-platform package and runs on Windows and OSX as well as on Linux.
The easiest way to installpytorch-3dunet package is via conda:
# Created new conda environment "3dunet" with the latest python version from the conda-forge channelconda create -n 3dunet python -c conda-forge -y# Activate the conda environmentconda activate 3dunet# pytorch-3dunet does not include PyTorch dependencies, so that one can install the desired PyTorch version (with/without CUDA support) separatelypip install torch torchvision# you may need to adjust the command above depending on your GPU and the CUDA version you want to use, e.g. for CUDA 12.6:# pip install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126# or for CPU-only version:# pip install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu# Install the latest pytorch-3dunet package from conda-forge channelconda install -c conda-forge pytorch-3dunet
After installation the following commands will be accessible within the conda environment:train3dunet for training the network andpredict3dunet for prediction (see below).
One can also install directly from source, i.e. go to the checkout directory and run:
pip install -e .PyTorch package comes with their own CUDA runtime libraries, so you don't need to install CUDA separately on your system.However, you must ensure that the PyTorch/CUDA version you choose is compatible with your GPU’s compute capability.SeePyTorch installation guide for more details.
Given thatpytorch-3dunet package was installed via conda as described above, you can train the network by simply invoking:
train3dunet --config <CONFIG>whereCONFIG is the path to a YAML configuration file that specifies all aspects of the training process.
In order to train on your own data just provide the paths to your HDF5 training and validation datasets in the config. Below are some example configs for segmentation and regression tasks:
- sample config for 3D semantic segmentation (cell boundary segmentation):train_config_segmentation.yaml
- sample config for 3D regression task (denoising):train_config_regression.yaml
- more configs can be found inresources directory
One can monitor the training progress with Tensorboardtensorboard --logdir <checkpoint_dir>/logs/ (you needtensorflow installed in your conda env), wherecheckpoint_dir is the path to the checkpoint directory specified in the config.
- When training with binary-based losses, i.e.:
BCEWithLogitsLoss,DiceLoss,BCEDiceLoss,GeneralizedDiceLoss:The target data has to be 4D (one target binary mask per output channel of the network). - When training with
WeightedCrossEntropyLoss,CrossEntropyLossthe target dataset has to be 3D label image as expected by the loss (see PyTorchdocumentation for cross entropy loss:https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss.html)
Given thatpytorch-3dunet package was installed via conda as described above, one can run the prediction via:
predict3dunet --config <CONFIG>In order to predict on your own data, just provide the path to your model as well as paths to HDF5 test files (see exampletest_config_segmentation.yaml).
- If you're running prediction for a large dataset, consider using
LazyHDF5DatasetandLazyPredictorin the config.This will save memory by loading data/saving predictions on the fly at the cost of slower prediction time.Seetest_config_lazy for an example config. - If your model predicts multiple classes (see e.g.train_config_multiclass), consider saving only the finalsegmentation instead of the probability maps which can be time and space consuming.To do so, set
save_segmentation: truein thepredictorsection of the config (seetest_config_multiclass).
By default, if multiple GPUs are available training/prediction will be run on all the GPUsusingDataParallel.If training/prediction on all available GPUs is not desirable, restrict the number of GPUs usingCUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES,e.g.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 train3dunet --config<CONFIG>
or
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 predict3dunet --config<CONFIG>
BCEWithLogitsLoss(binary cross-entropy)DiceLoss(standardDiceLossdefined as1 - DiceCoefficientused for binary semantic segmentation; when more than2 classes are present in the ground truth, it computes theDiceLossper channel and averages the values)BCEDiceLoss(Linear combination of BCE and Dice losses, i.e.alpha * BCE + beta * Dice,alpha, betacan bespecified in thelosssection of the config)CrossEntropyLoss(one can specify class weights via theweight: [w_1, ..., w_k]in thelosssection of theconfig)WeightedCrossEntropyLoss(see 'Weighted cross-entropy (WCE)' in the below paper for a detailed explanation)GeneralizedDiceLoss(see 'Generalized Dice Loss (GDL)' in the below paper for a detailed explanation) Note: use thisloss function only if the labels in the training dataset are very imbalanced e.g. one class having at least 3 ordersof magnitude more voxels than the others. Otherwise, use standardDiceLoss.
For a detailed explanation of some of the supported loss functions see:Generalised Dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations.
MSELoss(mean squared error loss)L1Loss(mean absolute error loss)SmoothL1Loss(less sensitive to outliers than MSELoss)WeightedSmoothL1Loss(extension of theSmoothL1Losswhich allows to weight the voxel values above/below a giventhreshold differently)
MeanIoU(mean intersection over union)DiceCoefficient(computes per channel Dice Coefficient and returns the average)If a 3D U-Net was trained to predict cell boundaries, one can use the following semantic instance segmentation metrics(the metrics below are computed by running connected components on threshold boundary map and comparing the resultedinstances to the ground truth instance segmentation):BoundaryAveragePrecision(Average Precision applied to the boundary probability maps: thresholds the output from thenetwork, runs connected components to get the segmentation and computes AP between the resulting segmentation and theground truth)AdaptedRandError(seehttp://brainiac2.mit.edu/SNEMI3D/evaluation for a detailed explanation)AveragePrecision(seehttps://www.kaggle.com/stkbailey/step-by-step-explanation-of-scoring-metric)
If not specifiedMeanIoU will be used by default.
PSNR(peak signal to noise ratio)MSE(mean squared error)
Training/predictions configs can be found in3DUnet_lightsheet_boundary.Pre-trained model weights availablehere.In order to use the pre-trained model on your own data:
- download the
best_checkpoint.pytorchfrom the above link - add the path to the downloaded model and the path to your data intest_config.yml
- run
predict3dunet --config test_config.yml - optionally fine-tune the pre-trained model with your own data, by setting the
pre_trainedattribute in the YAML config to point to thebest_checkpoint.pytorchpath
The data used for training can be downloaded from the following OSF project:
- training set:https://osf.io/9x3g2/
- validation set:https://osf.io/vs6gb/
- test set:https://osf.io/tn4xj/
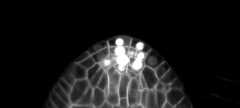
Sample z-slice predictions on the test set (top: raw input , bottom: boundary predictions):
Training/predictions configs can be found in3DUnet_confocal_boundary.Pre-trained model weights availablehere.In order to use the pre-trained model on your own data:
- download the
best_checkpoint.pytorchfrom the above link - add the path to the downloaded model and the path to your data intest_config.yml
- run
predict3dunet --config test_config.yml - optionally fine-tune the pre-trained model with your own data, by setting the
pre_trainedattribute in the YAML config to point to thebest_checkpoint.pytorchpath
The data used for training can be downloaded from the following OSF project:
- training set:https://osf.io/x9yns/
- validation set:https://osf.io/xp5uf/
- test set:https://osf.io/8jz7e/
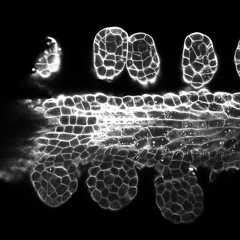
Sample z-slice predictions on the test set (top: raw input , bottom: boundary predictions):
Training/predictions configs can be found in3DUnet_lightsheet_nuclei.Pre-trained model weights availablehere.In order to use the pre-trained model on your own data:
- download the
best_checkpoint.pytorchfrom the above link - add the path to the downloaded model and the path to your data intest_config.yml
- run
predict3dunet --config test_config.yml - optionally fine-tune the pre-trained model with your own data, by setting the
pre_trainedattribute in the YAML config to point to thebest_checkpoint.pytorchpath
The training and validation sets can be downloaded from the following OSF project:https://osf.io/thxzn/
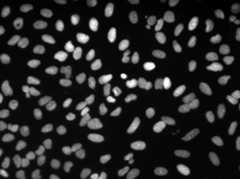
Sample z-slice predictions on the test set (top: raw input, bottom: nuclei predictions):
The data can be downloaded from:https://www.kaggle.com/c/data-science-bowl-2018/data
Training/predictions configs can be found in2DUnet_dsb2018.
Sample predictions on the test image (top: raw input, bottom: nuclei predictions):
If you want to contribute back, please make a pull request.
If you use this code for your research, please cite as:
@article {10.7554/eLife.57613,article_type = {journal},title = {Accurate and versatile 3D segmentation of plant tissues at cellular resolution},author = {Wolny, Adrian and Cerrone, Lorenzo and Vijayan, Athul and Tofanelli, Rachele and Barro, Amaya Vilches and Louveaux, Marion and Wenzl, Christian and Strauss, Sören and Wilson-Sánchez, David and Lymbouridou, Rena and Steigleder, Susanne S and Pape, Constantin and Bailoni, Alberto and Duran-Nebreda, Salva and Bassel, George W and Lohmann, Jan U and Tsiantis, Miltos and Hamprecht, Fred A and Schneitz, Kay and Maizel, Alexis and Kreshuk, Anna},editor = {Hardtke, Christian S and Bergmann, Dominique C and Bergmann, Dominique C and Graeff, Moritz},volume = 9,year = 2020,month = {jul},pub_date = {2020-07-29},pages = {e57613},citation = {eLife 2020;9:e57613},doi = {10.7554/eLife.57613},url = {https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.57613},keywords = {instance segmentation, cell segmentation, deep learning, image analysis},journal = {eLife},issn = {2050-084X},publisher = {eLife Sciences Publications, Ltd},}A development environment can be created via conda:
conda env create --file environment.yamlconda activate 3dunetpip install -e .Tests can be run viapytest.The device the tests should be run on can be specified with the--device argument (cpu,mps, orcuda - default:cpu).Linting is done viaruff (seepyproject.toml for configuration).
To release a new version ofpytorch-3dunet on theconda-forge channel, follow these steps:
- In the
mainbranch: runbumpversion patch(ormajororminor) - this will bump the version in.bumpversion.cfgand__version__.pyadd create a new tag - Run
git push && git push --tagsto push the changes to GitHub - Make a new release on GitHub using the new tag
- Generate the checksums for the new release using:
curl -sL https://github.com/wolny/pytorch-3dunet/archive/refs/tags/VERSION.tar.gz | openssl sha256. ReplaceVERSIONwith the new release version - Fork the
conda-forgefeedstock repository (https://github.com/conda-forge/pytorch-3dunet-feedstock) - Clone the forked repository and create a new PR with the following changes:
- Update the
versioninrecipe/meta.yamlto the new release version - Update the
sha256inrecipe/meta.yamlto the new checksum
- Update the
- Wait for the checks to pass. Once the PR is merged, the new version will be available on the
conda-forgechannel
About
3D U-Net model for volumetric semantic segmentation written in pytorch
Topics
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Sponsor this project
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.