- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork10
A simple approach to learning the beginnings of Redux in Swift.
License
juliobertolacini/ReduxPaperSwift
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
A simple approach to learning the beginnings of Redux in Swift.
Click here to change the language of this article to Portuguese.
Redux is the implementation of an architectural software pattern that prioritizes unidirectional data flow.Created from the Flux architecture (developed by Facebook), it has grown considerably in the development of applications and promises great advantages in its use.It is an alternative to other architectural patterns such as: MVC, MVVM and Viper.
One of the great promises of Redux is to create constraints that encourage a more organized software development and easier to test, so for these reasons, ends up reducing the complexity in the development phase as well as offering facilities in maintaining the application state and advanced debugging.
This article describes a simple approach to beginning to understand this new pattern.
- Basic level in building applications on iOS (Swift + Xcode).
- Knowledge ofObserver pattern.
- Know how to use theCocoaPods dependency system.
- State: Represents the state of the application. There must be only one, which can be divided into sub-states.
- Actions: These are simple objects that describe what the system can do. These objects can carry information or not, depending on the case. They are dispatched by the View layer as intentions to change the state of the application.
- Reducers: This is where we develop the main logic of the application. Reducers must be pure functions with no side effects and must be synchronous. They are the only objects that can create a new state for the application. They are given an action and the current state, and they return a new state.
Notice that the unidirectional flow happens when the View dispatches an Action. This Action is passed to the corresponding Reducer, so this Reducer generates a new State according to the previous Action, and the State is passed back to the View so that it is changed.
- Store: It is one of the most important components of this implementation. It is what aggregates all the components mentioned above and makes the flow work. View dispatches a new Action to the Store. The Store then passes this Action to Reducer along with the current State and then receives the Reducer's new State back. The View is warned whenever a new State is created, this is possible by implementing theObserver design pattern that allows View to become a "subscriber" of the Store to be notified.
My approach to begin to learn Redux is to build a sample application - a "Rock, Paper and Scissors" game - using a library called ReSwift that implements the concepts of this architecture in Swift.
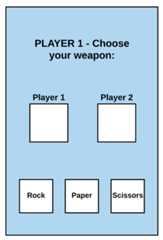
We begin by sketching what the application should look like. For simplicity, the application should work on a single ViewController, containing 3 buttons at the bottom (Rock, Paper and Scissors), 1 message field at the top, and 2 placeholders to show when a player has already made his move and at the end to reveal the weapons of the players.
To start the development I proposed a use case in which Player1 choosesScissors and Player2 choosesRock, resulting in Player2's victory. This flow would happen as follows:
Create a new "Single view application" project in Xcode and enable "Include Unit Tests" to be able to make a test using the concepts of Redux.
Install the"ReSwift" pod usingCocoaPods.
Next we will create the first component, theState. Looking at the images above, we can see clearly the parts of the app that will change during execution, each part of which consists of the state of the application. I then created aState.swift file and placed the state-forming structures inside it, along with possible template structures that form the concept of the application. It is important to point out that the structures must be immutable so that Redux works, only then we ensure that the State is changed exclusively by the Reducers, so I used Structs and Enums instead of Classes:
import ReSwift// MARK:- STATEstructAppState:StateType{varmessage:Messagevarturn:Turnvarplayer1Play:Playvarplayer2Play:Playvarresult:Result?init(){self.message=.player1chooseself.turn=Turn(player:.one)self.player1Play=Play(chosen:false, weapon:nil)self.player2Play=Play(chosen:false, weapon:nil)}}// MARK:- MODEL & OPTIONSenumMessage:String{case player1choose="PLAYER 1 - Choose your weapon:"case player2choose="PLAYER 2 - Choose your weapon:"case player1wins="PLAYER 1 WINS!"case player2wins="PLAYER 2 WINS!"case draw="DRAW!"}structTurn{varplayer:Player}enumPlayer{case onecase two}structPlay{varchosen:Boolvarweapon:Weapon?}enumWeapon:String{case rock="Rock"case paper="Paper"case scissors="Scissors"}enumResult{case drawcase player1winscase player2wins}
Now let's create an Action, which will be the description of an action that intends to change the State. In this case we have only one, ChooseWeaponAction, which is triggered when each player chooses a weapon:
import ReSwift// MARK:- ACTIONSstructChooseWeaponAction:Action{varweapon:Weapon}
Finally we shall build the Reducer. Here we filter the Action created, we take the current state of the application and generate a new State based on the logic that we will develop with the information contained in Action:
import ReSwift// MARK:- REDUCERSfunc appReducer(action:Action, state:AppState?)->AppState{ // creates a new state if one does not already existvarstate= state??AppState()switch action{caseletchooseWeaponAction asChooseWeaponAction:letturn= state.turnswitch turn.player{case.one: // create a playletplay=Play(chosen:true, weapon: chooseWeaponAction.weapon) state.player1Play= play // pass the turn to the next player state.turn=Turn(player:.two) // change the message state.message=.player2choosecase.two: // create a playletplay=Play(chosen:true, weapon: chooseWeaponAction.weapon) state.player2Play= play // calculate who wonletplayer1weapon= state.player1Play.weapon??.rockletplayer2weapon= state.player2Play.weapon??.rockswitch player1weapon{case.rock:switch player2weapon{case.rock: state.result=.draw state.message=.drawcase.paper: state.result=.player2wins state.message=.player2winscase.scissors: state.result=.player1wins state.message=.player1wins}case.paper:switch player2weapon{case.rock: state.result=.player1wins state.message=.player1winscase.paper: state.result=.draw state.message=.drawcase.scissors: state.result=.player2wins state.message=.player2wins}case.scissors:switch player2weapon{case.rock: state.result=.player2wins state.message=.player2winscase.paper: state.result=.player1wins state.message=.player1winscase.scissors: state.result=.draw state.message=.draw}}}default:break} // return the new statereturn state}
Done, simple like that, we've implemented a Redux pattern with unidirectional flow. To show the ease of testing this type of architecture, I built this XCTest class that tests application logic without even having built a UI Layer (View).
import XCTestimport ReSwift@testableimport ReduxPaperSwiftclassReduxPaperSwiftTests:XCTestCase{ // testing whether a rule works.func test1(){letstore=Store<AppState>(reducer: appReducer, state:nil) // Player 1 choose store.dispatch(ChooseWeaponAction(weapon:.rock)) // Player 2 choose store.dispatch(ChooseWeaponAction(weapon:.scissors)) // Check resultXCTAssertEqual(store.state.result,.player1wins)} // testing whether another rule works.func test2(){letstore=Store<AppState>(reducer: appReducer, state:nil) // Player 1 choose store.dispatch(ChooseWeaponAction(weapon:.rock)) // Player 2 choose store.dispatch(ChooseWeaponAction(weapon:.paper)) // Check resultXCTAssertEqual(store.state.result,.player2wins)}}
Finally, I created a ViewController with the characteristics shown in the sketch drawing, and made this ViewController become a "subscriber" of the Store, so I can perform a change in the views whenever the State changes. This happens with the implementation of the StoreSubscriber protocol:
import UIKitimport ReSwiftclassViewController:UIViewController,StoreSubscriber{@IBOutlet weakvarmessage:UILabel!@IBOutlet weakvarplaceholder1:UILabel!@IBOutlet weakvarplaceholder2:UILabel!@IBActionfunc rockButton(_ sender:Any){ store.dispatch(ChooseWeaponAction(weapon:.rock))}@IBActionfunc paperButton(_ sender:Any){ store.dispatch(ChooseWeaponAction(weapon:.paper))}@IBActionfunc scissorsButton(_ sender:Any){ store.dispatch(ChooseWeaponAction(weapon:.scissors))}overridefunc viewDidLoad(){ super.viewDidLoad() store.subscribe(self)}func newState(state:AppState){ message.text= state.message.rawValueif state.player2Play.chosen{ placeholder1.text= state.player1Play.weapon?.rawValue placeholder2.text= state.player2Play.weapon?.rawValue}else{ placeholder1.text= state.player1Play.chosen?"chosen":""}}}
About
A simple approach to learning the beginnings of Redux in Swift.
Topics
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.