- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork1
el-moudni-hicham/genetic-algorithm-find-word
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
- Genetic Algorithm Definition
- Genetic Algorithm Pseudocode
- Genetic Algorithm Steps
- Example Implementation in Java to Guess a Word
Genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionaryalgorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems by relyingon biologically inspired operators such as mutation, crossover and selection .
STARTGeneratetheinitialpopulationComputefitnessREPEATSelectionCrossoverMutationComputefitnessUNTILpopulationhasconvergedSTOP
Population ChromosomeGenesEncoding MethodsFitness FunctionFive phases are considered in a genetic algorithm :
- Initial population
- Fitness function
- Selection
- Crossover
- Mutation
Initial Population
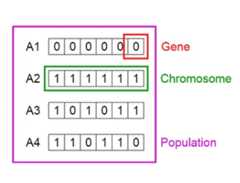
The process begins with a set of individuals which is called a Population. Each individual is a solution to the problem you want to solve.An individual is characterized by a set of parameters (variables) known as Genes. Genes are joined into a string to form a Chromosome (solution).
Fitness Function
The fitness function determines how fit an individual is (the ability of an individual to compete with other individuals). It gives a fitness score to each individual. The probability that an individual will be selected for reproduction is based on its fitness score.
Selection
The idea of selection phase is to select the fittest individuals and let them pass their genes to the next generation.Two pairs of individuals (parents) are selected based on their fitness scores.
Crossover
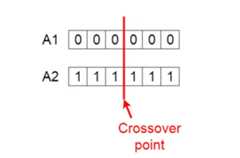
Crossover is the most significant phase in a genetic algorithm. For each pair of parents to be mated, a crossover point is chosen at random from within the genes.
Offspring are created by exchanging the genes of parents among themselves until the crossover point is reached. |  |
Mutation
Mutation occurs to maintain diversity within the population and prevent premature convergence.
Termination
The algorithm terminates if the population has converged. Then it is said that the genetic algorithm has provided a set of solutions to our problem.
Initial population
- Create Individual :
packagema.enset.entites;importjava.util.Random;publicclassIndividualimplementsComparable{// chromosomeprivatechargenes[] =newchar[4];privateintfitness;privateStringtarget ="sdia";privateStringalphabets ="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";publicIndividual() {for (inti=0 ;i <genes.length ;i++){genes[i] =alphabets.charAt(newRandom().nextInt(alphabets.length())); } }// Calculate Fitness Value FunctionpublicintgetFitness() {returnfitness; }publicchar[]getGenes() {returngenes; }@OverridepublicintcompareTo(Objecto) {Individualindividual = (Individual)o;if (this.getFitness() < ((Individual)o).getFitness())return -1;elseif (this.getFitness() > ((Individual)o).getFitness())return1;return0; }}
- Initialize Population :
publicvoidinitializePopulation(){for (inti =0;i <populaion ;i++) {individuals.add(newIndividual()); } }
Fitness function
publicvoidcalculateFitness(){fitness =0;intfitnessValues[] =newint[4];inti =0;for (intgene :genes) {intgeneValueFromTarget =gene -target.charAt(i);if (geneValueFromTarget <0)geneValueFromTarget =Math.abs(geneValueFromTarget);fitnessValues[i] =geneValueFromTarget;i ++; }for (intfv:fitnessValues) {fitness +=fv; } }
Selection
publicvoidselection(){firstFitness =individuals.get(0);secondFitness =individuals.get(1); }
Crossover
publicvoidcrossover(){intcrossoverPoint =1 +newRandom().nextInt(4);Individualindividual1 =newIndividual();Individualindividual2 =newIndividual();for (inti =0;i <individual1.getGenes().length;i++) {individual1.getGenes()[i] =firstFitness.getGenes()[i];individual2.getGenes()[i] =secondFitness.getGenes()[i]; }for (inti =0;i <crossoverPoint;i++) {individual1.getGenes()[i] =secondFitness.getGenes()[i];individual2.getGenes()[i] =firstFitness.getGenes()[i]; }individuals.set(0,individual1);individuals.set(1,individual2);//System.out.println("Crossover Point : " + crossoverPoint); }
Mutation
publicvoidmutation(){intindex =random.nextInt(4);for (inti =0;i <target.length();i++) {if(individuals.get(0).getGenes()[index] !=target.charAt(i))individuals.get(0).getGenes()[index] =target.charAt(random.nextInt(4));index =random.nextInt(4);if(individuals.get(1).getGenes()[index] !=target.charAt(i))individuals.get(1).getGenes()[index] =target.charAt(random.nextInt(4)); } }
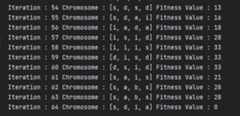
- TEST :Word to Guess
sdia
- TEST :Word to Guess
About
This repository contains a Java implementation of a genetic algorithm designed to find a specific word.
Topics
Resources
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.