- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork32
Large-Scale Visual Representation Model
License
deepglint/unicom
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
This repository focuses on building foundational visual models for large multimodal language models using large-scale datasets such as LAION400M and COYO700M. We employ sample-to-cluster contrastive learning to optimize performance. Our models are primarily used for multimodal visual large language models, such as LLaVA.
We adopted the officialLLaVA-NeXT and the official training datasetLLaVA-NeXT-Data for evaluating the foundational visual models.
The language model is Qwen2.5-7B.
| Vision Tower | RoPE2D | ChartQA | DocVQA | InfoVQA | OCRBench | MMMU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLIP (ViT-L-14-336px) | × | 66.52 | 75.21 | 38.88 | 525.00 | 44.20 |
| SigLIP (ViT-SO400M-384px) | × | 69.28 | 76.71 | 41.38 | 554.00 | 46.78 |
| DFN5B (ViT-H-14-378px) | × | 64.36 | 70.87 | 38.59 | 473.00 | 48.00 |
| HF:MLCD (ViT-L-14-336px) | × | 67.84 | 76.46 | 43.48 | 531.00 | 44.30 |
| HF:MLCD (ViT-bigG-14-336px) | √ | 71.07 | 79.63 | 44.38 | 572.00 | 46.78 |
| HF:MLCD (ViT-bigG-14-448px) | √ | 73.80 | 83.34 | 46.59 | 582.00 | 46.00 |
The results of the ImageNet linear probe are as follows:
| Model Name | ImageNet Linear Probe | Hugging Face |
|---|---|---|
| MLCD-ViT-B-32-224px | 79.1 | HF:MLCD-ViT-B-32-224px |
| MLCD-ViT-L-14-336px | 86.3 | HF:MLCD-ViT-L-14-336px |
| MLCD-ViT-bigG-14-224px | 87.1 | HF:MLCD-ViT-bigG-14-224px |
Here is an example of how to use theMLCDVisionModel from the Transformers library for feature extraction. Please note that this requires thetransformers library from themaster branch. We will update this with a specific version number in the future.
# pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers@v4.51.3-MLCD-previewimportrequestsfromPILimportImagefromtransformersimportAutoProcessor,MLCDVisionModelimporttorch# Load model and processormodel=MLCDVisionModel.from_pretrained("DeepGlint-AI/mlcd-vit-bigG-patch14-448")processor=AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("DeepGlint-AI/mlcd-vit-bigG-patch14-448")# Process single imageurl="http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"image=Image.open(requests.get(url,stream=True).raw)inputs=processor(images=image,return_tensors="pt")# Generate outputswithtorch.no_grad():outputs=model(**inputs)# Get visual featuresfeatures=outputs.last_hidden_stateprint(f"Extracted features shape:{features.shape}")
More details about MLCD-Embodied can be found in theMLCD-Embodied file.
| Dataset | Split | MLCD-Embodied-7B | LLaVA OneVision-7B | GPT-4v | GPT-4o |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vision Encoder | - | MLCD-ViT-L-14-336px | SigLIP | - | - |
| ChartQA | test | 83.0 | 80.0 | 78.5 | 85.7 |
| DocVQA | test | 91.6 | 87.5 | 88.4 | 92.8 |
| InfoVQA | val | 73.9 | 70.7 | - | - |
| InfoVQA | test | 70.0 | 68.8 | - | - |
| MMMU | val | 47.3 | 48.8 | 56.8 | 69.1 |
| MMStar | test | 58.5 | 61.7 | 57.1 | 63.9 |
| OCRBench | - | 749.0 | 697.0 | 656.0 | 805.0 |
| RealWorldQA | test | 68.9 | 66.3 | 61.4 | 58.6 |
| SeedBench | image | 74.9 | 75.4 | 49.9 | 76.2 |
| MME | test | 578/1603 | 418/1580 | 517/1409 | - |
More details about MLCD can be found in theMLCD.md file.
While CLIP models have shown excellence in many tasks via image-text contrastive learning, they often struggle with encoding complex semantic structures within images. To address this limitation, we introduceMulti-Label Cluster Discrimination (MLCD).
MLCD improves upon traditional approaches by clustering the the LAION dataset, which contains billions of images, into one million centers and assigning multiple closest clusters as labels to each image. This technique accounts for the presence of multiple objects within a single image. We also introduce a novel multi-label classification loss, which separately handles positive and negative class losses, minimizing label ambiguity. Our experiments demonstrate that MLCD achieves state-of-the-art performance in linear probe. Moreover, MLCD shows significant potential when integrated with multimodal large language models. The following two figures compare the evaluation performance of our model on MLLM and Linear Probe. The model we used is ViT-L-14@336px.
For image representation:
- ImageNet pretraining is not universal enough to generalize to diverse open-world objects.
- Supervised learning is not scalable because manual annotation of large-scale training data is time-consuming, costly, and even infeasible.
- Instance discrimination method (e.g., CLIP) can hardly encode the semantic structure of training data, because instance-wise contrastive learning always treats two samples as a negative pair, regardless of their semantic similarity.
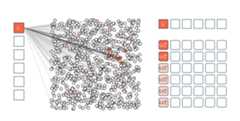
UNICOM demonstrates superior performance in image retrieval, thanks to its ability to cluster400000000 images into1000000 pseudo classes using joint textual and visual features extracted by the CLIP model. Additionally, our use of a margin-based softmax loss (ArcFace) and random partial class/feature (PartialFC) selections enhances the robustness and compactness of the feature embedding. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art unsupervised and supervised image retrieval approaches, making it a powerful tool for researchers and practitioners in the field.
For detailed instructions, please refer to the UNICOMDocumentation.
Thanks so much to all of our amazing contributors!
JiankangDeng | Daixiangzi | Xiang An | Yiyexy | xiaranqing | Athinklo |
Tanhuajie | ZhaoYan-ai | wkzhang636 |
This project would not have been possible without the invaluable contributions of the following individuals, who have been instrumental in data scraping and collection:
Thank you to all the contributors for their hard work and dedication!
| Contributor | Emial |
|---|---|
| Bin Qin | skyqin@gmail.com |
| Lan Wu | bah-wl@hotmail.com |
| Haiqiang Jiang | haiqiangjiang@deepglint.com |
| Yuling Wu | yulingwu@deepglint.com |
@inproceedings{yinxie_2025_rice, title={Region-based Cluster Discrimination for Visual Representation Learning}, author={Xie, Yin and Yang, Kaicheng and An, Xiang and Wu, Kun and Zhao, Yongle and Deng, Weimo and Ran, Zimin and Wang, Yumeng and Feng, Ziyong And Roy, Miles And Ismail, Elezi And Deng, Jiankang}, booktitle={ICCV}, year={2025}}@inproceedings{anxiang_2024_mlcd, title={Multi-label Cluster Discrimination for Visual Representation Learning}, author={An, Xiang and Yang, Kaicheng and Dai, Xiangzi and Feng, Ziyong and Deng, Jiankang}, booktitle={ECCV}, year={2024}}@inproceedings{anxiang_2023_unicom, title={Unicom: Universal and Compact Representation Learning for Image Retrieval}, author={An, Xiang and Deng, Jiankang and Yang, Kaicheng and Li, Jiawei and Feng, Ziyong and Guo, Jia and Yang, Jing and Liu, Tongliang}, booktitle={ICLR}, year={2023}}@inproceedings{anxiang_2022_partialfc, author={An, Xiang and Deng, Jiankang and Guo, Jia and Feng, Ziyong and Zhu, XuHan and Yang, Jing and Liu, Tongliang}, title={Killing Two Birds With One Stone: Efficient and Robust Training of Face Recognition CNNs by Partial FC}, booktitle={CVPR}, year={2022},}@inproceedings{deng_2019_arcface, title={Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition}, author={Deng, Jiankang and Guo, Jia and Xue, Niannan and Zafeiriou, Stefanos}, booktitle={CVPR}, year={2019}}We extend our deepest gratitude to the creators and contributors of the following projects:
- llava-next: The comprehensive codebase for training Vision-Language Models (VLMs).
- lmms-eval: The robust tool for evaluating Vision-Language Models (VLMs).
- OpenEQA: A wonderful benchmark for Embodied Question Answering.
- RoboVQA: Provide high level reasoning model and dataset for robotics.
Their exceptional work has been instrumental to our research and development efforts.
About
Large-Scale Visual Representation Model
Topics
Resources
License
Code of conduct
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Contributors12
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.