Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork102
☕ Symja - computer algebra language & symbolic math library. A collection of popular algorithms implemented in pure Java.
License
axkr/symja_android_library
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Note: this repository contains theJava 11 sources of the core modules. A minimal Android app example can be found in thesymja-example repository:
Try the full-blown Android or iOS apps:
or help testing the latestAndroid BETA version or the web demo atmatheclipse.org.
Read theSymja Manual 📘 for the description of the Symja language orbrowse the available functions 📗 . We encourage everyone to participate in ourWiki.
The different kinds of installations are described in theWiki Installation.
Features of the Symja language:
- arbitrary precision integers, rational and complex numbers. Polynomial, list functions andAssociations
- differentiation,integration,equation solving,linear algebra,number theory,combinatorial,logic and polynomial functions...
- unified connectivity and interoperability throughSymja functions for open source libraries likeHipparchus,Tablesaw,JGraphT,LogicNG,JAS Java Algebra System,apfloat...
- a general purposeTerm Rewriting System and Pattern Matching engine
- use human readable math expression strings or the internal abstract syntax tree (AST) representation to code in Java. See theUnit test examples
- twoJava servlet based notebook interfaces are available in the library. ASymja server for traditional math input and aMMA server for "Mathematica like syntax" input
- twoREPLs are available in the library. AConsole for standard math input and aMMAConsole for "Mathematica like syntax" input.
- new "script-functions" can be developed asPackages and loaded into the system
- developers can use Symja interactively in theJava jshell or with a call to to theJSON Web API Server
- theRubi symbolic integration rules are used to implement theIntegrate function, they can be systematically applied to determine the antiderivative of a wide variety of mathematical expressions
- compiling numeric functions with theJanino Java™ compiler
Appengine web interface symjaweb.appspot.com - available as open source in thisGithub repository
Android App Calculator N+ on Google play store - available as open source in thisGithub repository provides anIDE mode to calculate arbitrary Symja expressions.
Eclipse EASE extension - use Symja as a REPL in Eclipse with thisexample Github repository which contains some Symja example scripts.
To get an idea of the kinds of expressions Symja handles, see theJUnit tests in this file.
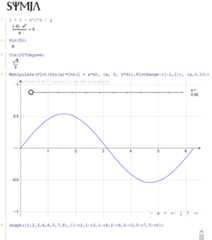
Manipulate(Plot3D(Sin(a * x * y), {x, -1.5, 1.5}, {y, -1.5, 1.5}), {a,1,5})
Plot(Piecewise({{x^2, x < 0}, {x, x >= 0&&x<1},{Cos(x-1), x >= 1}}), {x, -2, 12})
packageorg.matheclipse.core.examples;importorg.matheclipse.core.eval.ExprEvaluator;importorg.matheclipse.core.expression.F;importorg.matheclipse.core.interfaces.IAST;importorg.matheclipse.core.interfaces.IExpr;importorg.matheclipse.core.interfaces.ISymbol;importorg.matheclipse.parser.client.SyntaxError;importorg.matheclipse.parser.client.math.MathException;publicclassExample {publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args) {try {ExprEvaluatorutil =newExprEvaluator(false, (short)100);// Convert an expression to the internal Java form:// Note: single character identifiers are case sensitive// (the "D()" function identifier must be written as upper case// character)StringjavaForm =util.toJavaForm("D(sin(x)*cos(x),x)");// prints: D(Times(Sin(x),Cos(x)),x)System.out.println("Out[1]: " +javaForm.toString());// Use the Java form to create an expression with F.* static// methods:ISymbolx =F.Dummy("x");IASTfunction =F.D(F.Times(F.Sin(x),F.Cos(x)),x);IExprresult =util.eval(function);// print: Cos(x)^2-Sin(x)^2System.out.println("Out[2]: " +result.toString());// Note "diff" is an alias for the "D" functionresult =util.eval("diff(sin(x)*cos(x),x)");// print: Cos(x)^2-Sin(x)^2System.out.println("Out[3]: " +result.toString());// evaluate the last result (% or $ans contains "last answer")result =util.eval("%+cos(x)^2");// print: 2*Cos(x)^2-Sin(x)^2System.out.println("Out[4]: " +result.toString());// evaluate an Integrate[] expressionresult =util.eval("integrate(sin(x)^5,x)");// print: 2/3*Cos(x)^3-1/5*Cos(x)^5-Cos(x)System.out.println("Out[5]: " +result.toString());// set the value of a variable "a" to 10// Note: in server mode the variable name must have a preceding '$'// characterresult =util.eval("a=10");// print: 10System.out.println("Out[6]: " +result.toString());// do a calculation with variable "a"result =util.eval("a*3+b");// print: 30+bSystem.out.println("Out[7]: " +result.toString());// Do a calculation in "numeric mode" with the N() function// Note: single character identifiers are case sensistive// (the "N()" function identifier must be written as upper case// character)result =util.eval("N(sinh(5))");// print: 74.20321057778875System.out.println("Out[8]: " +result.toString());// define a function with a recursive factorial function definition.// Note: fac(0) is the stop condition.result =util.eval("fac(x_Integer):=x*fac(x-1);fac(0)=1");// now calculate factorial of 10:result =util.eval("fac(10)");// print: 3628800System.out.println("Out[9]: " +result.toString());function =F.Function(F.Divide(F.Gamma(F.Plus(F.C1,F.Slot1)),F.Gamma(F.Plus(F.C1,F.Slot2))));// eval function ( Gamma(1+#1)/Gamma(1+#2) ) & [23,20]result =util.evalFunction(function,"23","20");// print: 10626System.out.println("Out[10]: " +result.toString()); }catch (SyntaxErrore) {// catch Symja parser errors hereSystem.out.println(e.getMessage()); }catch (MathExceptionme) {// catch Symja math errors hereSystem.out.println(me.getMessage()); }catch (finalExceptionex) {System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); }catch (finalStackOverflowErrorsoe) {System.out.println(soe.getMessage()); }catch (finalOutOfMemoryErroroome) {System.out.println(oome.getMessage()); } }}
How to use Maven is described in theMaven wiki page.
First, you'll need a Java Development Kit (JDK) compatible with Java 11 or later.
The Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Eclipse is shipped with a suitable JDK, so you don't have to install a JDK by yourself.Install and open the latest version of the Eclipse development IDE for Java Developers:
a) Fork the Symja repository to use as a starting point.
- Navigate togithub.com/axkr/symja_android_library in your browser.
- Click the "Fork" button in the top-right of the page.
- Once your fork is ready, open the new repository's "Settings" by clicking the link in the menu bar on the left.
- Change the repository name to the name of your Library and save your changes.
b) Clone your new repository to your Eclipse workspace.
- Open Eclipse and select the "File -> Import..." menu item.
- Select "Git -> Projects from Git", and click "Next >".
- Select "URI" and click "Next >".
- Enter your repository's clone URL in the "URI" field. The remaining fields in the "Location" and "Connection" groups will get automatically filled in.
- Enter your Github credentials in the "Authentication" group, and click "Next >".
- Select the
masterbranch on the next screen, and click "Next >". - The default settings on the "Local Configuration" screen should work fine, click "Next >".
- Make sure "Import existing projects" is selected, and click "Next >".
- Eclipse should find and select the
symja_android_libraryautomatically, click "Finish".
See thisGit version control with Eclipse (EGit) - Tutorial for a general overview.
If you have any questions about using or developing for this project, send me anemail!
- the complete Symja system is published under the GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE Version 3 (GPL) starting with Symja version 2.0.0 parts are published under the Lesser GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE Version 3 (LGPL).
If you would like to use parts of the system here are some Maven module licenses:
- the maven modules:
parser, external, coreare published under LGPL license. - the maven modules:
gpl, api, ioare published under GPL license.
Here are some of the associatedJava library dependency licenses:
- theTilmanNeumann/java-math-library is published under the GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE license.
- theJAS Java Algebra System is published under the (LESSER) GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE license. The Java bytecode is dual licenced also under the Apache 2.0 license to allow usage in Android projects.
- theJGraphT Library is published under the Eclipse Public License (EPL) or (LESSER) GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE license.
- theapfloat project is published under the MIT License.
- theHipparchus Mathematics Library is published under the Apache software license
- theLogicNG project is published under the Apache software license
- theTablesaw is published under the Apache software license
Here are some of the associatedJavaScript licenses:
- thePaul Masson's Math project is published under the MIT license.
- thePaul Masson's MathCell project is published under the MIT license.
- theJSXGraph project is published under the GNU LGPL or MIT license.
About
☕ Symja - computer algebra language & symbolic math library. A collection of popular algorithms implemented in pure Java.
Topics
Resources
License
Contributing
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Sponsor this project
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.