Designed to be easy to use, extendable and optimized where it's possible.
An EventBus is a mechanism that allows different components to communicate with each other without knowing about each other. A component can send an Event to the EventBus without knowing who will pick it up or how many others will pick it up.
- interface based
- listeners priority sorting
- ability to send functions and messages
- local buses creation with the ability to subscribe as a listener
- timeline compatibility
- filtered messaging
- expandability
// subscriber class definitionpublicclassSampleListener:Subscriber,IListener<GlobalEvent>,// react on GlobalEvent(Enum) messagesIListener<IEvent<GlobalEvent>>,// react on IEvent<GlobalEvent> messagesIDamageTaker,IHandle<IDamageTaker>// provide IDamageTaker interface for invokation
// send enum event to the GlobalBusGlobalBus.Send(GlobalEvent.Activate);// send IEvent<GlobalEvent> with custom dataGlobalBus.SendEvent(GlobalEvent.Activate,1f);// send action to the GlobalBusGlobalBus.SendAction<IDamageTaker>(damageTaker=>damageTaker.TakeDamage(1));// send with filtrationGlobalBus.Send(GlobalEvent.Activate, sub=>subisUnit);
// none MonoBehaviour subscriberpublicclassSampleListenerClass:ISubscriberOptions,// optional priority and name optionsIListener<GlobalEvent>,IDamageTaker,IHandle<IDamageTaker>{// react on sent datapublicvoidReact(inGlobalEvente){if(e==GlobalEvent.GameStart){// do something}}// provide interface for method invocationpublicvoidIDamageTaker.Damage(intdmg){// do something}// subscriber extra optionspublicstringName=>name;// name for debugging purposespublicintPriority=>1;// execution order related to other subscribed listeners// subscription methods (bus can be any, in example used global bus singleton)publicvoidSubscribe()=>GlobalBus.Subscribe(this);publicvoidUnsubscribe()=>GlobalBus.Unsubscribe(this);}Through Unity Package Manager git URL:
https://github.com/NullTale/UnityEventBus.git
Or copy-paste somewhere inside your project Assets folder.
On OnEnable event Listener will connect to the desired bus and will start receiving messages from it.
usingUnityEngine;usingUnityEventBus;// same as SimpleListener : Subscriber, IListener<string>publicclassSimpleListener:Listener<string>{publicoverridevoidReact(instringe){Debug.Log(e);}}In the unity editor, you can set up the behavior in detail. Such as subscription targets and priority.
Note: Lower priority triggers first, highest last, equal invokes in order of subscription
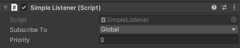
To create your custom listener you need to implement at least oneIListener<> interface and subscribe to the desired bus.
Note: Listener can have any number of IListener<> interfaces.
usingUnityEngine;usingUnityEventBus;publicclassSimpleListener:MonoBehaviour,IListener<string>{privatevoidStart(){// somewhere in code...// send string event to the global busGlobalBus.Send<string>("String event");}// subscribe to the global busprivatevoidOnEnable(){GlobalBus.Subscribe(this);}// unsubscribe from the global busprivatevoidOnDisable(){GlobalBus.UnSubscribe(this);}// react to an eventpublicvoidReact(instringe){Debug.Log(e);}}You can also implementISubscriberOptions interface to setup debug name and listener priority.
publicclassSimpleListener:MonoBehaviour,IListener<string>,ISubscriberOptions{publicstringName=>name;publicintPriority=>1;To create a local bus, you need to derive it from theEventBusBase class
Note: Event bus can be subscribed to the other buses like a listener, using Subscribe and UnSubscribe methods.
usingUnityEngine;usingUnityEventBus;publicclassUnit:EventBusBase{privatevoidStart(){// send event to thisthis.Send("String event");}}You can also derive it from theEventBus class to configure auto-subscription and priority.
Note: If EventBus implements any Subscribers interfaces, they will be automatically subscribed to it.

Sometimes it can be more convenient to look at listeners as a set of interfaces, theSendAction method extension is used for this. For an object to be an action target it must execute an interface IHandle<> with the interface type it provides.
publicclassUnit:EventBus{[ContextMenu("Heal Action")]publicvoidHeal(){// send invoke heal action on the IUnitHP interfacethis.SendAction<IUnitHP>(hp=>hp.Heal(1));}}publicinterfaceIUnitHP{voidHeal(intval);}// implement IHandle<IUnitHP> interface to be an action targetpublicclassUnitHP:Subscriber,IUnitHP,IHandle<IUnitHP>{publicintHP=2;publicvoidHeal(intval){HP+=val;}}Event is a message that contains keys and optional data. To send an Event, theSendEvent extension method is used. To receive events must be implementedIListener<IEvent<TEventKey>> interface, where TEventKey is a key of events, which listener wants to react.
usingUnityEngine;usingUnityEventBus;// unit derived from the EventBus class, he is receives events and propagate them to subscriberspublicclassUnit:EventBusBase{privatevoidStart(){// send creation event without datathis.SendEvent(UnitEvent.Created);}[ContextMenu("Damage")]publicvoidDamageSelf(){// send event with int datathis.SendEvent(UnitEvent.Damage,1);}[ContextMenu("Heal")]publicvoidHealSelf(){this.SendEvent(UnitEvent.Heal,1);}}// unit event keyspublicenumUnitEvent{Created,Damage,Heal}usingUnityEngine;usingUnityEventBus;// OnEnable will subscribe to the unit and start to listen messages// same as UnitHP : EventListener<UnitEvent>publicclassUnitHP:Subscriber,IListener<IEvent<UnitEvent>>{publicintHP=2;// reacts to UnitEventspublicoverridevoidReact(inIEvent<UnitEvent>e){switch(e.Key){// event with damage or heal key always containts int datacaseUnitEvent.Damage:HP-=e.GetData<int>();break;caseUnitEvent.Heal:HP+=e.GetData<int>();break;caseUnitEvent.Created:break;}}}
Also multiple data can be sent through an event.
// send multiple dataSendEvent(UnitEvent.Created,1,0.2f,this);
// get multiple datavar(n,f,unit)=e.GetData<int,float,Unit>();// orif(e.TryGetData(outintn,outfloatf,outUnitunit)){// do something with data}The small extension that allow you to useTimeline.SignalAsset as messages in order to.
React to signals.

Send signals from the director,

or through script or MonoBehaviour.

Request is needed to get permission for something from another subscriber. Request works just like Event, contains key and optional data, but it can be either approved or ignored and he will propagate until first approval. It is in fact a usable event with the only difference that you can get the result of execution. TheSendRequest method extension is used to send a Request.
publicclassUnit:EventBus{[ContextMenu("HealRequest ")]publicvoidHealRequest(){if(this.SendRequest(UnitEvent.Heal,1)){// request was approved// do something, play animation or implement logic}}}publicclassUnitHP:Subscriber,IListener<IRequest<UnitEvent>>{publicintHPMax=2;publicintHP=2;publicvoidReact(inIRequest<UnitEvent>e){switch(e.Key){caseUnitEvent.Heal:{// if can heal, approve heal requestvarheal=e.GetData<int>();if(heal>0&&HP<HPMax){HP+=heal;e.Approve();}}break;}}}





