- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork0
✨ Dive into image denoising magic! This project uses Attention U-Net and PatchGAN to tackle noise types like low Gaussian and salt-and-pepper noise. Perfect for computer vision, deep learning, and generative modeling enthusiasts. Restore clarity to noisy images with cutting-edge AI! 🚀🎨
MahanVeisi8/From-Chaos-to-Clarity-Denoising-Images-with-UNet-and-GANs
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Welcome to an exciting journey into the world of deep learning and image restoration! 🎉 In this project, we dive into the challenge of denoising grayscale facial images, taking on various levels of noise that can obscure the rich emotional expressions captured in the data. Leveraging cutting-edge architectures likeAttention U-Net andGANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), we aim to breathe life back into noisy images and showcase the power of modern neural networks.
The dataset at the heart of this project is derived from the well-knownFER2013 dataset, consisting of pixel-based grayscale images of facial expressions. Our goal? To strip away the noise and let the underlying emotions shine through.
Why does this matter? Noise in images can wreak havoc on tasks like emotion recognition and facial analysis. By addressing three distinct types of noise—low Gaussian noise,high Gaussian noise, andsalt-and-pepper noise—we're not just restoring clarity but also paving the way for more accurate downstream applications.
Here's what makes this project special:
- Attention U-Net Magic: A model that zooms in on the most relevant parts of noisy images, ensuring precision and high fidelity.
- PatchGAN Wizardry: A patch-based GAN approach that brings a unique perspective to denoising, ensuring both local and global coherence.
- Thorough Evaluation: With metrics likePSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio) andSSIM (Structural Similarity Index Measure), alongside stunning visualizations, we provide a comprehensive assessment of our models' performance.
By the end of this project, you’ll see how these advanced models tackle complex noise scenarios and how you can use these insights for your own image restoration challenges. Let’s bring these faces into focus! 😊
Getting started is easy and stress-free! This notebook is designed to run seamlessly on Google Colab, so there’s no complicated setup required. Here's what you’ll need:
- AGoogle Account (we're sure you already have one 😉).
- A workinginternet connection (because, you know, it's the 21st century).
Just hit theOpen in Colab badge above and watch the magic unfold. Colab will take care of everything—from installing the required libraries to preparing the environment. Within minutes, you'll be ready to explore the world of denoising with Attention U-Net and GANs! 🌟
Our dataset consists of compact, grayscale facial images, each sized at48x48 pixels—small but packed with emotional depth! To prepare these images for training, we focused on maintaining their integrity while ensuring uniformity. Each image represents a unique facial expression, making them a perfect candidate for our denoising tasks. 🎭
Here’s how we got the data ready for action:
- Loading and Preprocessing: We extracted images from theFER2013 dataset, applying pixel intensity normalization to ensure consistency across the dataset.
- Splitting the Dataset: The data was divided intotraining,validation, andtest sets, following predefined splits to ensure robust and reproducible results.
Here’s a glimpse of the raw grayscale images, full of potential but needing a bit of a cleanup:
To really test our models’ capabilities, we introducedthree distinct types of noise to mimic real-world scenarios where images might be degraded. These augmentations help us evaluate the robustness of our denoising models under different conditions:
- Low Gaussian Noise: A mild blur effect with a standard deviation of 0.2 and noise factor of 0.2.
- High Gaussian Noise: A heavier distortion with a standard deviation of 0.4 and noise factor of 0.3.
- Salt-and-Pepper Noise: Speckled noise with a noise factor of 0.1, randomly introducing white ("salt") and black ("pepper") pixels.
Here’s how the images look with each type of noise:
Now for the stars of the show! This project features two advanced architectures designed for image restoration:
- Attention U-Net: Equipped with attention mechanisms to focus on the most important regions, making it a champion for precise denoising.
- PatchGAN: A GAN-based model that takes a patch-based approach, balancing local and global noise reduction.
Let’s dive into their design and how they tackle these noisy challenges head-on! 🚀
TheAttention U-Net builds upon the classic U-Net architecture by incorporatingattention mechanisms, enabling the model to focus on relevant regions of the input dynamically. This enhancement ensures effective noise suppression while preserving essential structural and contextual features, making it highly suitable for image denoising tasks.
The Attention U-Net is divided into four components:
classAttentionUNet(nn.Module):def__init__(self,in_channels=1,out_channels=1,use_attention=True,debug=False):super(AttentionUNet,self).__init__()self.debug=debug# Encoderself.enc1=EncoderBlock(in_channels,16)self.enc2=EncoderBlock(16,32)self.enc3=EncoderBlock(32,64)self.enc4=EncoderBlock(64,128)# Bottleneckself.bottleneck=ConvBlock(128,256)# Decoderself.dec4=DecoderBlock(256,128,use_attention=use_attention,debug=debug)self.dec3=DecoderBlock(128,64,use_attention=use_attention,debug=debug)self.dec2=DecoderBlock(64,32,use_attention=use_attention,debug=debug)self.dec1=DecoderBlock(32,16,use_attention=False,debug=debug)# Final Outputself.final_conv=nn.Conv2d(16,out_channels,kernel_size=1)
- Encoder:
- Each
EncoderBlockconsists of convolutional layers for feature extraction and max-pooling for downsampling. - Optionalattention modules refine features by focusing on spatially important regions based on the input context.
- Each
classEncoderBlock(nn.Module):def__init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,use_attention=False,stride=2,padding=0,debug=False):super(EncoderBlock,self).__init__()self.conv=ConvBlock(in_channels,out_channels)self.pool=nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=stride,padding=padding)ifuse_attention:self.attention=AttentionBlock(out_channels,out_channels,out_channels)
Bottleneck:
- A dense
ConvBlockbridges the encoder and decoder, aggregating global context to capture high-level features.
- A dense
Decoder:
- Each
DecoderBlockupsamples the feature maps using transposed convolutions, enabling reconstruction at higher resolutions. - Skip connections integrate fine-grained details from the encoder for precise restoration.
- Attention mechanisms selectively refine the reconstructed features, helping prioritize meaningful information.
- Each
classDecoderBlock(nn.Module):def__init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,use_attention=False,debug=False):super(DecoderBlock,self).__init__()self.upconv=nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=2,stride=2)self.conv=ConvBlock(out_channels*2,out_channels)ifuse_attention:self.attention=AttentionBlock(out_channels,out_channels,out_channels)
- Output Layer:
- A single convolutional layer reduces the feature map to the target image dimensions, reconstructing the output to match the original image size (1 * 48 * 48).
The Attention U-Net was trained using a carefully designed configuration:
Loss Function: Mean Squared Error (MSE) ensures pixel-wise consistency between the denoised output and the clean ground truth. This choice balances simplicity and effectiveness for grayscale image restoration.
Optimization:
- Optimizer: Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of
1e-3ensures fast convergence. - Scheduler: A ReduceLROnPlateau scheduler dynamically lowers the learning rate when validation loss stagnates, preventing overfitting and improving generalization.
- Optimizer: Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of
ThePatchGAN framework combines the power of a generator (Attention U-Net) and a discriminator to refine the denoising process. The generator produces denoised outputs, while the discriminator evaluates their authenticity by focusing on both global structure and local detail. This dynamic adversarial training ensures that the denoised images are visually realistic and contextually accurate.
TheAttention U-Net, discussed earlier, serves as the generator in this setup. Its attention mechanisms allow it to focus on noise-free regions of the input, ensuring high-quality reconstruction of the denoised output.
The discriminator,PatchGANDiscriminator, takes the denoised output from the generator and evaluates it against the ground truth (clean image). It does this by processing pairs of noisy-clean images or noisy-generated images and assessing their "realness" at a patch level.
classPatchGANDiscriminator(nn.Module):def__init__(self,in_channels=2,base_channels=32,stride=[2,2,2,2,2,2],padding=[0,0,0,0,0,0],use_fc=False,global_pooling=False,debug=False):super(PatchGANDiscriminator,self).__init__()self.debug=debugself.use_fc=use_fcself.global_pooling=global_pooling# Encoder layersself.enc1=EncoderBlock(in_channels,base_channels,use_attention=True,stride=stride[0],padding=padding[0],debug=debug)self.enc2=EncoderBlock(base_channels,base_channels*2,use_attention=False,stride=stride[1],padding=padding[1],debug=debug)self.enc3=EncoderBlock(base_channels*2,base_channels*4,use_attention=True,stride=stride[2],padding=padding[2],debug=debug)# Final convolutionself.final_conv=nn.Conv2d(base_channels*2,1,kernel_size=2,stride=stride[5],padding=padding[5])# Fully connected layersifself.use_fc:self.fc_dim=12*12self.fc=nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(base_channels*2,self.fc_dim),nn.Tanh(),# Activation functionnn.Linear(self.fc_dim,self.fc_dim),nn.Tanh() )defforward(self,x,y):combined=torch.cat([x,y],dim=1)# Encoder forward passfeatures,downsampled=self.enc1(combined)features,downsampled=self.enc2(downsampled)features,downsampled=self.enc3(downsampled)out=self.final_conv(features)# Shape: (B, 1, H', W')ifself.use_fc:batch_size,channels,height,width=features.shapeifself.global_pooling:pooled_features=torch.mean(features,dim=[2,3])flattened=pooled_features.view(batch_size,-1)else:flattened=features.view(batch_size,-1)fc_out=self.fc(flattened)out=fc_out.view(batch_size,1,height,width)returnout
The discriminator operates ontwo inputs, concatenated channel-wise:
- A noisy image (real or generated).
- A clean image (ground truth or generated).
By processing these inputs through its encoder layers, the discriminator outputs a matrix ofpatch-based predictions, where each score corresponds to the "realness" of a patch in the image.
To stabilize training,label smoothing is applied:
- Real patches are labeled as0.9, preventing the discriminator from becoming overly confident.
- Fake patches are labeled as0.1, encouraging the generator to refine its outputs.
The training process involves a careful balance between the generator and discriminator. Thegenerator loss combines two objectives:
- Reconstruction loss (L2): Ensures pixel-level accuracy by minimizing the difference between the denoised output and the clean image.
- Adversarial loss: Encourages the generator to produce images that the discriminator classifies as "real".
Thediscriminator loss evaluates how effectively the discriminator distinguishes between real and fake patches. It combines the binary cross-entropy losses for real and fake predictions.
gen_loss=l2_loss+0.001*adversarial_lossdisc_loss= (real_loss+fake_loss)/2
Training is optimized using Adam for both generator and discriminator, with a learning rate of1e-3. AReduceLROnPlateau scheduler is used to dynamically adjust the learning rate when validation loss plateaus, ensuring better generalization.
This combination of patch-based evaluation, adversarial loss, and careful optimization results in a robust denoising process, capable of producing visually coherent and contextually accurate outputs.
After training the models, it's time to put them to the test! We evaluated theAttention U-Net andPatchGAN on the noisy test set acrossthree distinct tasks, each addressing a specific type of noise. These tasks simulate real-world noise scenarios, challenging the models to restore clarity and preserve structural details.
Here’s a breakdown of the tasks:
- Task 1: Denoising images corrupted withLow Gaussian Noise—a mild yet noticeable distortion.
- Task 2: TacklingHigh Gaussian Noise—a more aggressive form of degradation.
- Task 3: ManagingSalt-and-Pepper Noise—a speckled, impulsive noise pattern.
In this task, we focus on denoising grayscale images withlow Gaussian noise, which mimics mild real-world distortions. Both theAttention U-Net andPatchGAN models were trained and evaluated for this purpose. Below, we present the denoised results and analyze the performance of the models.
TheAttention U-Net showed impressive performance in denoising low Gaussian noise. Below are some reconstructed samples: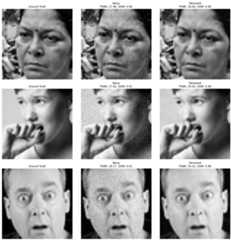
ThePatchGAN model was also tested, and while it produced satisfactory outputs, theAttention U-Net was more consistent in metrics. Here are some results from the PatchGAN model:
The evaluation was conducted on thetest set, and the results for both models are summarized below:
| Model | Loss | PSNR | SSIM | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attention U-Net | 0.0039 | 30.1480 | 0.9593 | In low-noise scenarios, Attention U-Net excels due to its focused attention mechanisms, achieving high fidelity and structural similarity. |
| PatchGAN | 0.0064 | 21.9678 | 0.9221 | The PatchGAN struggled slightly due to its reliance on adversarial training, which can overemphasize visual realism over quantitative accuracy. |
In the second task, we tackled the challenge of denoising grayscale images corrupted withhigh Gaussian noise, which mimics severe real-world distortions. This task pushed the limits of bothAttention U-Net andPatchGAN, evaluating their robustness in reconstructing heavily degraded images.
TheAttention U-Net proved to be a strong contender, leveraging its attention mechanisms to selectively focus on key areas of the image. Here are some reconstructed samples:
ThePatchGAN, while making modest improvements, struggled to handle the intensity of high Gaussian noise. Below are some generated outputs:
The comparative results on thetest set are summarized below:
| Model | Loss | PSNR | SSIM | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attention U-Net | 0.0161 | 23.9465 | 0.8720 | The U-Net demonstrates its robustness in handling high noise levels, though the complexity of this task led to a drop in metrics compared to Task 1. |
| PatchGAN | 0.0270 | 15.6816 | 0.7745 | PatchGAN struggled to capture finer details under severe noise. A simpler GAN architecture might achieve better results by focusing more on structural accuracy. |
The results highlight that whileAttention U-Net outshinesPatchGAN, the increased noise severity remains a significant challenge for both models. These findings pave the way for future innovations, such as refining GAN architectures or introducing advanced loss functions tailored to handle intense noise scenarios.
For our final task, we explored the ability ofAttention U-Net to tacklesalt-and-pepper noise, a common form of impulse noise characterized by random "salt" (white) and "pepper" (black) pixels. While traditional techniques like median filtering are effective, we evaluated the performance of a deep learning approach on this challenge.
TheAttention U-Net excelled at restoring clarity to images corrupted by salt-and-pepper noise, effectively suppressing artifacts while preserving details. Below are some reconstructed samples:
Thetest set results for salt-and-pepper noise are summarized below:
| Model | Loss | PSNR | SSIM | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attention U-Net | 0.0037 | 30.3950 | 0.9774 | The model achieved impressive results, demonstrating its ability to handle impulse noise with fidelity comparable to classical median filtering techniques. |
Salt-and-pepper noise is traditionally managed using simple filtering techniques like themedian filter, which is computationally efficient and effective:
Image took fromthis aricle
However, theAttention U-Net showed that deep learning models can match or even exceed classical methods, especially when integrated into larger pipelines. On the other hand, theGAN model struggled with this task, underscoring the need for specialized architectures or pre-processing steps for sparse, abrupt noise patterns. Future work could focus on:
- Designinghybrid approaches combining deep learning with classical filtering for optimal performance.
- Exploringbetter custom GAN architectures tailored for impulse noise scenarios.
- Trying simpler GAN generator and discriminators and reach a higher performance results.
- Investigatingdomain adaptation techniques for models trained on one noise type to generalize better to other noise types.
In this project, we journeyed through the challenges of denoising grayscale facial emotion images using advanced architectures likeAttention U-Net andPatchGAN. Here’s what we learned:
- Attention U-Net's Superiority: Across all tasks, theAttention U-Net consistently outperformed thePatchGAN, showcasing its robustness and adaptability to diverse noise types.
- The Potential of GANs: AlthoughPatchGAN struggled with structural fidelity, it laid a foundation for exploring refined GAN architectures in future work.
- Noise-Specific Strategies Matter: From low Gaussian noise to salt-and-pepper noise, each task demanded unique model capabilities, reinforcing the importance of tailoring approaches to specific noise types.
This exploration not only demonstrated the power of deep learning in denoising but also highlighted areas for future innovation. Whether it's refining architectures, experimenting with hybrid methods, or tackling new noise patterns, the journey to crystal-clear imagery is far from over!
If you found this project exciting or helpful, please considerstarring it on GitHub! ⭐
Your support helps inspire more innovative projects and keeps the momentum going. 🚀
About
✨ Dive into image denoising magic! This project uses Attention U-Net and PatchGAN to tackle noise types like low Gaussian and salt-and-pepper noise. Perfect for computer vision, deep learning, and generative modeling enthusiasts. Restore clarity to noisy images with cutting-edge AI! 🚀🎨
Topics
Resources
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.



