The ‘FastKRR’ implements its core computational operations in C++ via‘RcppArmadillo’, enabling faster performance than pure R, improvednumerical stability, and parallel execution with OpenMP where available.On systems without OpenMP support, the package automatically falls backto single-threaded execution with no user configuration required. Forefficient model selection, it integrates with ‘CVST’ to providesequential-testing cross-validation that identifies competitivehyperparameters without exhaustive grid search. The package offers aunified interface for exact kernel ridge regression and three scalableapproximations—Nyström, Pivoted Cholesky, and Random FourierFeatures—allowing analyses with substantially larger sample sizes thanare feasible with exact KRR. It also integrates with the ‘tidymodels’ecosystem via the ‘parsnip’ model specification ‘krr_reg’, the S3 method‘tunable.krr_reg()’, and the direct fitting helper ‘fit_krr()’.
Dependencies: Rcpp, RcppArmadillo, CVST,parsnip
This package usesCVST (GPL ≥ 2). Overall license:GPL (≥ 2).
FastKRR is available both on CRAN (stable release) and GitHub(development version).
This installs the latest stable version. On macOS (with Clangcompiler), CRAN binaries are built without OpenMP support. If you needOpenMP, see the note below about installing from source.
# CRAN binary (no OpenMP on macOS)install.packages("FastKRR")# CRAN source build (enables OpenMP if configured)# install.packages("FastKRR", type="source")This installs the development version (always built from source).
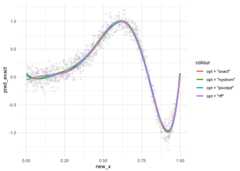
# install.packages("pak")pak::pak("kybak90/FastKRR")This is a basic example of fitting a Gaussian kernel ridge regressionestimator to a dataset\({(x_i,y_i)}_{i=1}^n\) using (1) exact computation, (2) pivoted Choleskydecomposition, (3) Nyström approximation, and (4) random Fourierfeatures.
library(FastKRR)# example data setset.seed(1)n=1000rho=1X=runif(n,0,1)y=sin(2*pi*X^3)+rnorm(n,0,0.1)# model fitting - exactmodel_exact=fastkrr(X, y,kernel ="gaussian",rho = rho,opt ="exact",verbose =FALSE)# model fitting - pivotedmodel_pivoted=fastkrr(X, y,kernel ="gaussian",rho = rho,opt ="pivoted",verbose =FALSE)# model fitting - nystrommodel_nystrom=fastkrr(X, y,kernel ="gaussian",rho = rho,opt ="nystrom",verbose =FALSE)# model fitting - rffmodel_rff=fastkrr(X, y,kernel ="gaussian",rho = rho,opt ="rff",verbose =FALSE)# predictionnew_n=500new_x=matrix(runif(new_n,0,1),nrow = new_n)pred_exact=predict(model_exact, new_x)pred_pivoted=predict(model_pivoted, new_x)pred_nystrom=predict(model_nystrom, new_x)pred_rff=predict(model_rff, new_x)The visualization of the fitted results is shown below.
library(ggplot2)data=data.frame(new_x)data$pred_exact=as.numeric(pred_exact)data$pred_pivoted=as.numeric(pred_pivoted)data$pred_nystrom=as.numeric(pred_nystrom)data$pred_rff=as.numeric(pred_rff)data_train=data.frame(x = X,y = y)ggplot(data = data)+geom_line(aes("x"= new_x,"y"= pred_exact,color ='opt = "exact"'),linewidth=1.2)+geom_line(aes("x"= new_x,"y"= pred_pivoted,color ='opt = "pivoted"'),linewidth=1.2)+geom_line(aes("x"= new_x,"y"= pred_nystrom,color ='opt = "nystrom"'),linewidth=1.2)+geom_line(aes("x"= new_x,"y"= pred_rff,color ='opt = "rff"'),linewidth=1.2)+geom_point(data = data_train,aes(x = x,y = y),col ="gray",alpha =0.2)+theme_minimal()
# Ensure Command Line Tools (if not already installed)xcode-select --install || true# Install/update Homebrew libompbrew updatebrew install libomp~/.R/Makevars (works for Apple Silicon & Intel)Copy the block below into~/.R/Makevars (create the fileif it does not exist).
# OpenMP on macOS with Apple Clang # Try to detect Homebrew prefix; fallback covers both Apple Silicon & Intel.HOMEBREW_PREFIX := $(shell brew --prefix 2>/dev/null)ifeq ($(strip $(HOMEBREW_PREFIX)),) HOMEBREW_PREFIX := /opt/homebrewendif# Include & lib paths (also add Intel path as extra fallback)CPPFLAGS += -I$(HOMEBREW_PREFIX)/opt/libomp/include -I/usr/local/opt/libomp/includeLDFLAGS += -L$(HOMEBREW_PREFIX)/opt/libomp/lib -L/usr/local/opt/libomp/lib# Standard R variables for OpenMPSHLIB_OPENMP_CFLAGS = -Xpreprocessor -fopenmpSHLIB_OPENMP_CXXFLAGS = -Xpreprocessor -fopenmpSHLIB_OPENMP_FCFLAGS = -fopenmpSHLIB_OPENMP_FFLAGS = -fopenmpSHLIB_OPENMP_LIBS = -lompRestart R after editing
~/.R/Makevarsso the flags arepicked up.
By default, CRAN binary packages on macOS are built without OpenMP,because Apple’s toolchain does not enable it when CRAN compilesbinaries. To enable OpenMP, you must install from source after settingup your system:
# Install from CRAN sourceinstall.packages("FastKRR",type ="source")# Or install directly from GitHub (also source build)pak::pak("kybak90/FastKRR")# example data setset.seed(1)n=1000rho=1X=runif(n,0,1)y=sin(2*pi*X^3)+rnorm(n,0,0.1)# model fitting - nystrommodel_nystrom=fastkrr(X, y,kernel ="gaussian",rho = rho,opt ="nystrom",verbose =FALSE)model_nystrom$n_threads# >1 indicates OpenMP used by FastKRR (default 4)#> NULLThe following code chunk inspects the dynamic libraries linked to thecompiled FastKRR shared object (.so or.dylib).
otool -L contains a line withlibomp.dylib,libomp.dylib is absent, the package was compiledwithout OpenMP support.is_macos= (Sys.info()[["sysname"]]=="Darwin")if (is_macos) { so_dir=system.file("libs", .Platform$r_arch,package ="FastKRR")if (so_dir=="") so_dir=system.file("libs",package ="FastKRR") so_files=list.files(so_dir,pattern ="\\.(so|dylib)$",full.names =TRUE) so=if (length(so_files)) so_files[[1]]else""cat("FastKRR shared object:", so,"\n")if (nzchar(so)) { cmd=paste("otool -L",shQuote(so))cat(system(cmd,intern =TRUE),sep ="\n") }else {cat("No shared object found. Is FastKRR installed with compiled code?\n") }}else {cat("Skipping otool check (not macOS).\n")}When you run this on macOS, a successful OpenMP build will show aline such as:
/Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.3-arm64/Resources/lib/libomp.dylibThis confirms that OpenMP is enabled for FastKRR on your system.