miclustThis package performs cluster analysis with selection of the finalnumber of clusters and an optional variable selection procedure. Thepackage is designed to integrate the results of multiple imputation todeal with missing raw data while accounting for the uncertainty thatsuch imputations introduce in the final results.
The last version released on CRAN can be installed within an Rsession by executing:
install.packages("miclust")Once the package has been installed, a summary of the main functionsis available using thehelp function:
library(miclust)#>#> This is miclust 1.2.6. For details, use:#> > help(package = 'miclust')#>#> To cite the methods in the package use:#> > citation('miclust')help(miclust)Dataminhanes is a list with 101 data sets. The firstdata set containsnhanesdata from themicepackage. The remaining data sets were obtained by applying the multipleimputation functionmice, from the same package. The firststep of the analysis is to apply thegetdata function tominhanes, resulting inminhanes1, a list withtwo objects:rawdata, adata.frame containingthe raw data, andimpdata, alist containingthe imputed data sets.getdata standardizes all variables,so categorical variables need to have numeric values. Standardization isperformed by centering all variables at the mean and then dividing bythe standard deviation (or the difference between the maximum and theminimum values for binary variables). Such a standardization is appliedonly to the imputed data sets, except in the case of analyzing just theraw data (i.e. complete cases analysis), in which raw data are alsointernally standardized.
library(miclust)data(minhanes)### data preparation:minhanes1<-getdata(data = minhanes)class(minhanes1)#> [1] "list" "midata"### raw data:minhanes1$rawdata#> age bmi hyp chl#> 1 1 NA NA NA#> 2 2 22.7 1 187#> 3 1 NA 1 187#> 4 3 NA NA NA#> 5 1 20.4 1 113#> 6 3 NA NA 184#> 7 1 22.5 1 118#> 8 1 30.1 1 187#> 9 2 22.0 1 238#> 10 2 NA NA NA#> 11 1 NA NA NA#> 12 2 NA NA NA#> 13 3 21.7 1 206#> 14 2 28.7 2 204#> 15 1 29.6 1 NA#> 16 1 NA NA NA#> 17 3 27.2 2 284#> 18 2 26.3 2 199#> 19 1 35.3 1 218#> 20 3 25.5 2 NA#> 21 1 NA NA NA#> 22 1 33.2 1 229#> 23 1 27.5 1 131#> 24 3 24.9 1 NA#> 25 2 27.4 1 186### first (standardized) imputed data set:minhanes1$impdata[[1]]#> age bmi hyp chl#> 1 -0.9149325 2.0012331 -0.24 -0.1489984#> 2 0.2889260 -0.9445072 -0.24 -0.1227663#> 3 -0.9149325 0.4582263 -0.24 -0.1227663#> 4 1.4927846 -0.2898982 0.76 0.6904293#> 5 -0.9149325 -1.4822217 -0.24 -2.0639429#> 6 1.4927846 0.1776796 0.76 -0.2014626#> 7 -0.9149325 -0.9912650 -0.24 -1.9327823#> 8 -0.9149325 0.7855307 -0.24 -0.1227663#> 9 0.2889260 -1.1081594 -0.24 1.2150716#> 10 0.2889260 -1.4822217 -0.24 -0.1227663#> 11 -0.9149325 0.6686363 -0.24 0.9789826#> 12 0.2889260 0.1543007 -0.24 0.3756439#> 13 1.4927846 -1.1782961 -0.24 0.3756439#> 14 0.2889260 0.4582263 0.76 0.3231797#> 15 -0.9149325 0.6686363 -0.24 -0.1227663#> 16 -0.9149325 0.4582263 -0.24 -0.1227663#> 17 1.4927846 0.1075429 0.76 2.4217489#> 18 0.2889260 -0.1028671 0.76 0.1920191#> 19 -0.9149325 2.0012331 -0.24 0.6904293#> 20 1.4927846 -0.2898982 0.76 -0.1489984#> 21 -0.9149325 -1.4822217 -0.24 -1.5917648#> 22 -0.9149325 1.5102763 -0.24 0.9789826#> 23 -0.9149325 0.1776796 -0.24 -1.5917648#> 24 1.4927846 -0.4301716 -0.24 0.3231797#> 25 0.2889260 0.1543007 -0.24 -0.1489984Multiple imputation clustering process with backward variableselection:
### using only the imputations 1 to 50 for the clustering process and exploring### 2 vs. 3 clusters:minhanes1clust<-miclust(data = minhanes1,search ="backward",ks =2:3,usedimp =1:50,seed =4321)#> ....imp 5....imp 10....imp 15....imp 20....imp 25....imp 30....imp 35....imp 40....imp 45....imp 50#>#> Analysis done.minhanes1clust#>#> Results using 50 imputations:#> ------------------------------------------------#>#> k=V1 k=V2#> Frequency of selection (%) 56.00 44.00#> Median number of selected variables 1.0 2.0### optimal number of clustersminhanes1clust$kfin#> [1] 2Selection frequency of the variables for the optimal number ofclusters:
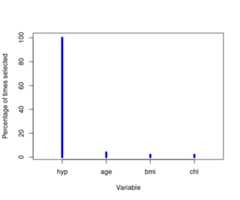
y<-getvariablesfrequency(minhanes1clust)y#> $percfreq#> [1] 100 4 2 2#>#> $varnames#> [1] "hyp" "age" "bmi" "chl"plot(y$percfreq,type ="h",main ="",xlab ="Variable",ylab ="Percentage of times selected",xlim =0.5+c(0,length(y$varnames)),lwd =5,col ="blue",xaxt ="n")axis(1,at =1:length(y$varnames),labels = y$varnames)
Graphical representation of the results:
plot(minhanes1clust)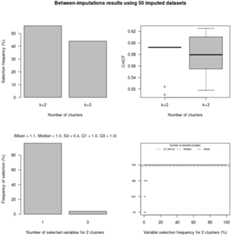
Default summary for the optimal number of clusters:
summary(minhanes1clust)#> Warning in summary.miclust(minhanes1clust): 'quantilevars' not provided. Setting it to 0.5.#>#> Results using:#> 50 imputed data sets for the cluster analysis#> 100 imputed data sets for the descriptive summary#> 2 as the final number of clusters#> -----------------------------------------------------------#>#> Presence of the variables in the subset of selected variables:#> Variable Presence(%)#> 1 hyp 100#> 2 age 4#> 3 bmi 2#> 4 chl 2#>#> Selected variables:#> [1] "hyp"#>#> Cohen's kappa between-imputations distribution (99 comparisons):#> 2.5% 25% 50% mean 75% 97.5%#> 0.48 0.65 0.78 0.75 0.88 1.00#>#> Between-imputation clusters size distribution (100 imputations):#> size min. 2.5% 25% 50% mean 75% 97.5% max.#> cluster 1 7 4 4 6 7 6.5 7 9 10#> cluster 2 18 15 16 18 18 18.5 19 21 21#>#> Probability of assignment to the cluster distribution (100 imputations):#> min Q1 Q2 Q3 max#> Assigned to cluster 1 0.51 0.54 1 1 1#> Assigned to cluster 2 0.52 0.93 1 1 1#>#> Within-cluster summary (100 imputations):#> %miss. %miss.(cl.1) %miss.(cl.2) mean (cl.1) sd (cl.1) mean (cl.2)#> hyp 0 0 0 2 0 1#> sd (cl.2)#> hyp 0Summary forcing 3 clusters:
summary(minhanes1clust,k =3)#> Warning in summary.miclust(minhanes1clust, k = 3): 'quantilevars' not provided. Setting it to 0.5.#>#> Results using:#> 50 imputed data sets for the cluster analysis#> 100 imputed data sets for the descriptive summary#> 3 as the final number of clusters#> -----------------------------------------------------------#>#> Presence of the variables in the subset of selected variables:#> Variable Presence(%)#> 1 hyp 96#> 2 age 94#> 3 bmi 46#> 4 chl 30#>#> Selected variables:#> [1] "hyp" "age"#>#> Cohen's kappa between-imputations distribution (99 comparisons):#> 2.5% 25% 50% mean 75% 97.5%#> 1 1 1 1 1 1#>#> Between-imputation clusters size distribution (100 imputations):#> size min. 2.5% 25% 50% mean 75% 97.5% max.#> cluster 1 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12#> cluster 2 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7#> cluster 3 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6#>#> Probability of assignment to the cluster distribution (100 imputations):#> min Q1 Q2 Q3 max#> Assigned to cluster 1 1 1 1 1 1#> Assigned to cluster 2 1 1 1 1 1#> Assigned to cluster 3 1 1 1 1 1#>#> Within-cluster summary (100 imputations):#> %miss. %miss.(cl.1) %miss.(cl.2) %miss.(cl.3) mean (cl.1) sd (cl.1)#> hyp.mean 0 0 0 0 1 0#> age.mean 0 0 0 0 1 0#> mean (cl.2) sd (cl.2) mean (cl.3) sd (cl.3)#> hyp.mean 1.4 0.55 1.5 0.58#> age.mean 2.0 0.00 3.0 0.00The methodology used in the package is described in