prismThis package allows users to access and visualize data from theOregon State PRISM project. Data areall in the form of gridded rasters for the continental US at 4 differenttemporal scales: daily, monthly, annual, and 30 year normals. Please seetheir webpage for a full description of the data products, orseetheir overview.
prism is available on CRAN:
install.packages("prism")Or the development version can be installed from GitHub withdevtools:
# install.packages("devtools")library(devtools)install_github("ropensci/prism")The overall work flow in the prism package is (links go to details onthis page):
prism_set_dl_dir(). This is now referred to as the “prismarchive”.get_prism_*(). Each folder, or variable,timestep, day/month/year is stored in a single folder in the archive andreferred to as prism data (pd).prism_archive_*(). Or interact withthe prism data:pd_*().The remainder of this README provides examples following this workflow.
Data are available in 4 different temporal scales as mentioned above.At each temporal scale, there are 11 different parameters/variablesavailable. Keep in mind these are modeled parameters, not measured.Please see thefulldescription for how they are calculated.
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
| tmean | Mean temperature |
| tmax | Maximum temperature |
| tmin | Minimum temperature |
| tdmean | Mean dew point temperature |
| ppt | Total precipitation (rain and snow) |
| vpdmin | Daily minimum vapor pressure deficit |
| vpdmax | Daily maximum vapor pressure deficit |
| solclear | Solar radiation (clear sky) |
| solslope | Solar radiation (sloped) |
| soltotal | Solar radiation (total) |
| soltrans | Cloud transmittance |
Normals (4km or 800m resolution) based on 1991-2020average:
Important .bilfiles are no longer available in .bil format. Theget_prism_normals() functions still work and will downloadthe data in GeoTiff format.But - the rest of the prismR package has not been updated to work with GeoTiff, so none of theother functions will work with the 30-year normal data, e.g.,prism_archive_subset(temp_period = "monthly normals") willreturncharacter(0) and plotting functions will notwork.
| Variable | Annual | Monthly | Daily |
|---|---|---|---|
| tmean | X | X | X |
| tmax | X | X | X |
| tmin | X | X | X |
| tdmean | X | X | X |
| ppt | X | X | X |
| vpdmin | X | X | X |
| vpdmax | X | X | X |
| solclear | 800m | 800m | |
| solslope | 800m | 800m | |
| soltotal | 800m | 800m | |
| soltrans | 800m | 800m |
Daily, monthly, and annual data:
| Variable | Annual (1895-present) | Monthly (1895-present) | Daily (1981-present) |
|---|---|---|---|
| tmean | X | X | X |
| tmax | X | X | X |
| tmin | X | X | X |
| tdmean | X | X | X |
| ppt | X | X | X |
| vpdmin | X | X | X |
| vpdmax | X | X | X |
| solclear | |||
| solslope | |||
| soltotal | |||
| soltrans |
Before downloading any data, set the directory that the prism datawill be saved to:
library(prism)#> Be sure to set the download folder using `prism_set_dl_dir()`.prism_set_dl_dir("~/prismtmp")This is now referred to as the “prism archive”. Theprism_archive_*() functions allow the user to searchthrough the archive. The prism archive contains “prism data”. The prismdata are referred to by their folder names, even though the “real” dataare the .bil, .txt, and other files that exist in the folder. The prismdata (pd) can be accessed using thepd_*()functions.
Normals are based on the latest 30-year period; currently 1991 -2020. Normals can be downloaded in two resolutions, 4km and 800m, and aresolution must be specified. They can be downloaded for a given day,month, vector of days/months, or annual averages for all 30 years.
# Download March 14 30-year average precip. Note the year is ignoredget_prism_normals('ppt','4km',day =as.Date('2025-03-14'))# Download the January - June 30-year averages at 4km resolutionget_prism_normals(type="tmean",resolution ="4km",mon =1:6,keepZip =FALSE)# Download the 30-year annual average precip and annual average temperatureget_prism_normals("ppt","4km",annual =TRUE,keepZip =FALSE)get_prism_normals("tmean","4km",annual =TRUE,keepZip =FALSE)If the archive has not already been set, calling any of theget_prism_*() functions will prompt the user to specify thedirectory. prism data are downloaded as zip files and then unzipped. IfthekeepZip argument isTRUE the zip file willremain on your machine, otherwise it will be automatically deleted.
Let us download daily average temperatures from June 1 to June 14,2013. We can also download January average temperature data from 1982 to2014. Finally, we will download annual average precipitation for 2000 to2015.Note that resolution must now be specified for all datadownloads.
get_prism_dailys(type ="tmean",minDate ="2013-06-01",maxDate ="2013-06-14",resolution ="4km",keepZip =FALSE)get_prism_monthlys(type ="tmean",years =1982:2014,mon =1,resolution ="4km",keepZip =FALSE)get_prism_annual(type ="ppt",years =2000:2015,resolution ="4km",keepZip =FALSE)Note that for daily data you need to give a well formed date stringin the form of “YYYY-MM-DD”.
You can view all the prism data you have downloaded with a simplecommand:prism_archive_ls(). This function gives a list offolder names, i.e., prism data (pd). All the functions inthe prism package work off of one or more of these folder names(pd).
## Truncated to keep file list shortprism_archive_ls()#> [1] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191004"#> [2] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191401"#> [3] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191402"#> [4] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191403"#> [5] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191404"#> [6] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191405"#> [7] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191406"#> [8] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191407"#> [9] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191408"#> [10] "prism_ppt_us_25m_191409"....While prism functions use this folder format, other files may need anabsolute path (e.g. theraster package). Thepd_to_file() function conveniently returns the absolutepath. Alternatively, you may want to see what the normal name for theproduct is (not the file name), and we can get that with thepd_get_name() function.
## Truncated to keep file list shortpd_to_file(prism_archive_ls()[1:10])#> [1] "C:\\Users\\RAButler\\Documents\\prismtmp\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191004\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191004.bil"#> [2] "C:\\Users\\RAButler\\Documents\\prismtmp\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191401\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191401.bil"#> [3] "C:\\Users\\RAButler\\Documents\\prismtmp\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191402\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191402.bil"#> [4] "C:\\Users\\RAButler\\Documents\\prismtmp\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191403\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191403.bil"#> [5] "C:\\Users\\RAButler\\Documents\\prismtmp\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191404\\prism_ppt_us_25m_191404.bil"....pd_get_name(prism_archive_ls()[1:10])#> [1] "Apr 1910 - 4km resolution - Precipitation"#> [2] "Jan 1914 - 4km resolution - Precipitation"#> [3] "Feb 1914 - 4km resolution - Precipitation"#> [4] "Mar 1914 - 4km resolution - Precipitation"#> [5] "Apr 1914 - 4km resolution - Precipitation"....Finally,prism_archive_subset() is a convenient way tosearch for specific parameters, time steps, days, months, years, orranges of days, months, years.Note that resolution must bespecified for all archive subset operations.
# we know we have downloaded June 2013 daily data, so lets search for thoseprism_archive_subset("tmean","daily",mon =6,resolution ="4km")#> [1] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130601" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130602"#> [3] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130603" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130604"#> [5] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130605" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130606"#> [7] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130607" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130608"#> [9] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130609" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130610"#> [11] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130611" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130612"#> [13] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130613" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130614"# or we can look for days between June 7 and June 10prism_archive_subset("tmean","daily",minDate ="2013-06-07",maxDate ="2013-06-10",resolution ="4km")#> [1] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130607" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130608"#> [3] "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130609" "prism_tmean_us_25m_20130610"You can easily make a quick plot of your data using the output ofprism_archive_ls() orprism_archive_subset()withpd_image().
# Plot the precipitation in 2000ppt2002<-prism_archive_subset("ppt","annual",year =2002,resolution ="4km")pd_image(ppt2002)
It is easy to load the prism data with the raster package. This timewe will look at the difference in precipitation between 2011 and 2002.Conveniently, we already downloaded these data. We just need to grabthem out of our archive.
library(raster)#> Warning: package 'raster' was built under R version 4.5.1#> Loading required package: sp#> Warning: package 'sp' was built under R version 4.5.1# knowing the name of the files you are after allows you to find them in the# list of all files that exist# ppt2002 <- "prism_ppt_us_25m_2002"# ppt2011 <- "prism_ppt_us_25m_2011"# but we will use prism_archive_subset() to find the files we needppt2002_name<-prism_archive_subset("ppt","annual",year =2002,resolution ="4km")ppt2011_name<-prism_archive_subset("ppt","annual",year =2011,resolution ="4km")# raster needs a full path, not the "short" prism data nameppt2002<-pd_to_file(ppt2002_name)ppt2011<-pd_to_file(ppt2011_name)## Now we'll load the rasters.ppt2002_rast<-raster(ppt2002)ppt2011_rast<-raster(ppt2011)# Now we can do simple subtraction to get the anomaly by subtracting 2014# from the 30 year normal mapdiff_calc<-function(x, y) {return(x- y)}anom_rast<- raster::overlay(ppt2002_rast, ppt2011_rast,fun = diff_calc)plot(anom_rast)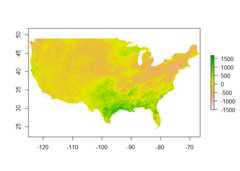
The plot shows which regions were wetter in 2011 than 2002 (and thereverse). It also shows how easy it is to use the raster library to workwith prism data. The package provides a simple framework to work with alarge number of rasters that you can easily download and visualize oruse with other data sets.
You can also visualize a single point across multiple prism datafiles (slice) usingpd_plot_slice(). This procedure willtake a set of rasters, create a “raster::stack”, extractdata at a point, and then create a ggplot2 object.
Let’s now make a plot of January temperatures in Boulder between 1982and 2014. First we’ll grab all the data from the US (downloaded in theprevious step), and then give our function a point to get data from. Thepoint must be a vector in the form of longitude, latitude. Becausepd_plot_slice() returns a gg object, it can be combinedwith other ggplot functions.
library(ggplot2)#> Warning: package 'ggplot2' was built under R version 4.5.1# data already exist in the prism dl dirboulder<-c(-105.2797,40.0176)# prism_archive_subset() will return prism data that matches the specified# variable, time step, years, months, days, etc.to_slice<-prism_archive_subset("tmean","monthly",mon =1,resolution ="4km")p<-pd_plot_slice(to_slice, boulder)# add a linear average and titlep+stat_smooth(method="lm",se =FALSE)+theme_bw()+ggtitle("Average January temperature in Boulder, CO 1982-2014")#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'
Finally, the prism data are in a form that can be used with leafletmaps (with the help of the raster package). Theleaflet packageallows you to easily make JavaScript maps using theleaflet mapping framework using prismdata. These can easily be hosted on websites likeRpubs or your own site. Here is a simpleexample of plotting the30-year normal for annualtemperature. If you run this code you will have an interactive map,instead of just the screen shot shown here.
library(leaflet)library(raster)library(prism)# January 2002 average temperature has already been downloadednorm<-prism_archive_subset("tmean","monthly",mon =1,year =2002,resolution ="4km")rast<-raster(pd_to_file(norm))# Create color palette and plotpal<-colorNumeric(c("#0000FF","#FFFF00","#FF0000"),values(rast),na.color ="transparent")leaflet()%>%addTiles(urlTemplate ='http://server.arcgisonline.com/ArcGIS/rest/services/World_Imagery/MapServer/tile/{z}/{y}/{x}' )%>%addRasterImage(rast,colors = pal,opacity=.65)%>%addLegend(pal = pal,values =values(rast),title ="Deg C")[