treemapify providesggplot2 geoms for drawingtreemaps.
Install the release version of treemapify from CRAN:
install.packages("treemapify")
If you want the development version, install it from GitHub:
devtools::install_github("wilkox/treemapify")
treemapify includes an example dataset containing statistics aboutthe G-20 group of major world economies.
library(ggplot2)library(treemapify)#> systemfonts and textshaping have been compiled with different versions of Freetype. Because of this, textshaping will not use the font cache provided by systemfontsG20#> region country gdp_mil_usd hdi econ_classification#> 1 Africa South Africa 384315 0.629 Developing#> 2 North America United States 15684750 0.937 Advanced#> 3 North America Canada 1819081 0.911 Advanced#> 4 North America Mexico 1177116 0.775 Developing#> 5 South America Brazil 2395968 0.730 Developing#> 6 South America Argentina 474954 0.811 Developing#> 7 Asia China 8227037 0.699 Developing#> 8 Asia Japan 5963969 0.912 Advanced#> 9 Asia South Korea 1155872 0.909 Advanced#> 10 Asia India 1824832 0.554 Developing#> 11 Asia Indonesia 878198 0.629 Developing#> 12 Eurasia Russia 2021960 0.788 Developing#> 13 Eurasia Turkey 794468 0.722 Developing#> 14 Europe European Union 16414483 0.876 Advanced#> 15 Europe Germany 3400579 0.920 Advanced#> 16 Europe France 2608699 0.893 Advanced#> 17 Europe United Kingdom 2440505 0.875 Advanced#> 18 Europe Italy 2014079 0.881 Advanced#> 19 Middle East Saudi Arabia 727307 0.782 Developing#> 20 Oceania Australia 1541797 0.938 Advanced#> hemisphere#> 1 Southern#> 2 Northern#> 3 Northern#> 4 Northern#> 5 Southern#> 6 Southern#> 7 Northern#> 8 Northern#> 9 Northern#> 10 Northern#> 11 Southern#> 12 Northern#> 13 Northern#> 14 Northern#> 15 Northern#> 16 Northern#> 17 Northern#> 18 Northern#> 19 Northern#> 20 SouthernIn a treemap, each tile represents a single observation, with thearea of the tile proportional to a variable. Let’s start by drawing atreemap with each tile representing a G-20 country. The area of the tilewill be mapped to the country’s GDP, and the tile’s fill colour mappedto its HDI (Human Development Index).geom_treemap() is thebasic geom for this purpose.
ggplot(G20,aes(area = gdp_mil_usd,fill = hdi))+geom_treemap()
This plot isn’t very useful without the knowing what country isrepresented by each tile.geom_treemap_text() can be usedto add a text label to each tile. It uses theggfittext package toresize the text so it fits the tile. In addition to standard textformatting aesthetics you would use ingeom_text(), likefontface orcolour, we can pass additionaloptions specific for ggfittext. For example, we can place the text inthe centre of the tile withplace = "centre", and expand itto fill as much of the tile as possible withgrow = TRUE.
ggplot(G20,aes(area = gdp_mil_usd,fill = hdi,label = country))+geom_treemap()+geom_treemap_text(fontface ="italic",colour ="white",place ="centre",grow =TRUE)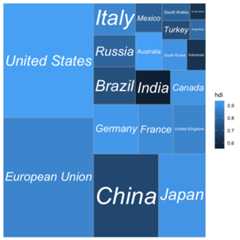
geom_treemap() supports subgrouping of tiles within atreemap by passing asubgroup aesthetic. Let’s subgroup thecountries by region, draw a border around each subgroup withgeom_treemap_subgroup_border(), and label each subgroupwithgeom_treemap_subgroup_text().geom_treemap_subgroup_text() takes the same arguments fortext placement and resizing asgeom_treemap_text().
ggplot(G20,aes(area = gdp_mil_usd,fill = hdi,label = country,subgroup = region))+geom_treemap()+geom_treemap_subgroup_border()+geom_treemap_subgroup_text(place ="centre",grow = T,alpha =0.5,colour ="black",fontface ="italic",min.size =0)+geom_treemap_text(colour ="white",place ="topleft",reflow = T)
Note that Argentina is not labelled.geom_treemap_text()will hide text labels that cannot fit a tile without being shrunk belowa minimum size, by default 4 points. This can be adjusted with themin.size argument.
Up to three nested levels of subgrouping are supported with thesubgroup2 andsubgroup3 aesthetics. Bordersand text labels for these subgroups can be drawn withgeom_treemap_subgroup2_border(), etc. Note that ggplot2draws plot layers in the order that they are added. This means it ispossible to accidentally hide one layer of subgroup borders withanother. Usually, it’s best to add the border layers in order fromdeepest to shallowest, i.e.geom_treemap_subgroup3_border()thengeom_treemap_subgroup2_border() thengeom_treemap_subgroup_border().
ggplot(G20,aes(area =1,label = country,subgroup = hemisphere,subgroup2 = region,subgroup3 = econ_classification))+geom_treemap()+geom_treemap_subgroup3_border(colour ="blue",size =1)+geom_treemap_subgroup2_border(colour ="white",size =3)+geom_treemap_subgroup_border(colour ="red",size =5)+geom_treemap_subgroup_text(place ="middle",colour ="red",alpha =0.5,grow = T)+geom_treemap_subgroup2_text(colour ="white",alpha =0.5,fontface ="italic")+geom_treemap_subgroup3_text(place ="top",colour ="blue",alpha =0.5)+geom_treemap_text(colour ="white",place ="middle",reflow = T)
As demonstrated, there is no assurance that the resulting plot willlook good.
Like any ggplot2 plot, treemapify plots can be faceted, scaled,themed, etc.
ggplot(G20,aes(area = gdp_mil_usd,fill = region,label = country,subgroup = region))+geom_treemap()+geom_treemap_text(grow = T,reflow = T,colour ="black")+facet_wrap(~ hemisphere)+scale_fill_brewer(palette ="Set1")+theme(legend.position ="bottom")+labs(title ="The G-20 major economies by hemisphere",caption ="The area of each tile represents the country's GDP as a proportion of all countries in that hemisphere",fill ="Region" )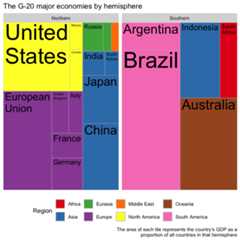
The default algorithm for laying out the tiles is the ‘squarified’algorithm. This tries to minimise the tiles’ aspect ratios, making surethere are no long and flat or tall and skinny tiles. While ‘squarified’treemaps are aesthetically pleasing, the downside is that the positionof tiles within the plot area can change dramatically with even smallchanges to the dataset. This makes it difficult to compare treemapsside-by-side, or create animated treemaps.
By providing thelayout = "fixed" option to treemapifygeoms, an alternative layout algorithm is used that will always positionthe tiles based on the order of observations in the data frame. It’svery important that the same value forlayout is passed toall treemapify geoms, otherwise different layers of the plot might notshare the same layout.
With the help oflayout = "fixed", and with thegganimatepackage, it becomes possible to create animated treemaps showinge.g. change over time.
library(gganimate)library(gapminder)p<-ggplot(gapminder,aes(label = country,area = pop,subgroup = continent,fill = lifeExp ))+geom_treemap(layout ="fixed")+geom_treemap_text(layout ="fixed",place ="centre",grow =TRUE,colour ="white")+geom_treemap_subgroup_text(layout ="fixed",place ="centre")+geom_treemap_subgroup_border(layout ="fixed")+transition_time(year)+ease_aes('linear')+labs(title ="Year: {frame_time}")anim_save("man/figures/animated_treemap.gif",animation =animate( p,renderer =gifski_renderer()),nframes =48)