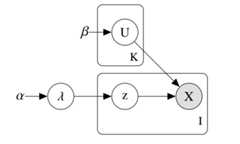
The goal of mixdir is to cluster high dimensional categoricaldatasets.
It can
mixdir(select_latent=TRUE))A detailed description of the algorithm and the features of thepackage can be found in the the accompanyingpaper.If you find the package useful please cite
C. Ahlmann-Eltze and C. Yau, “MixDir: Scalable Bayesian Clusteringfor High-Dimensional Categorical Data”, 2018 IEEE 5th InternationalConference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Turin, Italy,2018, pp. 526-539.
install.packages("mixdir")# Or to get the latest version from githubdevtools::install_github("const-ae/mixdir")Clustering themushroomdata set.

# Loading the library and the datalibrary(mixdir)set.seed(1)data("mushroom")# High dimensional dataset: 8124 mushroom and 23 different featuresmushroom[1:10,1:5]#> bruises cap-color cap-shape cap-surface edible#> 1 bruises brown convex smooth poisonous#> 2 bruises yellow convex smooth edible#> 3 bruises white bell smooth edible#> 4 bruises white convex scaly poisonous#> 5 no gray convex smooth edible#> 6 bruises yellow convex scaly edible#> 7 bruises white bell smooth edible#> 8 bruises white bell scaly edible#> 9 bruises white convex scaly poisonous#> 10 bruises yellow bell smooth edibleCalling the clustering functionmixdir on a subset ofthe data:
# Clustering into 3 latent classesresult<-mixdir(mushroom[1:1000,1:5],n_latent=3)Analyzing the result
# Latent class of of first 10 mushroomshead(result$pred_class,n=10)#> [1] 3 1 1 3 2 1 1 1 3 1# Soft Clustering for first 10 mushroomshead(result$class_prob,n=10)#> [,1] [,2] [,3]#> [1,] 3.103495e-07 1.055098e-05 9.999891e-01#> [2,] 9.998594e-01 4.683764e-06 1.359291e-04#> [3,] 9.998944e-01 3.111462e-06 1.025194e-04#> [4,] 5.778033e-04 7.114603e-08 9.994221e-01#> [5,] 3.662625e-07 9.999992e-01 4.183025e-07#> [6,] 9.996461e-01 8.764031e-08 3.537838e-04#> [7,] 9.998944e-01 3.111462e-06 1.025194e-04#> [8,] 9.997331e-01 5.822320e-08 2.668420e-04#> [9,] 5.778033e-04 7.114603e-08 9.994221e-01#> [10,] 9.999999e-01 5.850067e-09 9.845112e-08pheatmap::pheatmap(result$class_prob,cluster_cols=FALSE,labels_col =paste("Class",1:3))
# Structure of latent class 1# (bruises, cap color either yellow or white, edible etc.)purrr::map(result$category_prob,1)#> $bruises#> bruises no#> 0.9998223256 0.0001776744#>#> $`cap-color`#> brown gray red white yellow#> 0.0001775934 0.0001819672 0.0001776373 0.4079822666 0.5914805356#>#> $`cap-shape`#> bell convex flat sunken#> 0.3926736 0.4767291 0.1304197 0.0001776#>#> $`cap-surface`#> fibrous scaly smooth#> 0.0568571 0.4871396 0.4560033#>#> $edible#> edible poisonous#> 0.9998223174 0.0001776826# The most predicitive features for each classfind_predictive_features(result,top_n=3)#> column answer class probability#> 19 cap-color yellow 1 0.9993990#> 22 cap-shape bell 1 0.9990947#> 1 bruises bruises 1 0.7089533#> 48 edible poisonous 3 0.9980468#> 15 cap-color red 3 0.8462032#> 9 cap-color brown 3 0.6473043#> 5 bruises no 2 0.9990364#> 11 cap-color gray 2 0.9978218#> 32 cap-shape sunken 2 0.9936162# For example: if all I know about a mushroom is that it has a# yellow cap, then I am 99% certain that it will be in class 1predict(result,c(`cap-color`="yellow"))#> [,1] [,2] [,3]#> [1,] 0.999399 0.0003004692 0.0003004907# Note the most predictive features are different from the most typical onesfind_typical_features(result,top_n=3)#> column answer class probability#> 1 bruises bruises 1 0.9998223#> 43 edible edible 1 0.9998223#> 19 cap-color yellow 1 0.5914805#> 3 bruises bruises 3 0.9995546#> 27 cap-shape convex 3 0.7460615#> 9 cap-color brown 3 0.6746224#> 44 edible edible 2 0.9995310#> 5 bruises no 2 0.9713177#> 35 cap-surface fibrous 2 0.7355413Dimensionality Reduction
# Defining Featuresdef_feat<-find_defining_features(result, mushroom[1:1000,1:5],n_features =3)print(def_feat)#> $features#> [1] "cap-color" "bruises" "edible"#>#> $quality#> [1] 74.35146# Plotting the most important features gives an immediate impression# how the cluster differplot_features(def_feat$features, result$category_prob)#> Loading required namespace: ggplot2#> Loading required namespace: tidyr
The package implements a variational inference algorithm to solve aBayesian latent class model (LCM).